Blogs

How to Use Mu-Metal Shielding in Magnetic Phonograph Cartridges: A Step-by-Step Guide
Overview
The article provides a comprehensive step-by-step guide on how to effectively use mu-metal shielding in magnetic phonograph cartridges to mitigate magnetic interference and enhance audio performance. It details the necessary materials, precise application techniques, and safety precautions, underscoring the importance of proper installation and maintenance to ensure optimal functionality of the shielding in various environments.
Introduction
In the realm of audio technology, the pursuit of superior sound quality is paramount, and one of the unsung heroes in this quest is mu-metal. This specialized nickel-iron alloy is celebrated for its exceptional magnetic shielding properties, making it an indispensable component in devices such as phonograph cartridges.
As urban environments become increasingly saturated with electronic devices, the need for effective magnetic interference mitigation grows ever more critical. Understanding the unique characteristics of mu-metal—its high permeability and low coercivity—empowers procurement managers and audio professionals alike to enhance equipment performance and reliability.
This article delves into the properties, applications, and practical implementation of mu-metal, offering a comprehensive guide that not only addresses common challenges but also outlines essential safety precautions and maintenance strategies to ensure long-term efficacy in audio applications.
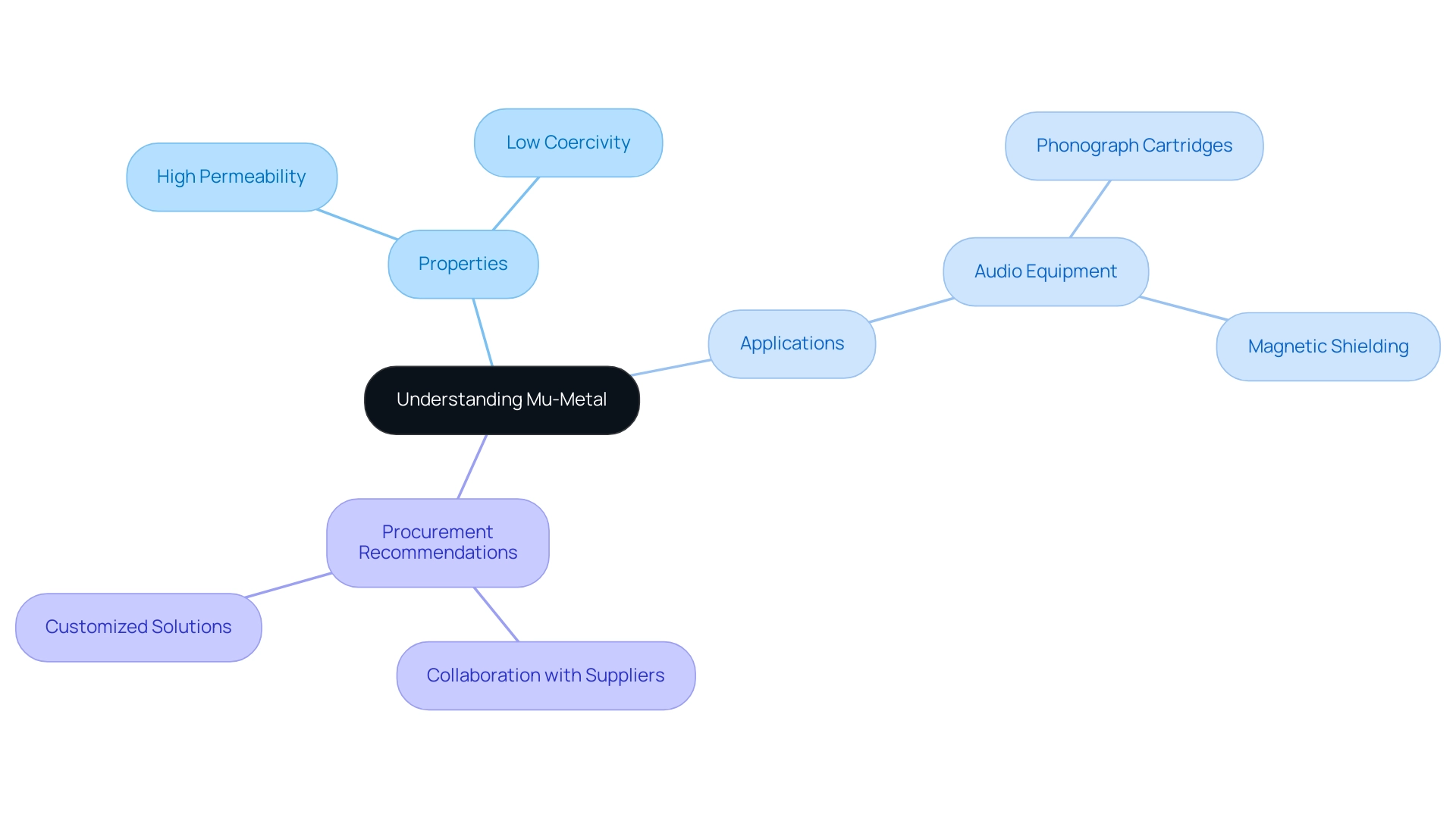
Understanding Mu-Metal: Properties and Applications in Audio Equipment
