Blogs

How to Prevent Monel Corrosion: Essential Steps for Longevity
Overview
To prevent Monel corrosion and ensure the longevity of Monel alloys, essential strategies include regular cleaning, applying protective coatings, implementing cathodic protection, controlling environmental conditions, and conducting routine inspections. The article emphasizes that these proactive measures, supported by advancements like graphene coatings and regular maintenance protocols, significantly enhance the durability of Monel in corrosive environments, ultimately mitigating deterioration risks.
Introduction
In the realm of materials engineering, Monel stands out as a versatile and robust nickel-copper alloy, celebrated for its remarkable resistance to corrosion and ability to withstand extreme temperatures. With a composition that typically includes about 67% nickel and 30% copper, Monel not only boasts impressive mechanical properties but also plays a critical role in industries ranging from marine engineering to electrical applications.
However, as procurement managers delve into the intricacies of material selection, it becomes essential to recognize the inherent vulnerabilities of Monel, particularly in chloride-rich environments where corrosion can pose significant operational challenges.
This article explores the following topics:
- The composition and properties of Monel
- The corrosion challenges it faces
- Effective strategies for maintenance and prevention
Ultimately, this guide aims to assist professionals in making informed decisions about the best materials for their specific needs.
Understanding Monel: Composition and Properties
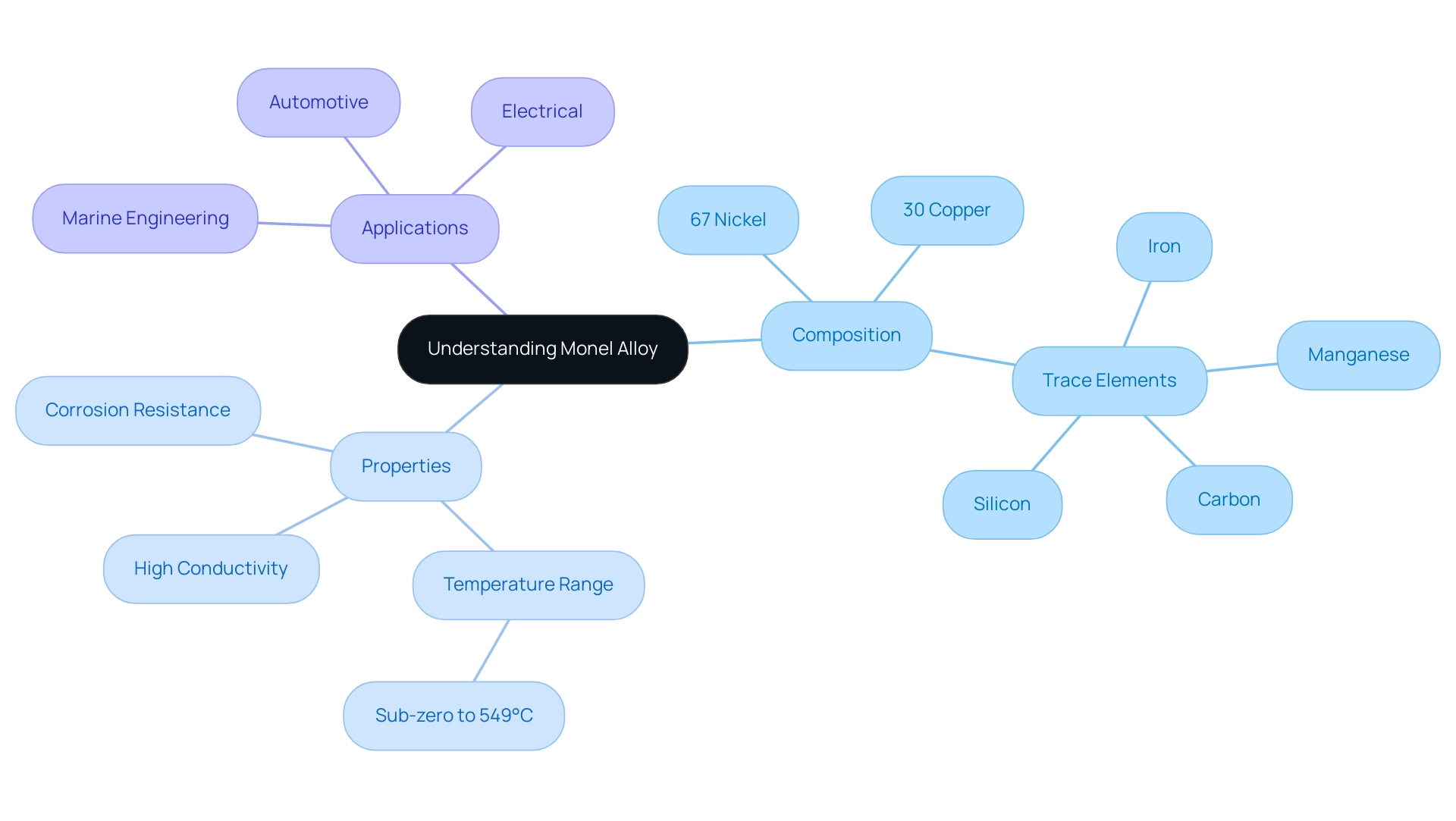
This specialized nickel-copper alloy is celebrated for its remarkable ability to resist monel corrosion, high strength, and capacity to endure extreme temperature fluctuations, with the alloy 400 capable of withstanding temperatures from sub-zero to 549°C. Typically, Monel comprises approximately 67% nickel and 30% copper, supplemented by trace amounts of iron, manganese, carbon, and silicon. This unique composition not only imparts impressive mechanical properties but also enhances its resistance to harsh environments, including seawater and acidic conditions, effectively combating monel corrosion.
