Blogs

Understanding Nickel-Based Super-Alloys: A Comprehensive Tutorial on Properties and Applications
Overview
Nickel-based super-alloys are characterized by their high strength, corrosion resistance, and ability to perform under extreme temperatures, making them essential in applications like jet engines and gas turbines. The article highlights advancements in manufacturing techniques, such as additive manufacturing and optimized processing, which enhance their mechanical properties and address challenges like material costs and sustainability, thus reinforcing their critical role in modern engineering.
Introduction
Nickel-based superalloys have emerged as pivotal materials in high-performance applications, particularly within the aerospace and energy sectors. Their unique combination of high strength, exceptional corrosion resistance, and the ability to withstand extreme temperatures makes them indispensable in modern engineering.
As industries strive for greater efficiency and performance, understanding the fundamental properties, innovative manufacturing techniques, and the evolving landscape of these alloys becomes crucial. This article delves into the key characteristics of nickel-based superalloys, exploring their mechanical properties, the latest advancements in production methods, and the challenges faced in a rapidly changing market.
By examining these elements, procurement managers can make informed decisions that align with both current demands and future trends in this vital field.
Fundamental Properties of Nickel-Based Superalloys
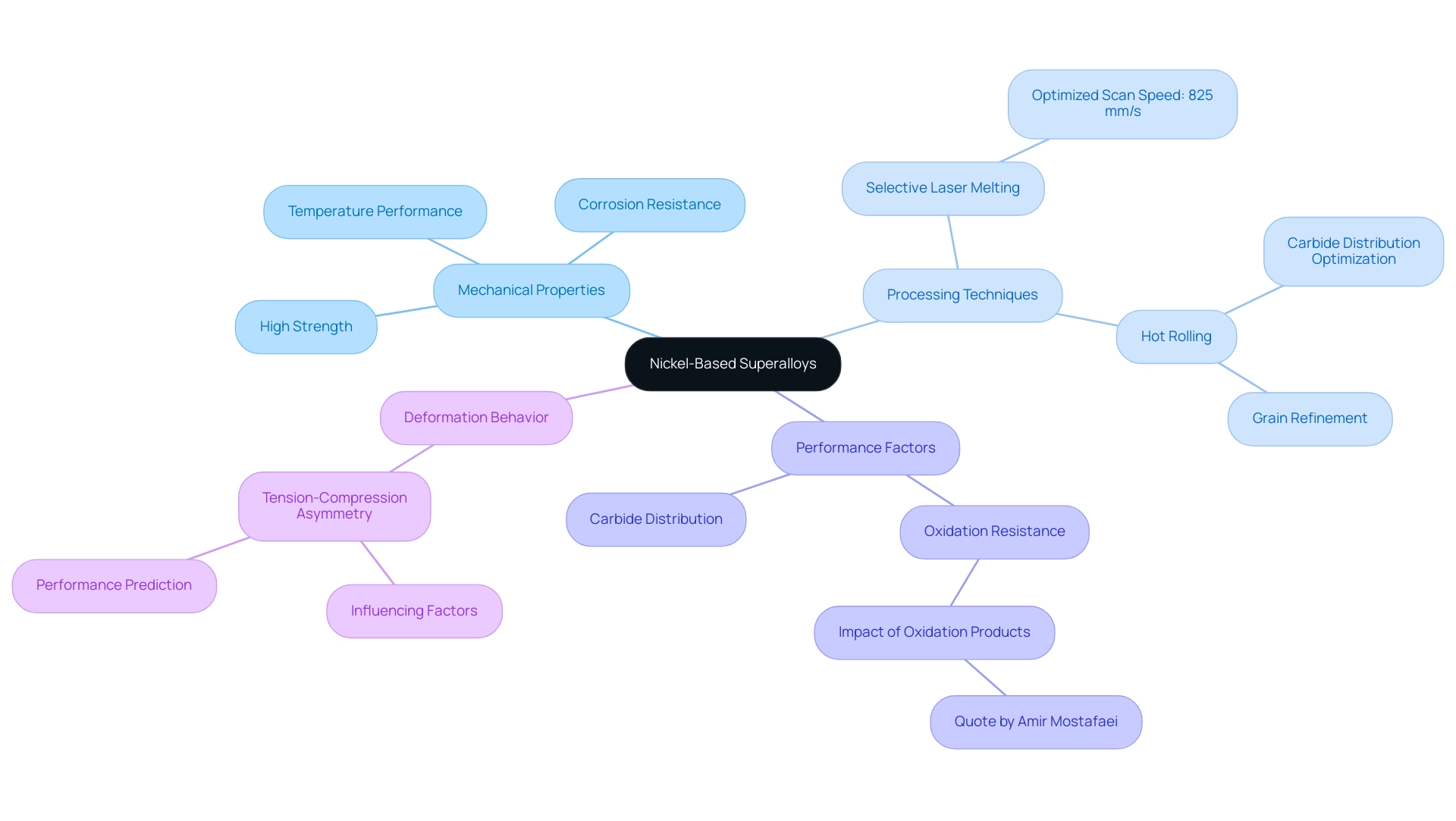