This specialized nickel-iron alloy is renowned for its remarkable magnetic protection capabilities. It boasts a high permeability, estimated at around 100,000, allowing it to efficiently redirect magnetic fields—an essential characteristic for applications in audio equipment, especially in phonograph cartridges that utilize mumetal shielding in magnetic phonograph cartridges. The alloy’s low coercivity facilitates easy magnetization, thereby minimizing residual magnetism, which can adversely affect audio performance.
This property is particularly advantageous in environments prone to strong magnetic interference, such as urban landscapes or areas populated with electronic devices. With nickel production growth exceeding 10% in the last two years, driven largely by laterite ores, the availability of mu-metal is increasingly relevant. As mentioned by Outokumpu, the Finnish metallurgical firm that pioneered flash smelting technology, understanding the properties of mu-metal is essential for professionals aiming to improve audio equipment performance through effective protection solutions.
Furthermore, it is recommended for procurement managers to collaborate with reputable suppliers and manufacturers of electrical insulation and high-temperature materials, including those specializing in Beryllium Copper, to ensure quality sourcing. Recent advancements in mu-metal applications further highlight its growing significance in audio technology, particularly through mumetal shielding in magnetic phonograph cartridges, showcasing its versatility and effectiveness in mitigating magnetic interference. Particular providers of Mu-metal and Beryllium Copper can offer customized solutions that satisfy the distinct needs of various magnetic protection applications.
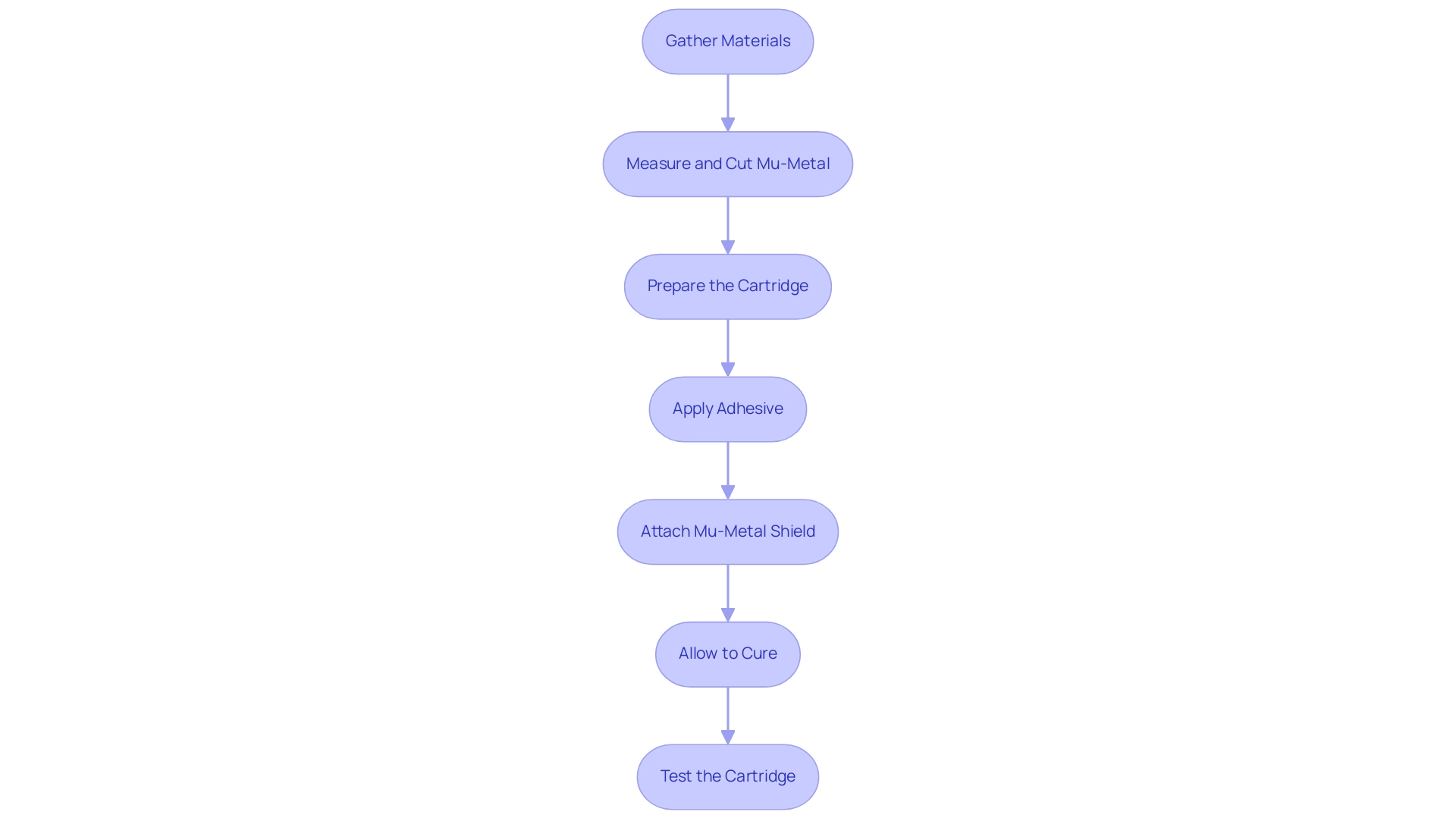
Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing Mu-Metal Shielding in Phonograph Cartridges
- Gather Materials: Begin by sourcing high-quality mu-metal sheets or foils, an appropriate adhesive for metal bonding, and essential tools such as non-sparking tools from reputable suppliers like [Supplier Name] or [Supplier Name]. Additionally, ensure you have scissors or a craft knife for precise cutting. It’s imperative to maintain a clean workspace to prevent any contamination that could compromise the integrity of the shielding.