Such attributes, including high conductivity and durability, are vital for choosing the right uses in industries like marine engineering, automotive, and electrical sectors. For example, its durability makes it a perfect choice for parts subjected to monel corrosion, ensuring longevity and dependability in essential uses. Additionally, Domadia provides a diverse range of copper-nickel alloys that are high-conductivity solutions suitable for various uses and are effective against monel corrosion.
Our non-sparking tools are essential for ensuring safety in explosive environments. According to Huaxiao Metal:
- “Versatility: Easily fabricated, welded, and machined, making it a top choice for manufacturers.”
Additionally, the K-500 variant exhibits outstanding durability against deterioration and is especially appropriate for maritime uses, like pump shafts and impellers, which underscores the alloy’s practical benefits in actual situations, particularly in resisting monel corrosion.
Explore our extensive product catalog to find the perfect solution for your project needs, including Mica Tape Products designed for high-temperature resistance and electrical insulation.
Corrosion Challenges: Why Monel is Vulnerable
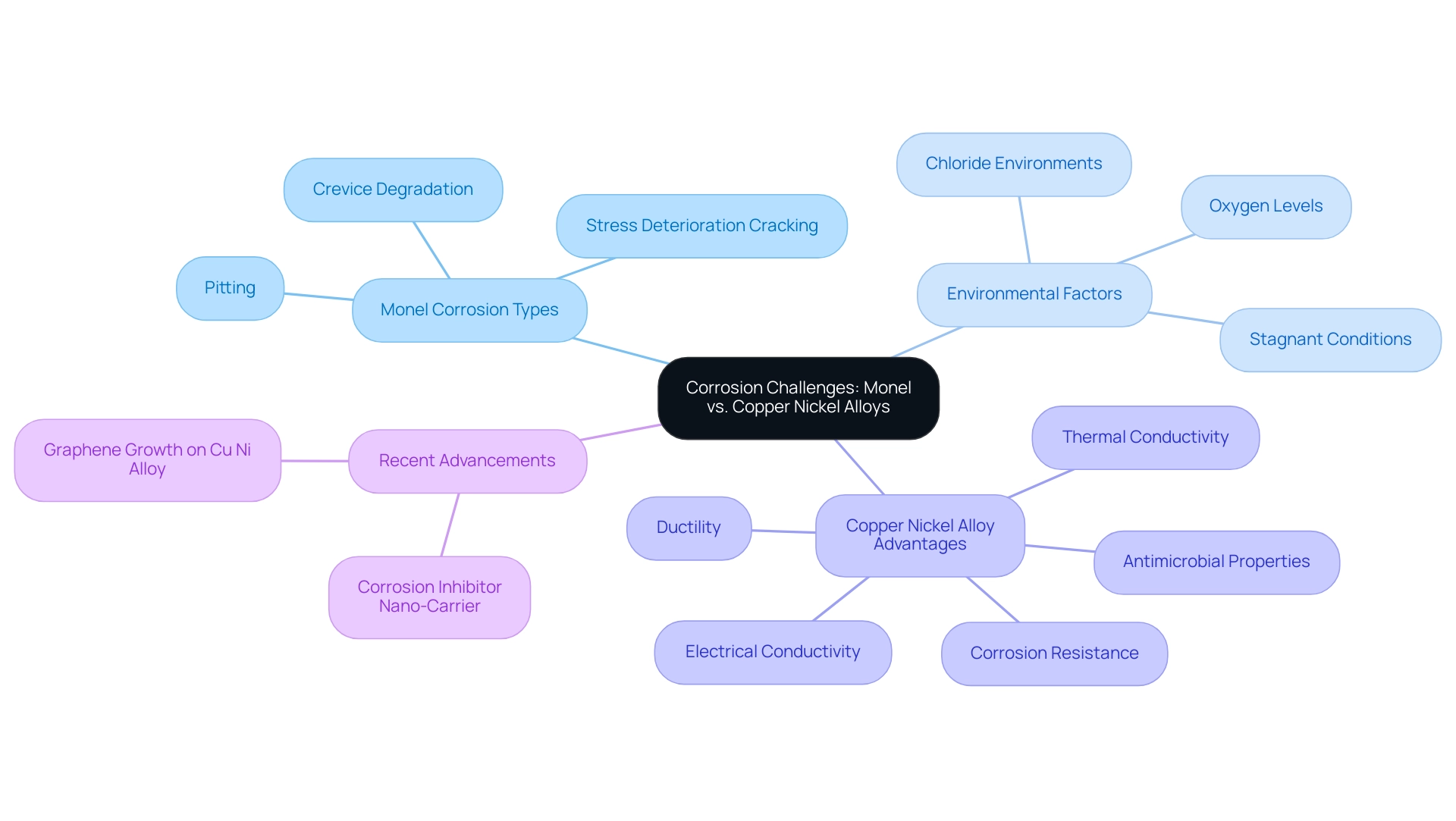
This alloy shows considerable weaknesses to deterioration, particularly in chloride-heavy settings such as seawater or salt mist, which can lead to monel corrosion. The most common types of attack, including monel corrosion through pitting and crevice degradation, are often intensified by low levels of oxygen and stagnant conditions. Significantly, stress deterioration cracking can also happen when the alloy is subjected to tensile stress in environments that promote monel corrosion.