Nickel-based advanced alloys stand out due to their remarkable mechanical properties, which encompass high strength, outstanding corrosion resistance, and the ability to maintain performance under elevated temperatures. These alloys typically consist of a substantial nickel content complemented by chromium, cobalt, and other elements that enhance their overall characteristics. By employing specific processing techniques, such as Selective Laser Melting (SLM) with an optimized scan speed of 825 mm/s, the microstructure of nickel-based advanced alloys can be meticulously tailored, leading to improved resistance to deformation under stress and enhanced oxidation resistance.
Recent advancements in hot rolling have demonstrated a notable improvement in mechanical properties through optimized carbide distribution and grain refinement. Such enhancements are critical, as Amir Mostafaei notes, because these oxidation products can negatively affect the functionality of components made from nickel-based super-alloys. Furthermore, the tension-compression asymmetry observed in nickel-based super-alloys, as highlighted in a recent case study, demonstrates that their deformation behavior varies under tensile and compressive loads.
This phenomenon is influenced by multiple factors and is crucial for predicting performance under different loading conditions. Commonly utilized in high-demand uses such as jet engines and gas turbines, these materials are engineered to endure extreme thermal conditions while preserving their structural integrity, showcasing their vital role in modern engineering solutions.
Manufacturing Techniques and Innovations in Nickel-Based Superalloys
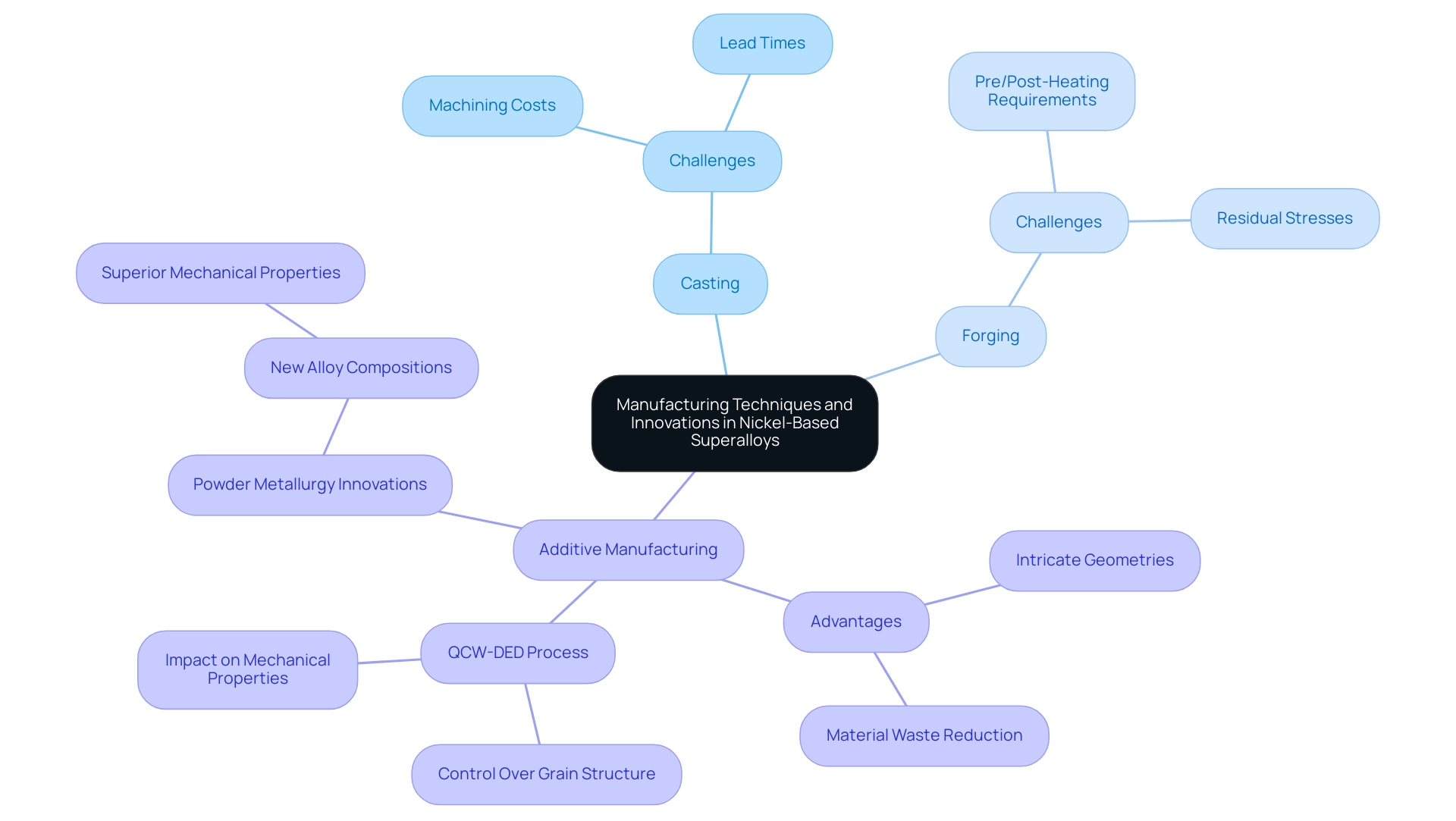