- Measure and Cut Mu-Metal: Accurately measure the dimensions of the phonograph cartridge that needs protection. Cut the mu-metal sheets to the precise size needed for mu-metal shielding in magnetic phonograph cartridges, ensuring there are no gaps that might expose it to magnetic interference.
Prepare the Cartridge: Thoroughly clean the surface of the phonograph cartridge to facilitate optimal adhesion. Remove any dust, grease, or residues that could hinder the bonding process, thereby ensuring a secure application.
- Apply Adhesive: Evenly apply a thin layer of adhesive to the side of the mu-metal sheets that will come into contact with the cartridge. Adhere strictly to the adhesive manufacturer’s instructions for best results, as this will enhance the durability of your shield.
- Attach Mu-Metal Shield: Position the mu-metal sheet around the cartridge with care, pressing firmly to create a solid bond. Pay particular attention to the edges, ensuring there are no openings that could permit magnetic interference, which is crucial for effective mu-metal shielding in magnetic phonograph cartridges.
Allow to Cure: Allow the adhesive to cure according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. This step is critical; a properly cured adhesive will ensure that the bond can withstand the mechanical stresses encountered during use.
- Test the Cartridge: After the adhesive has fully cured, conduct a test on the phonograph cartridge to confirm its functionality. Listen for any improvements in sound quality and a significant decrease in background noise, which are indicators that the mu-metal shielding in magnetic phonograph cartridges has been successfully applied.