Recent studies suggest that the deterioration rates of this alloy in chloride environments can escalate dramatically due to monel corrosion, leading to severe operational challenges. In contrast, copper nickel alloys offer substantial advantages in these environments, as detailed in the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs). They are famous for their strong resistance to corrosion, especially in oceanic uses, effectively combating the pitting and crevice corrosion that impact the alloy.
Moreover, their outstanding thermal and electrical conductivity renders them perfect for electrical uses, meeting the performance requirements that Monel frequently does not satisfy. Furthermore, their good ductility and ease of fabrication enhance their usability in various projects, allowing for more versatile uses. The antimicrobial properties of copper nickel alloys also make them suitable for applications where hygiene is paramount, which is a critical consideration in many industries.
While nickel-based alloys, including Monel, rely significantly on chromium levels for improving durability against deterioration, it is important to consider monel corrosion resistance, which makes copper nickel alloys a strong alternative in demanding environments. Recent advancements in durability technologies, including innovative solutions like a novel inhibitor nano-carrier developed by encapsulating zinc acetylacetonate in beta-cyclodextrin, highlight ongoing improvements in the field. According to R.K. Singh Raman, the only reported study on graphene growth on a Cu Ni alloy (75 wt% Cu, 25 wt% Ni) for resistance to deterioration indicated that the formation of a multilayer graphene provided an order of magnitude improvement in resistance.
Such insights emphasize the significance of comprehending the operational conditions for specific components while showcasing copper nickel alloys as a strategic choice for procurement managers seeking dependable solutions.