The production of nickel-based super-alloys encompasses a variety of techniques, including casting, forging, and notably, additive manufacturing (3D printing). The latter has seen a significant rise in popularity, primarily due to its capacity to fabricate intricate geometries while minimizing material waste—a critical consideration in today’s manufacturing landscape. Traditional methods, such as casting and forging, often necessitate substantial machining, which can escalate production costs and extend lead times.
Advancements in manufacturing methods are presently focused on improving process efficiency and optimizing the attributes of these materials, all while accommodating the production of customized components tailored to specific application requirements. Notably, the QCW-DED process exemplifies a cutting-edge advancement that facilitates precise control over grain structure and texture in nickel-based super-alloys, significantly impacting their mechanical properties. Recent studies have shown that heat treatment can result in an increase in hardness within the deposition zone but a reduction in hardness in the heat-affected zone (HAZ), highlighting the importance of process control.
Furthermore, recent advancements in powder metallurgy have produced new alloy compositions that demonstrate superior mechanical properties, paving the way for improved operation in challenging environments. As ACY and KCC acknowledge the funding support of the ‘High Entropy Materials Center’, it is clear that collaborative efforts are driving innovation in this field. Furthermore, a case study on modeling hydrogen embrittlement during SSRT tests demonstrated how cracks in embrittled samples initiated at grain boundaries, underscoring the critical challenges faced in nickel-based super-alloys production.
As the industry evolves, the integration of these manufacturing innovations is poised to redefine the standards of nickel-based super-alloys production in 2024 and beyond.