In the context of professional audio equipment, it’s worth noting that such equipment generally comes equipped with a 3-wire line cord, which emphasizes the importance of proper protection to prevent interference. As Jim Rozen stated, ‘Two of my patents wouldn’t have been possible if an appropriate superconducting shield inside nested mu-metal shields… did not exclude some (although not all) magnetic flux, reducing the field below that of the mu metal alone.’ This highlights the critical role of effective shielding in environments prone to explosive reactions.
The Audio Engineering Society advocates for careful design and installation practices, as improper grounding can lead to hum and buzz in audio systems, making the choice of materials and tools, including suppliers of non-sparking tools like [Supplier Name] and electrical insulation materials such as [Product Type], essential for safety and effectiveness.
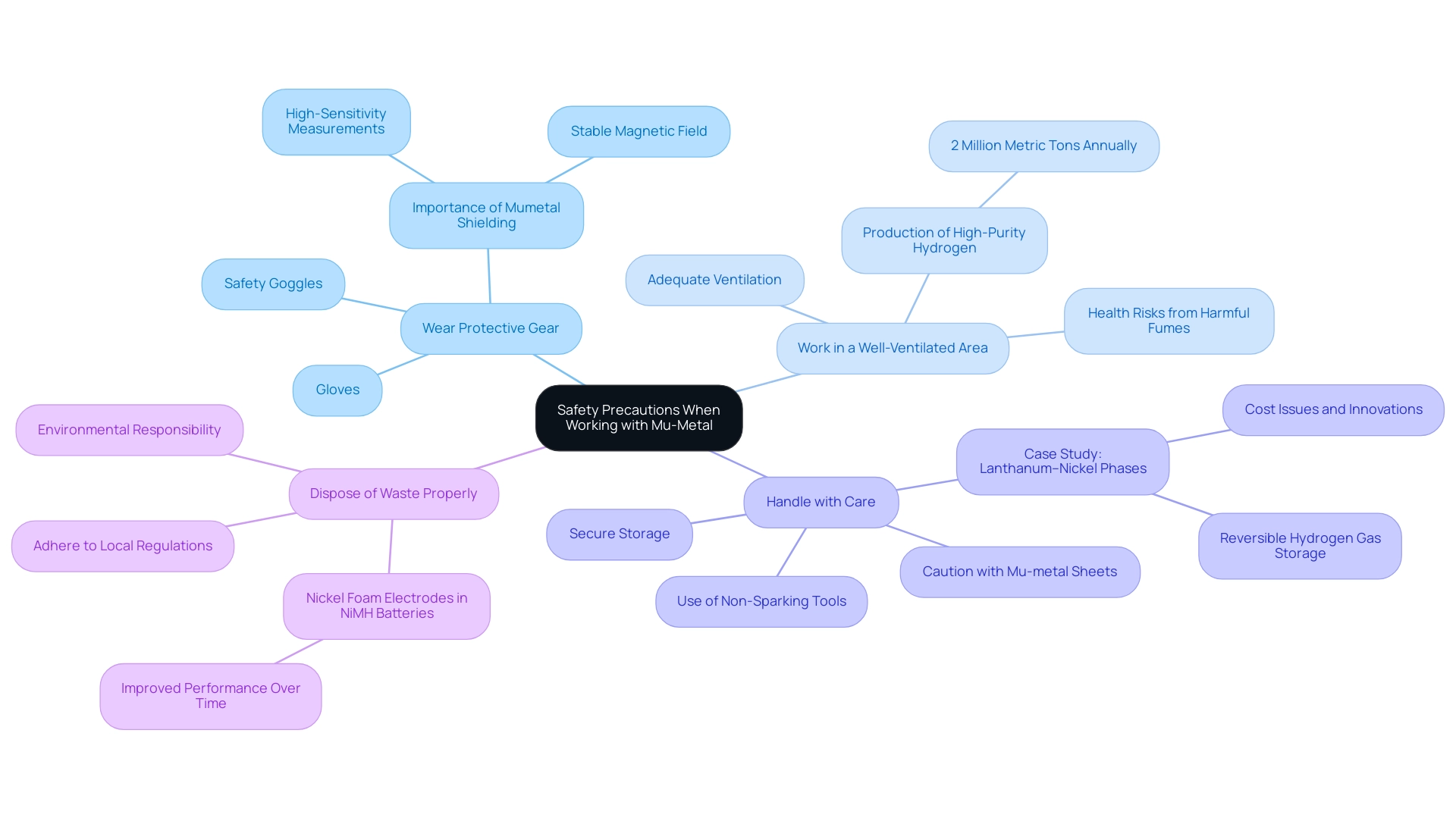
Safety Precautions When Working with Mu-Metal
When working with the alloy, it is crucial to adhere to the following safety precautions to ensure a safe working environment:
- Wear Protective Gear: Always use gloves to safeguard your hands from sharp edges and safety goggles to protect your eyes from potential debris during cutting operations. As Jin Li highlights, mumetal shielding in magnetic phonograph cartridges is essential in various high-sensitivity measurements to ensure a stable and weak magnetic field, underscoring the importance of careful handling. The design typically includes three coils for homogeneous fields and five for linear magnetic field gradients, emphasizing the critical nature of precision in these applications.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: Adequate ventilation is essential when using adhesives, as harmful fumes can pose health risks. If possible, conduct your work outdoors or in a space with robust airflow to mitigate these hazards. Approximately 2 million metric tons of high-purity hydrogen are produced annually worldwide by AELs, highlighting the relevance of safety in handling substances like mumetal shielding in magnetic phonograph cartridges for industrial applications.