Essential Strategies for Preventing Monel Corrosion
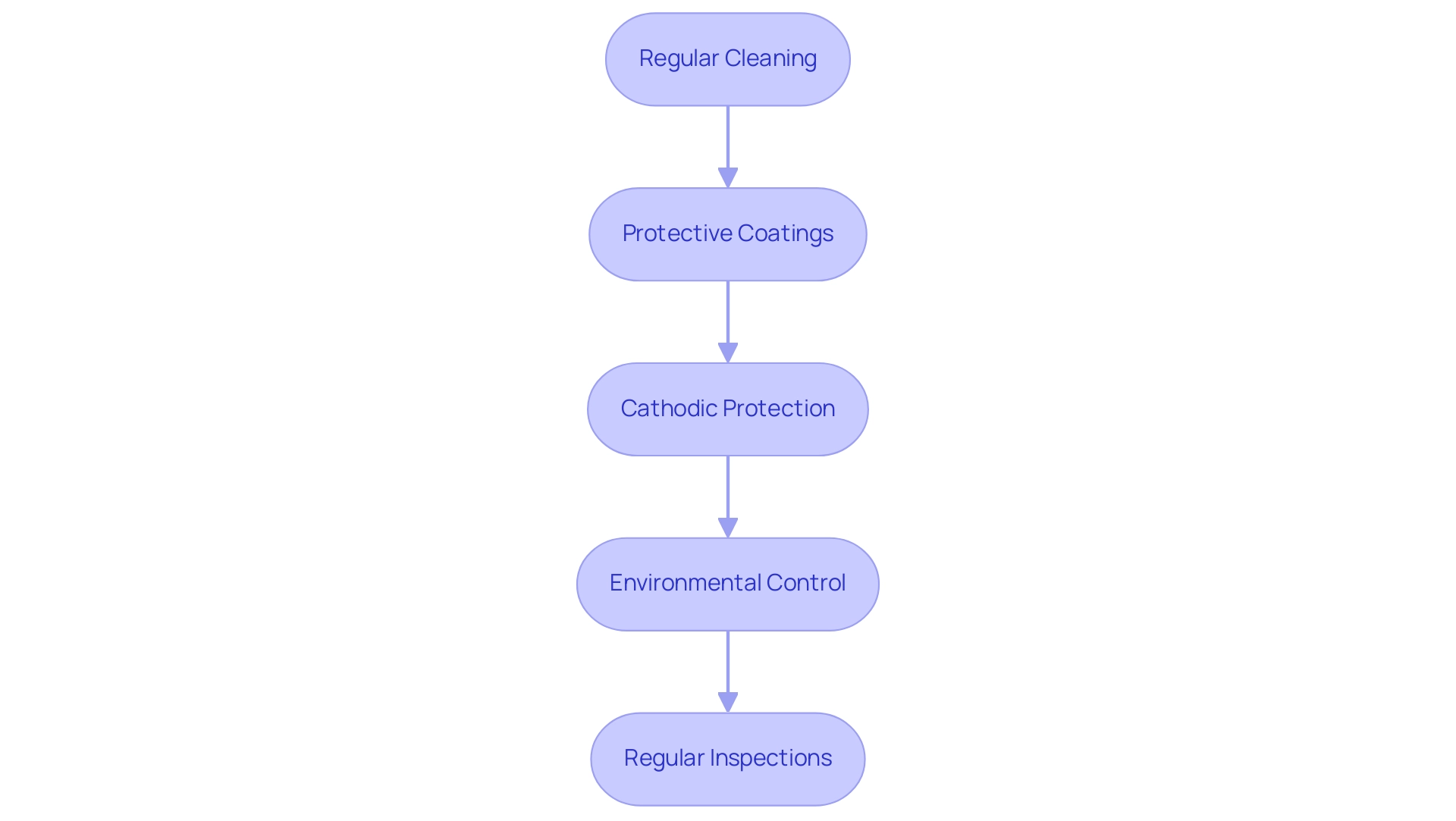
To effectively prevent corrosion in Monel alloys, the following strategies should be employed:
Regular Cleaning: It is crucial to maintain these surfaces through regular cleaning to eliminate corrosive agents, such as salt and dirt. Utilize mild detergents, steering clear of abrasive materials that could compromise the alloy’s surface integrity.
Protective Coatings: Apply protective coatings specifically formulated for the alloy, which greatly improve its durability against harsh environments. Recent developments, like multilayer graphene coatings on a specific alloy, have been demonstrated to significantly enhance durability against rust, especially in oceanic environments. As noted by Kalathur Santhanam, “Corrosion Protection of Alloy Coated with Graphene Quantum Dots Starts with a Surge,” which emphasizes the initial effectiveness of such coatings. Additionally, the Nyquist plot for a metal coated with graphene quantum dots (GQD) indicates a lower polarization resistance compared to other materials, suggesting better coupling and a higher initial degradation current.