Future Trends and Challenges in Nickel-Based Superalloys
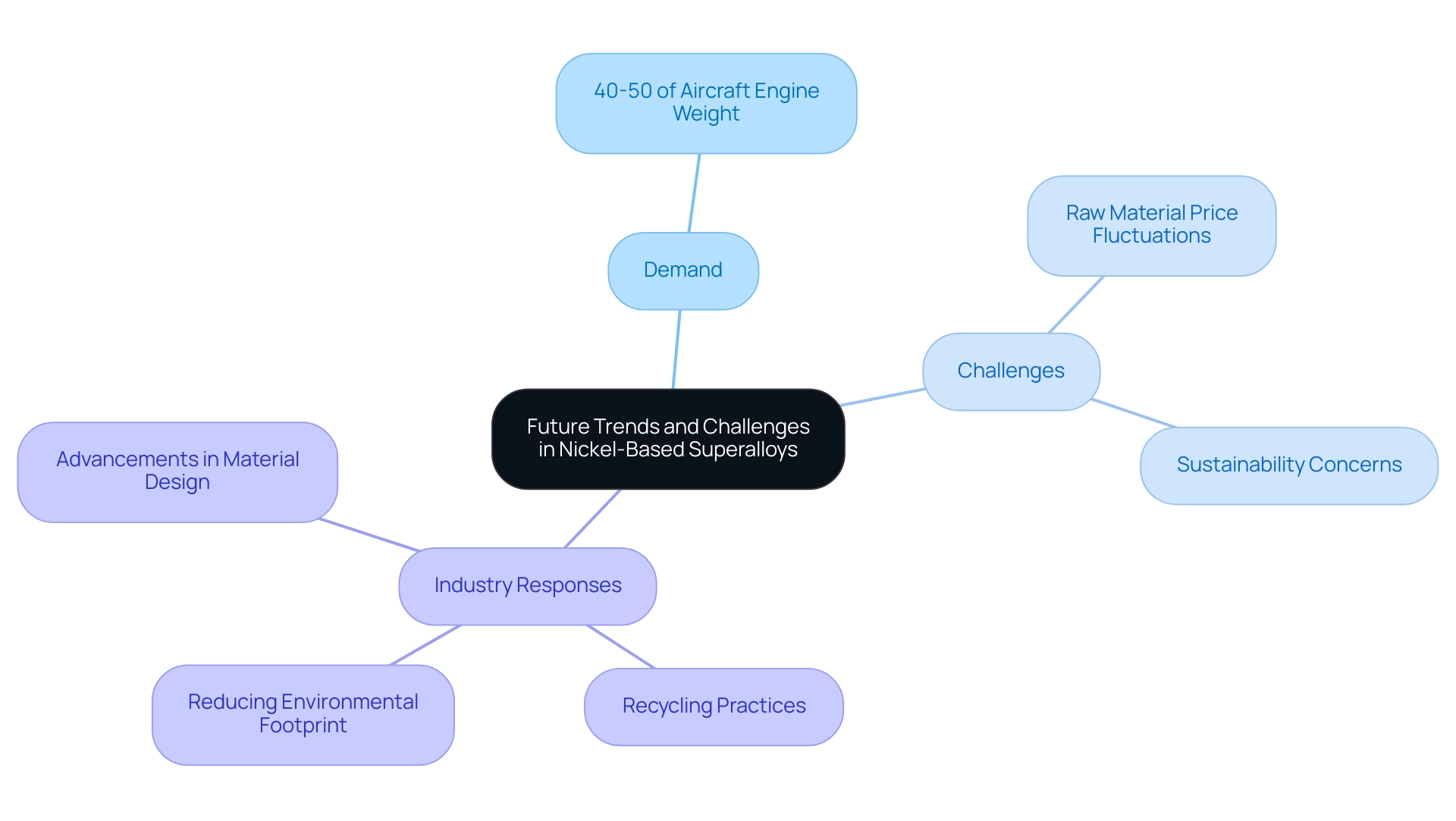
The demand for nickel-based super-alloys is on an upward trajectory, particularly in the aerospace and energy sectors, where these alloys play a vital role in improving functionality and efficiency. Notably, nickel-based super-alloys usually constitute around 40 to 50 percent of the total weight of an aircraft engine, underscoring their significance in aerospace applications. However, this growth is accompanied by significant challenges, including fluctuations in raw material prices and pressing sustainability concerns.