- Handle with Care: Exercise caution when managing Mu-metal sheets to avoid cuts or injuries. Always store supplies securely when not in use to prevent accidents and ensure that they do not become a safety hazard. Furthermore, Non-Sparking Tools are the ideal substitute for non-sparking application purposes in explosive potential environments, emphasizing the need for safe practices in handling sensitive substances. A case study on the Lanthanum–Nickel phases illustrates the importance of safety regarding substances, as the Lani active component was initially too expensive for standard applications, prompting innovations in safer, more economical alternatives.
- Dispose of Waste Properly: Adhere to local regulations for disposing of any residual substances or adhesive containers. This practice not only promotes environmental responsibility but also aligns with best practices in safety management by incorporating mumetal shielding in magnetic phonograph cartridges, which will enhance safety and mitigate risks associated with working with Mu-metal. The use of nickel foam electrodes in modern NiMH batteries demonstrates enhanced performance over time, further highlighting the significance of safe handling practices in the context of advancing technologies.
For procurement managers, it’s essential to consider suppliers and manufacturers of electrical insulation options, including high-temperature fabrics and metals. Key product tags to note include Beryllium Copper, Kovar, Mu-Metal, and Nickel materials, which can aid in customer inquiries and sourcing decisions.
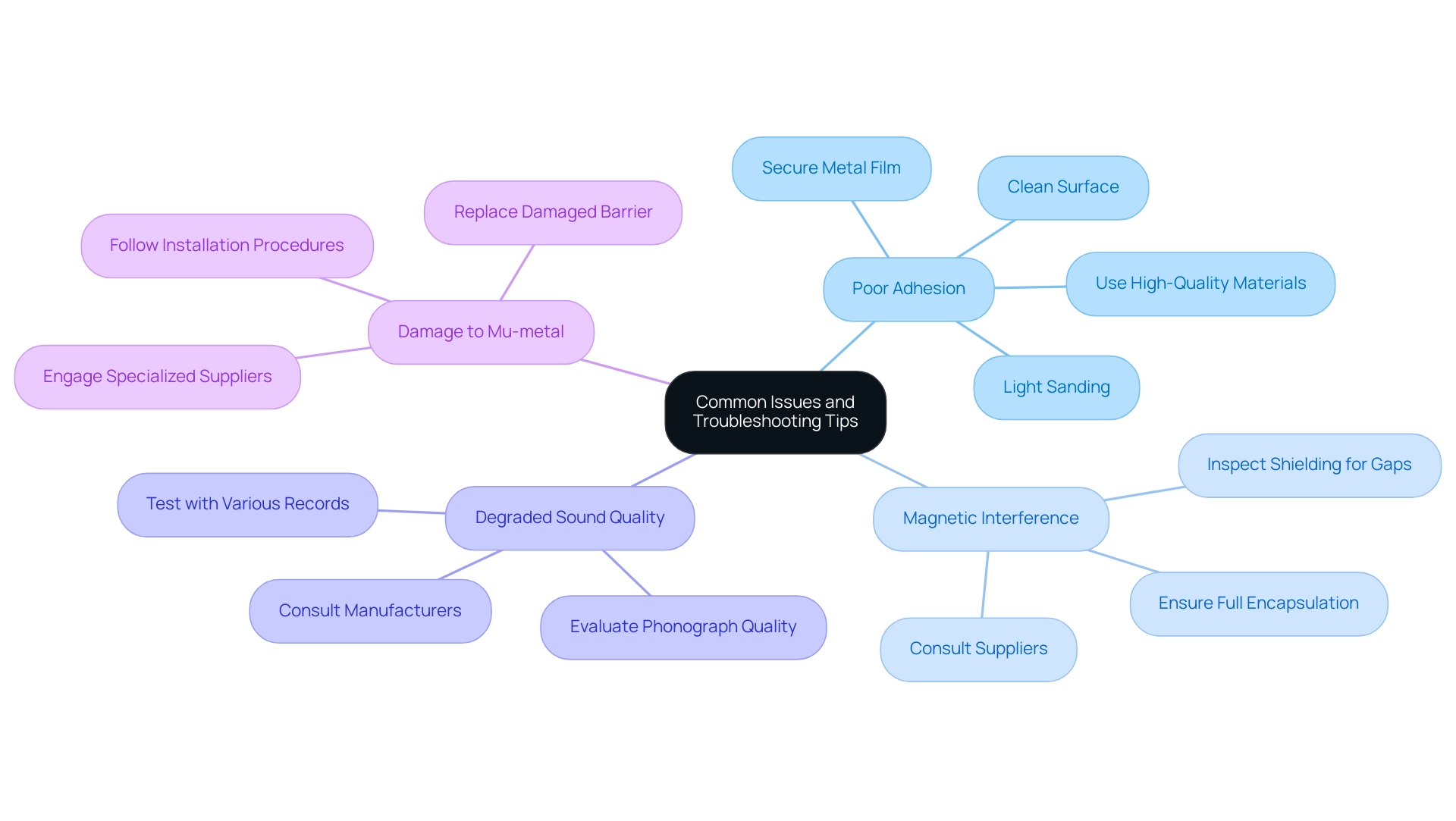
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