Cathodic Protection: The installation of cathodic protection systems, including sacrificial anodes, is essential for preventing galvanic deterioration in marine applications. By diverting decay away from the alloy surface, this technique extends the lifespan of the material.
Environmental Control: Whenever feasible, control the environmental conditions to prevent Monel corrosion in components. Reducing humidity and limiting exposure to damaging substances can significantly lessen risks of deterioration.
Regular Inspections: Conduct routine inspections to detect early signs of corrosion. Proactive identification and resolution of potential issues can avert more extensive damage, ensuring the longevity of the components.
In a recent FTIR analysis of a metal coated with graphene quantum dots, the results demonstrated vibrational peaks indicative of hydroxide formation, thus confirming the protective behavior of the GQD coating over time. This corresponds with observations that the kind of coating used can significantly affect the corrosion rate; particularly, GQD coatings initially cause a spike in corrosion, succeeded by a notable reduction, highlighting the significance of choosing suitable protective measures for relevant applications.
Maintenance and Monitoring: Key to Longevity of Monel
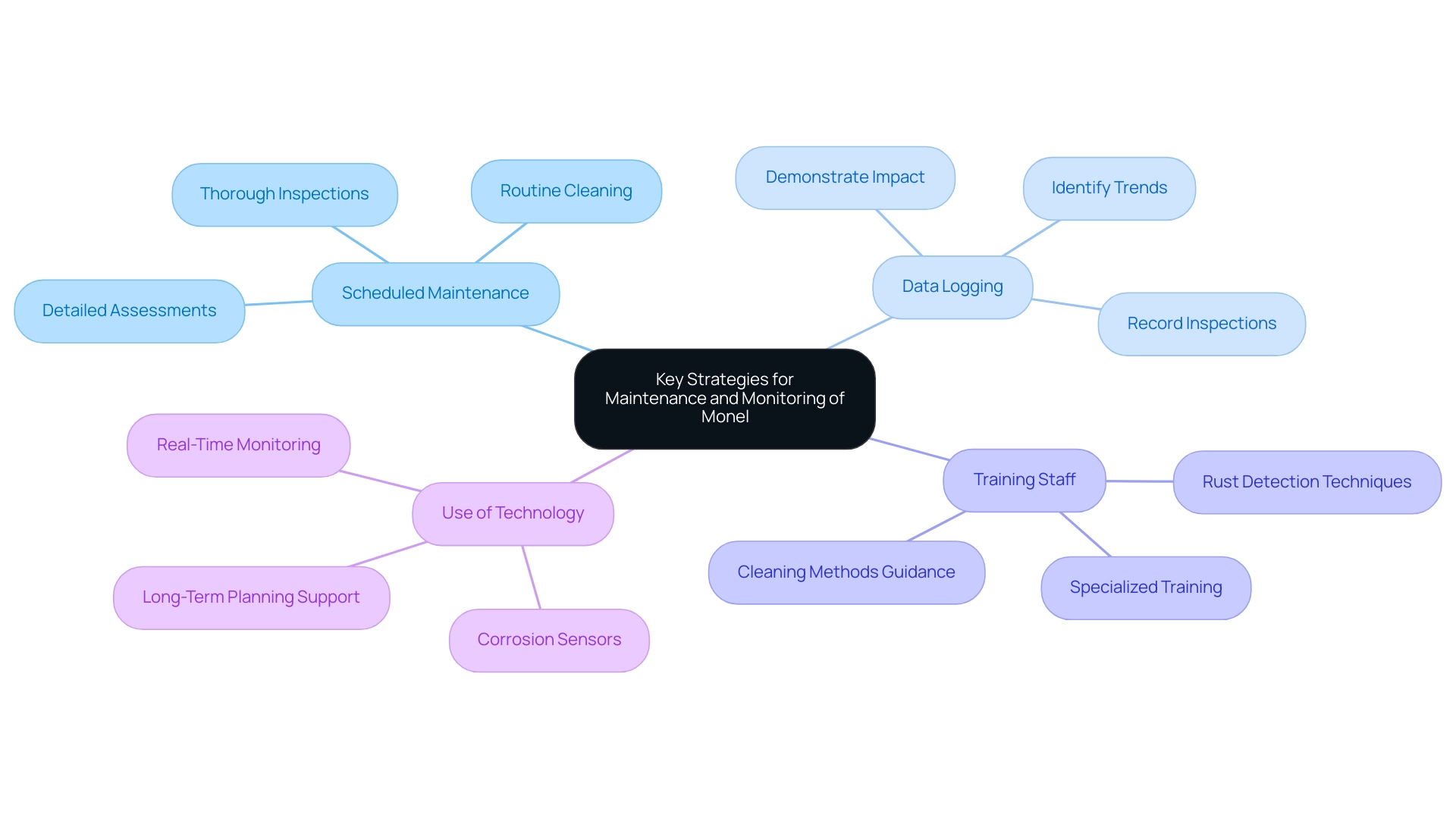
To secure the longevity and performance of Monel components, it is essential to implement a comprehensive maintenance and monitoring program that encompasses several critical strategies:
Scheduled Maintenance: Establish a rigorous maintenance schedule that includes routine cleaning, thorough inspections, and detailed assessments of the metal components. This proactive method is essential in avoiding deterioration and addressing wear before it leads to significant issues. In the case of Monel-coated heat exchangers used in chemical processing facilities, regular maintenance to prevent monel corrosion has been shown to enhance thermal efficiency and reduce energy consumption significantly.