Joel John, Manager – International Business and Partner Relations, states, ‘Thank you for your interest in our research report,’ highlighting the industry’s focus on addressing these challenges. Industry researchers are actively involved in the creation of lighter, more cost-effective material compositions that meet rigorous performance standards without compromising quality. Concurrently, the sector is increasingly adopting sustainable practices, such as:
- The recycling of metal components
- The reduction of the environmental footprint associated with manufacturing processes
The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in the shutdown of multiple manufacturing plants worldwide, adversely affecting the demand for nickel-based super-alloys across various applications in the short term. Despite this slowdown, the nickel-based super-alloys market is anticipated to offer immense opportunities in the long run as economic conditions improve. Looking forward, the incorporation of advanced computational techniques for material design is expected to transform the industry, allowing the swift development of substances that are specifically customized to particular functional criteria.
This strategic focus not only addresses current challenges but also positions the market to capitalize on emerging opportunities in the years to come.
Mechanical Properties and Performance Metrics of Nickel-Based Superalloys
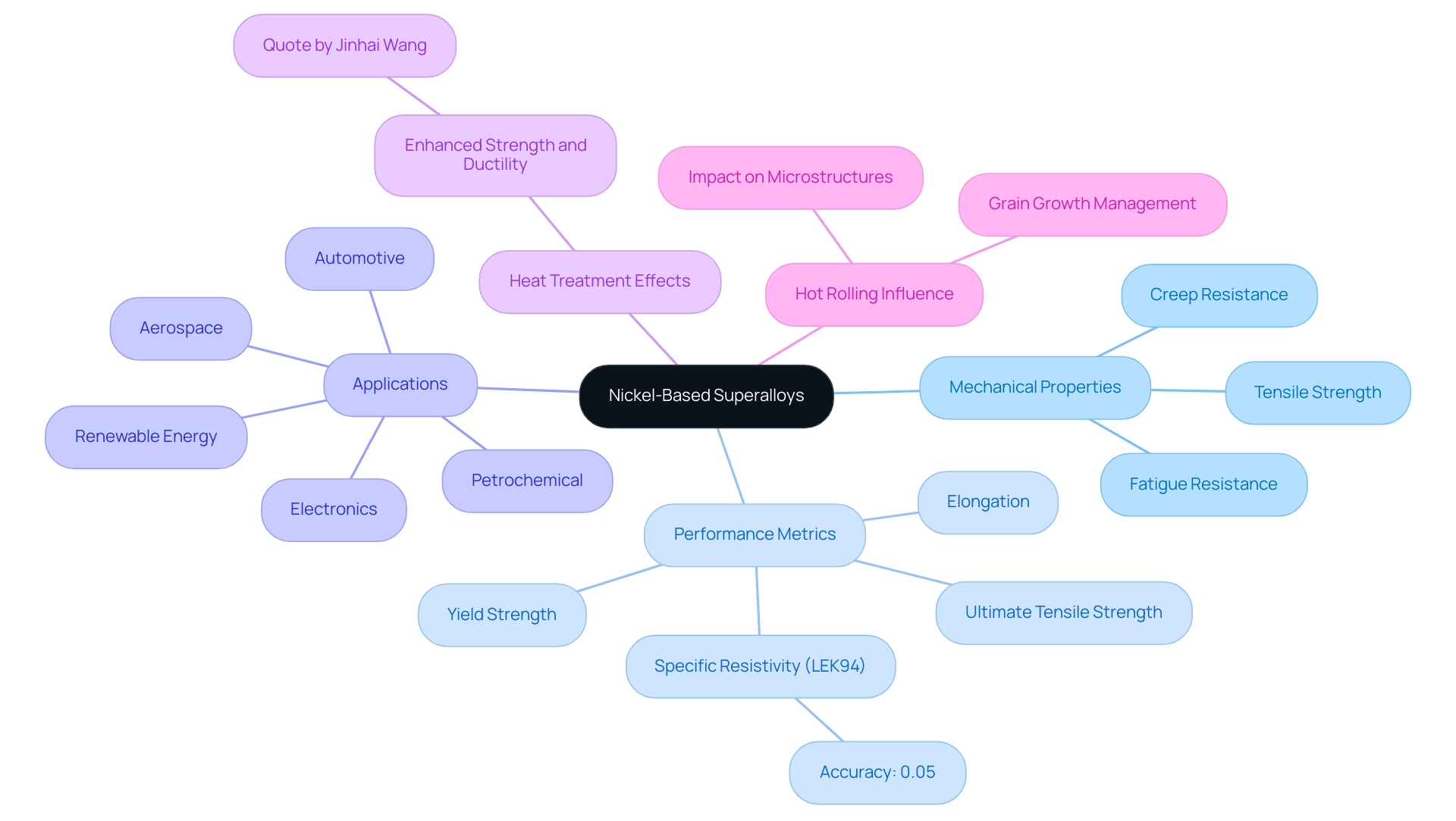
Renowned for their exceptional mechanical properties, nickel-based super-alloys exhibit high tensile strength, impressive fatigue resistance, and outstanding creep resistance. These materials are defined by crucial metrics such as yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, and elongation, which are vital for assessing their suitability for diverse applications. In the aerospace sector, for example, these materials must endure extreme temperatures often exceeding 1,000°C while maintaining their structural integrity.
The specific resistivity measurement accuracy for alloys such as LEK94 is approximately 0.05%, which underscores their reliability in high-performance environments; this accuracy is crucial for procurement managers when selecting materials that must perform under stringent conditions. Furthermore, the behavior of nickel-based super-alloys under diverse loading conditions can be systematically assessed using standardized testing methods. As Jinhai Wang aptly states,
The applied heat treatment enhanced strength remarkably by retaining ductility.