- Poor Adhesion: When encountering difficulties with inadequate sticking of magnetic metal barriers, it is essential to verify that the surface of the cartridge is meticulously clean and free of any grease. A light sanding of the area can significantly enhance adhesion, promoting a more reliable bond. Moreover, consider how securing the metal film to the ferrite barrier can significantly affect the overall efficiency of mumetal shielding in magnetic phonograph cartridges. For optimal results, sourcing high-quality magnetic shielding material from reputable suppliers, along with products such as Kapton Tapes for secure attachment, can also bolster performance.
- If magnetic interference persists as a problem, it is necessary to conduct a thorough inspection of the mumetal shielding in magnetic phonograph cartridges for any gaps. The protective cover must fully encapsulate the cartridge, leaving no openings that could compromise performance. It’s important to note that the drive frequency can vary continuously from .008 Hz to 12 kHz, and this may affect the effectiveness of mumetal shielding in magnetic phonograph cartridges. Interacting with suppliers of high-quality electrical insulation products, including Silica Coated Fabrics, can offer valuable insights on minimizing these interferences.
- Degraded Sound Quality: If the anticipated improvements in sound quality are not realized, consider evaluating other potential factors affecting performance. This includes assessing the quality of the phonograph and the condition of the records. Testing with various records can aid in isolating the root cause of the sound issues. The case study results indicate that while substances like AD-MU-78 and CP-EXP-1184 exhibit stable shielding characteristics below 1 kHz, their performance diverges at higher frequencies, which may impact sound quality. Consulting with manufacturers of high-temperature materials may also provide additional solutions.