Data Logging: Maintain meticulous records of all inspections and maintenance activities. This practice is crucial for identifying trends over time and spotting areas that may require additional focus, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of maintenance efforts. The data collected can be instrumental in demonstrating the positive impacts of maintenance on operational efficiency, as evidenced by the reduction in energy consumption observed in the aforementioned case study.
Training Staff: Equip maintenance personnel with specialized training tailored to the unique requirements of the material. This encompasses guidance on suitable cleaning methods and the most recent rust detection techniques, ensuring that personnel are well-equipped to handle specific components efficiently.
Use of Technology: Utilize sophisticated monitoring technologies, such as corrosion sensors, which provide real-time information on the status of alloy components in essential uses. The integration of such technology not only aids in immediate detection of potential issues but also supports long-term planning and resource allocation.
The successful implementation of these strategies is exemplified in case studies, such as the use of heat exchangers resistant to monel corrosion in chemical processing facilities, where the application of comprehensive monitoring and maintenance significantly enhanced thermal efficiency and reduced energy consumption by optimizing aging parameters and maximizing precipitation strengthening effects. As noted by Springer Nature, “Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.” This legal context emphasizes the significance of sharing best practices in maintenance of the alloy.
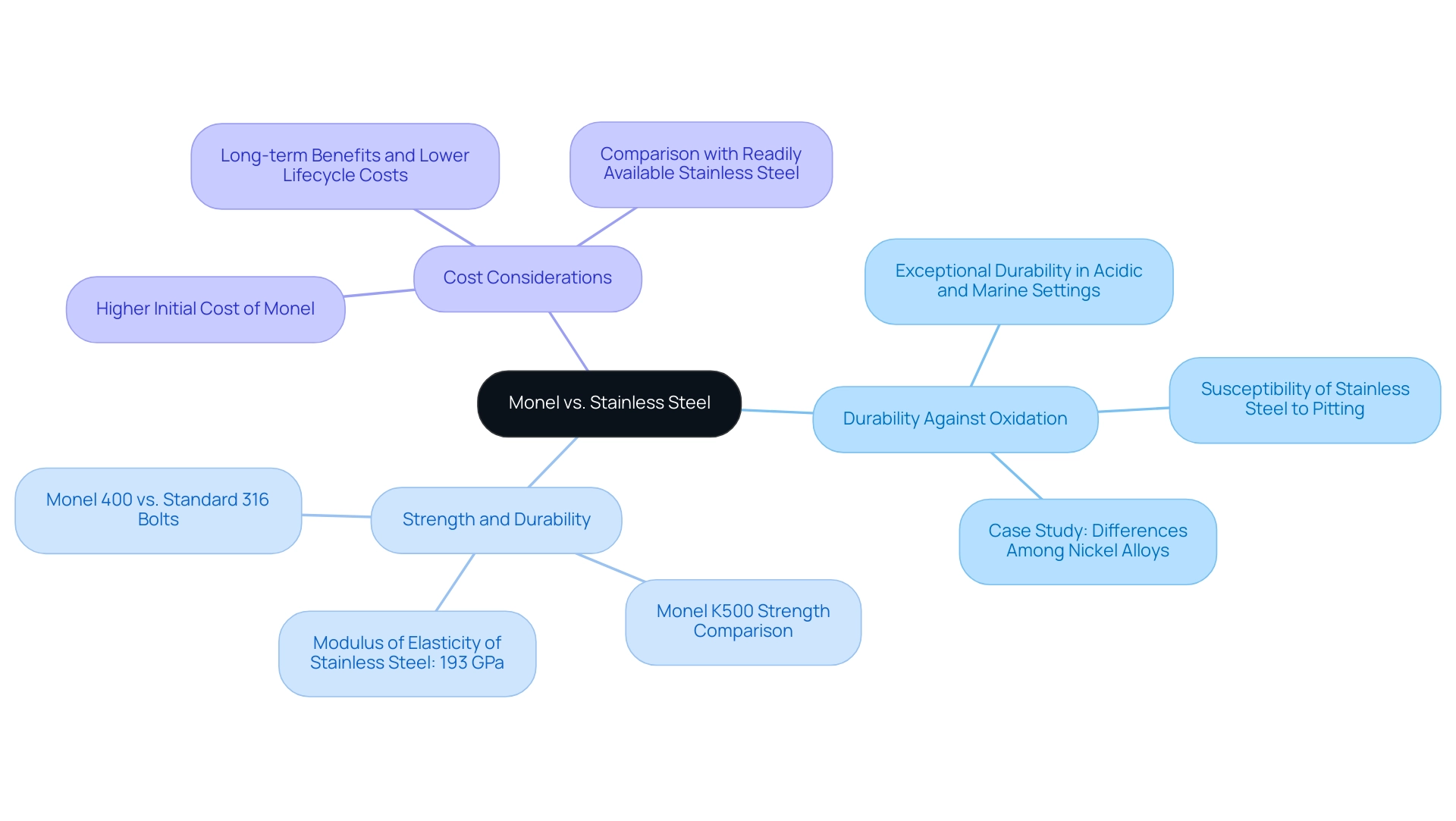
Monel vs. Stainless Steel: A Comparative Analysis
Evaluating this alloy against stainless steel requires a thorough examination of various essential aspects:
Durability Against Oxidation: This material is noted for its exceptional durability against oxidation, especially in acidic and marine settings. This contrasts with stainless steel, which can be susceptible to pitting and crevice degradation when exposed to chloride-rich conditions. Recent reports, including a case study titled ‘Differences Among Nickel Alloys,’ have underscored this alloy’s effectiveness in harsh environments, showcasing its advantages over stainless steel.