This emphasizes the essential balance between strength and effectiveness that is crucial in high-temperature situations, especially regarding material selection. Additionally, for those interested in the DOMADIA Nickel Molybdenum Iron Alloy, it can be conveniently purchased online through our user-friendly website, which offers easy navigation and a straightforward checkout process, ensuring a seamless procurement experience. The mixture is particularly beneficial across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, petrochemical, electronics, and renewable energy.
Furthermore, our Mica Tape products are specifically crafted to offer high-temperature resistance and outstanding electrical insulation, rendering them essential in contexts where safety and effectiveness are crucial. Understanding these factors, including the high-temperature resistance of up to 1,000°C and the dielectric strength essential for electrical applications, is essential for procurement decisions, as managing grain growth during the hot working of these alloys directly informs their performance in demanding applications.
Conclusion
The exploration of nickel-based superalloys highlights their indispensable role in high-performance applications, particularly within the aerospace and energy sectors. These materials are characterized by their remarkable mechanical properties, including high strength, exceptional corrosion resistance, and the ability to withstand extreme temperatures. The innovative manufacturing techniques, such as additive manufacturing and advanced heat treatment processes, are transforming the production landscape, allowing for the creation of customized components that meet rigorous industry demands.
As the market continues to evolve, procurement managers face both opportunities and challenges. The rising demand for these superalloys is tempered by factors such as raw material price fluctuations and sustainability concerns. However, the ongoing development of lighter, more cost-effective alloy compositions, alongside a commitment to sustainable practices, positions the industry for future growth. The integration of advanced computational methods in alloy design promises to further enhance the performance characteristics of nickel-based superalloys, paving the way for new innovations.
In summary, understanding the fundamental properties and the latest advancements in manufacturing techniques is crucial for making informed procurement decisions. As the landscape of nickel-based superalloys continues to shift, staying abreast of these trends will empower professionals to navigate challenges effectively while capitalizing on emerging opportunities in this vital field.