- Damage to Mu-metal: In instances where the Mu-metal barrier has sustained damage, replacement is often the only viable solution. Ensure that any new barrier is installed correctly, adhering to the established procedures outlined in this guide to guarantee optimal performance. When sourcing replacements, it is advisable to engage with specialized suppliers to ensure that the new materials, such as high-quality Silica Coated Fabrics, meet the necessary specifications for effective magnetic protection.
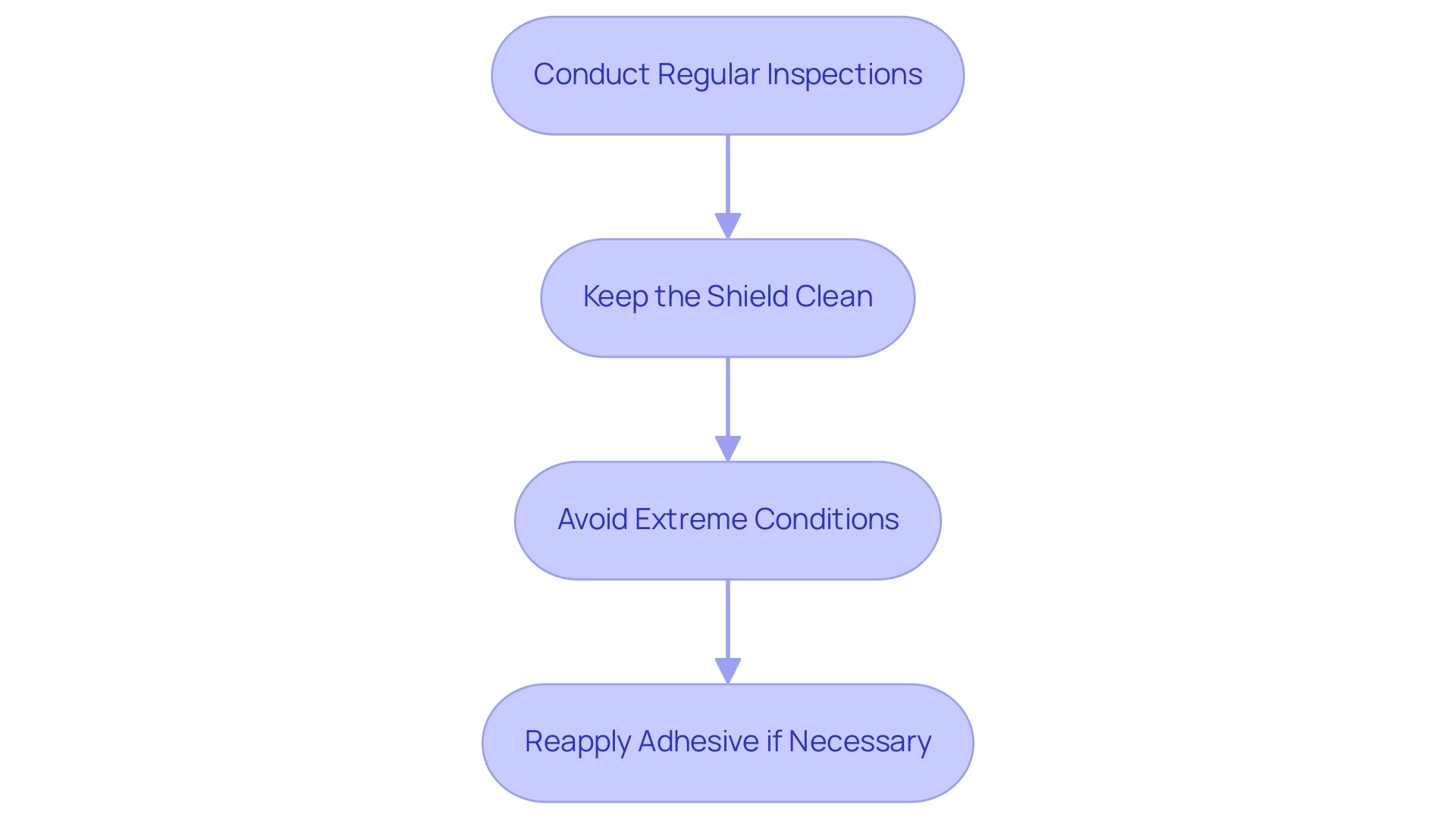
Maintaining Mu-Metal Shields for Long-Term Performance
To ensure optimal performance of your Mu-metal protection, adherence to a structured maintenance routine is essential:
- Regular Inspections: Conduct periodic inspections of the Mu-metal barrier to identify any signs of wear, damage, or loosening. Addressing these issues promptly is crucial to prevent further degradation of the shield’s protective capabilities.
