Blogs
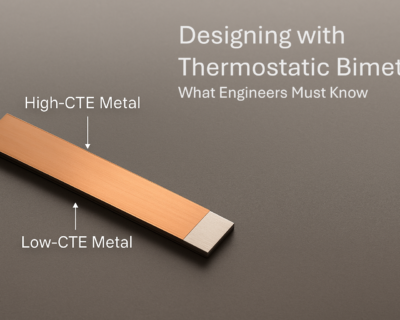
What Makes It Tick: Properties of Thermostatic Bimetals
What makes a simple strip of bonded metal so reliable that we trust it to protect circuits, regulate temperatures, and even trigger fire alarms?
It’s not just clever design—it’s the material properties at work.
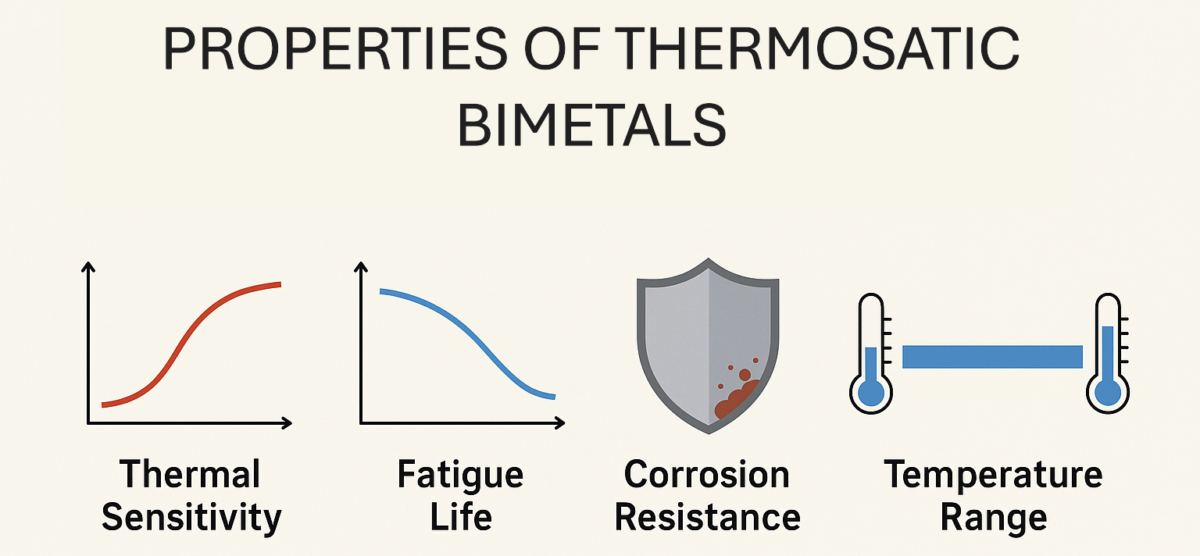
From thermal sensitivity to fatigue life and corrosion resistance, thermostatic bimetals are finely tuned to perform precisely in the harshest, most demanding environments. In this blog, we dive into the physical and mechanical properties that make thermostatic bimetals tick—literally and figuratively.
1. Thermal Sensitivity: Precision at the Molecular Level
The most defining property of a thermostatic bimetal is its ability to bend predictably with temperature.
This is achieved through:
- The difference in thermal expansion coefficients (CTE) between the bonded metals
- The geometry and thickness of the strip
- The modulus of elasticity of each layer
A well-designed bimetal responds in a linear or snap-action manner, delivering:
- High sensitivity (as low as 0.05 mm/°C deflection)
- Repeatable, predictable behavior across thousands of cycles
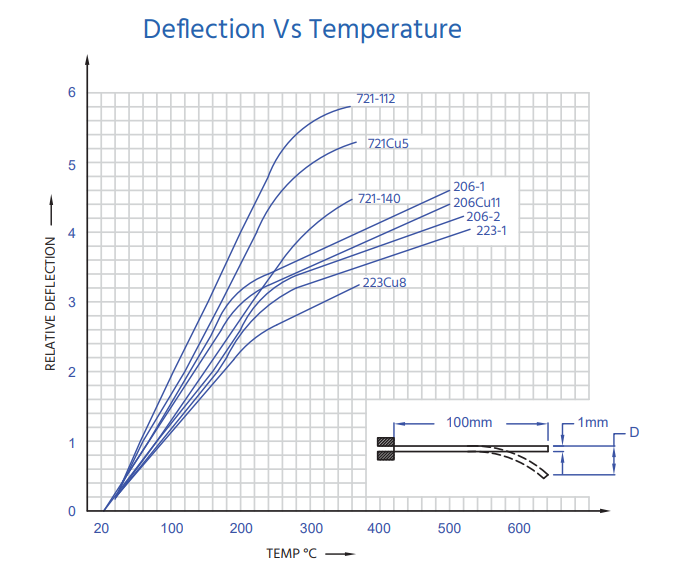
The deflection-temperature curve is like a thermal fingerprint of each bimetal.