Strength and Durability: This material not only excels in corrosion resistance but also demonstrates remarkable strength, especially at elevated temperatures. As Kathleen observes, alloy 400 will offer slightly enhanced strength compared to standard 316 bolts, while alloy K500 will have more than double the strength. This characteristic makes this alloy particularly suitable for applications subjected to thermal stress, ensuring reliability and longevity. For comparison, stainless steel has a modulus of elasticity of 193 GPa, which is relevant when evaluating material performance under load.
Cost Considerations: The cost of this nickel-copper alloy is generally higher than that of stainless steel, primarily due to its scarcity and the complexity of its production. However, the long-term benefits of Monel’s durability and performance in extreme environments often justify the initial investment, leading to lower lifecycle costs, particularly in applications where Monel corrosion is significant, such as marine engineering and chemical processing, where its unique properties are maximally leveraged. In contrast, stainless steel is typically employed in less aggressive environments, making it a common choice for general applications. Understanding these distinctions is vital for procurement managers tasked with selecting the most suitable materials for specific projects.
Conclusion
Monel’s exceptional properties, including its robust corrosion resistance and ability to withstand extreme temperatures, make it a valuable material in various industries. However, it is crucial to acknowledge the vulnerabilities that Monel faces, particularly in chloride-rich environments where corrosion can severely impact operational efficiency. The exploration of effective maintenance and prevention strategies, such as:
- Regular cleaning
- Protective coatings
- Cathodic protection
highlights the importance of proactive measures to ensure the longevity of Monel components.
Moreover, the comparative analysis of Monel against stainless steel underscores its unique advantages, particularly in demanding applications where strength and corrosion resistance are paramount. While the initial costs of Monel may be higher, the long-term benefits and reduced lifecycle costs often justify the investment, making it a strategic choice for procurement managers.
In conclusion, understanding the intricate balance between Monel’s strengths and its corrosion vulnerabilities is essential for informed decision-making in material selection. By employing comprehensive maintenance strategies and recognizing the contexts in which Monel excels, professionals can maximize the performance and reliability of their projects, ensuring successful outcomes in challenging environments.