- Keep Clean: Accumulated dust and debris can adversely affect shielding performance. Utilize a soft, dry cloth to gently clean the surface, avoiding abrasive items that may scratch the Mu-metal.
- Avoid Extreme Conditions: Shield longevity can be compromised by exposure to extreme temperatures and humidity. It is advisable to store the phonograph in a stable environment when not in use, thus protecting the adhesive and the material’s integrity.
- Reapply Adhesive if Necessary: If signs of peeling or lifting are evident, it is important to reapply adhesive to maintain a secure fit. This proactive approach can significantly extend the lifespan of mumetal shielding in magnetic phonograph cartridges, which typically averages several years based on usage and care practices.
These maintenance strategies are critical for preserving the performance of mumetal shielding in magnetic phonograph cartridges, especially in audio equipment where electromagnetic interference can severely impact sound quality. Furthermore, utilizing Mica Tape products, such as Mica Insulation Tape, Mica Tape for Electrical, and Mica Sheet Tape, with high-temperature resistance and electrical insulation properties can enhance the performance of protective barriers in challenging applications. Mica Insulation Tape, for instance, is designed for high-temperature resistance in electrical engineering applications, ensuring durability and reliability.
Mica Tape for Electrical offers excellent flame resistance and dielectric strength, making it essential for fire-resistant cables and insulation systems. According to industry insights, mumetal shielding in magnetic phonograph cartridges can markedly enhance the reliability of devices. As illustrated in a case study involving inductive type proximity sensors, the application of mumetal shielding in magnetic phonograph cartridges resulted in improved performance and dependability.
Furthermore, as mentioned by Ali Ghasemi, ‘This chapter elucidates the principles of magnetic phenomena and associated theories to offer a foundation for those with minimal knowledge of magnetism and related effects,’ emphasizing the significance of grasping these principles when preserving protection. Furthermore, the historical significance of materials used for shielding is underscored by the production of the new nickel–iron accumulator starting in 1901, which paved the way for advancements in magnetic protection solutions.
Conclusion
The exploration of mu-metal reveals its vital role in enhancing audio equipment performance through effective magnetic shielding. This specialized nickel-iron alloy, with its impressive high permeability and low coercivity, is essential for mitigating the impacts of magnetic interference prevalent in today’s electronic-saturated environments. By implementing mu-metal in devices such as phonograph cartridges, audio professionals can significantly improve sound quality and reliability.
The step-by-step guide provided underscores practical methods for integrating mu-metal shielding, while emphasizing the importance of safety precautions during implementation. Attention to detail in measurement, preparation, and application ensures optimal performance and longevity of the shielding. Additionally, addressing common issues such as poor adhesion and persistent magnetic interference with proactive troubleshooting strategies can further enhance the effectiveness of mu-metal solutions.
Maintaining mu-metal shields is equally critical for sustaining their protective capabilities over time. Regular inspections, cleanliness, and appropriate environmental considerations are necessary to prolong their efficacy. By adhering to these maintenance practices, audio equipment can achieve consistent performance, ultimately leading to improved sound quality and user satisfaction.
In conclusion, understanding and effectively utilizing mu-metal not only empowers procurement managers and audio professionals to make informed decisions but also highlights the strategic importance of quality materials in audio technology. As the demand for high-performance audio solutions continues to grow, investing in mu-metal shielding is a critical step toward achieving superior sound quality and reliability in audio applications.