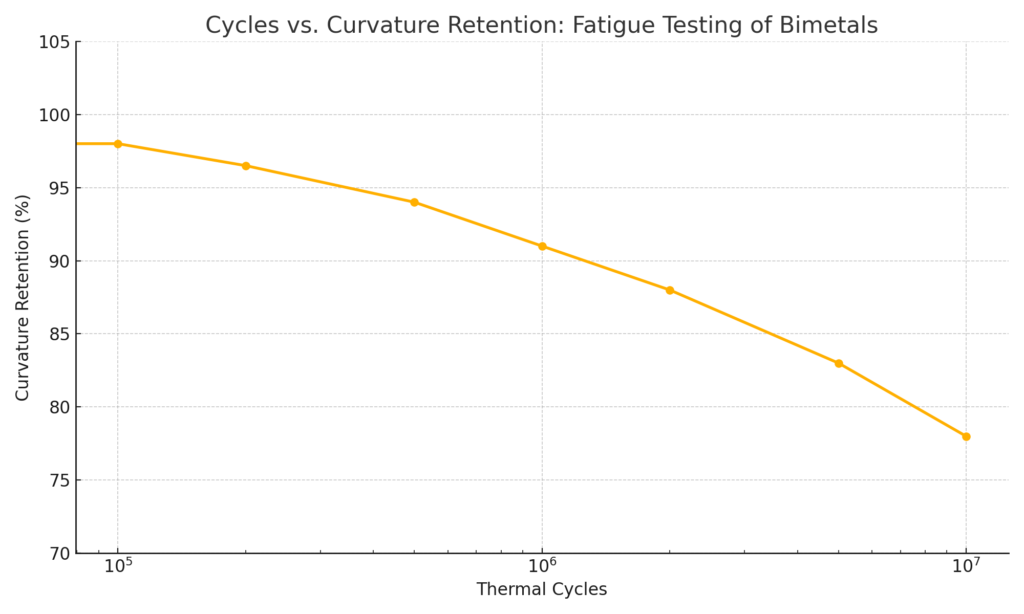
2. Stress-Strain Behavior and Fatigue Life
Every time a bimetal bends, it experiences mechanical strain. That makes stress-strain performance a key design factor.
🔧 Key Mechanical Properties:
- Elastic modulus – Determines flexibility vs. stiffness
- Yield strength – Limits how far it can bend without deforming
- Fatigue resistance – Ability to handle millions of cycles without cracking or weakening
Thermostatic bimetals are typically tested to:
- 100,000 to 10,000,000 thermal cycles
- ±90° bending range (in coiled forms)
- <5% loss of deflection over time
✅ When designed well, a bimetal strip can function reliably for decades.
3. Range of Motion: From Micro-Bends to Full Rotations
Depending on the form and thickness, thermostatic bimetals can produce:
- Micro-deflection – In flat strips used in thermal switches
- Rotational motion – In spirals and coils (e.g., dial thermometers)
- Snap-displacement – In bi-stable systems like fire alarms
This flexibility is why bimetals are used in such diverse mechanisms, from compact relays to heavy-duty thermal regulators.
4. Corrosion Resistance: Built for Longevity
In many environments—kitchens, industrial plants, vehicles—bimetals face moisture, heat, and chemicals.
Typical strategies to enhance corrosion resistance:
- Use stainless steel or Invar as the low-expansion layer
- Apply nickel plating or anti-corrosive coatings
- Choose compatible metal pairs to reduce galvanic corrosion
🧪 A bimetal that resists rust is a bimetal that lasts longer—and performs better.
5. Temperature Range: Designed to Perform Under Pressure
Thermostatic bimetals are customized for a wide range of environments:
| Application | Typical Operating Range |
| Household appliances | −20°C to +150°C |
| Automotive thermostats | −40°C to +125°C |
| Industrial/HVAC systems | −40°C to +300°C |
| Aerospace-grade bimetals | −70°C to +400°C (special alloys) |
These ranges depend on:
- The metal pair’s expansion characteristics
- Heat treatment methods
- Desired activation threshold
Summary: The Engineered Excellence of Bimetals
Thermostatic bimetals are more than simple materials—they’re precision tools.
| Property | Why It Matters |
| Thermal Sensitivity | Enables accurate temperature response |
| Stress-Strain Behavior | Supports mechanical reliability over time |
| Fatigue Resistance | Extends operating lifespan |
| Corrosion Resistance | Protects against environmental damage |
| Temperature Range | Adapts bimetals for specific use-cases |
⚡ The real magic of bimetals isn’t that they move—it’s that they move predictably, reliably, and forever.
🔗 Next Up: Blog 6 – Design Considerations
In our next post, we’ll explore how engineers design with thermostatic bimetals, including tips on thickness, mounting, deflection tuning, and choosing between linear or snap-action responses.
Got questions? or got an ideas—we’re always ready to dive deeper!
Contact our experts today!
Talk to: Er.Pankaj Domadia | Kairav Domadia | Aadil Domadia | Pragati Sanap | Pooja N N | Shivani Kanojia
Read our previous blog on https://domadia.net/thermostatic-bimetal/domadia-testing-thermostatic-bimetals/