Blogs

How to Execute the Inconel 625 Welding Procedure: A Step-by-Step Guide
Overview:
The article focuses on the detailed procedures and considerations for executing the Inconel 625 welding procedure, emphasizing the importance of material properties, welding techniques, and post-welding inspections. It supports this by outlining the unique characteristics of Inconel 625 that influence welding, such as its resistance to corrosion and oxidation, and highlights best practices in welding preparation, technique selection (primarily TIG welding), and the necessity of thorough inspections to ensure structural integrity and compliance with industry standards.
Introduction
Inconel 625 stands out as a premier choice in the realm of high-performance alloys, revered for its exceptional resistance to extreme temperatures and corrosive environments. Comprising a unique blend of nickel, molybdenum, and iron, this alloy is engineered to excel in demanding applications across aerospace, chemical processing, and marine industries.
The impressive mechanical properties of Inconel 625, coupled with its high-temperature stability and weldability, make it an indispensable material for critical components where reliability is paramount. As industries evolve and the need for advanced materials intensifies, understanding the intricacies of Inconel 625—from its properties and welding techniques to post-welding inspections—becomes essential for procurement managers and engineers alike.
This article delves into the essential aspects of Inconel 625, providing insights that empower professionals to make informed decisions in their procurement and application processes.
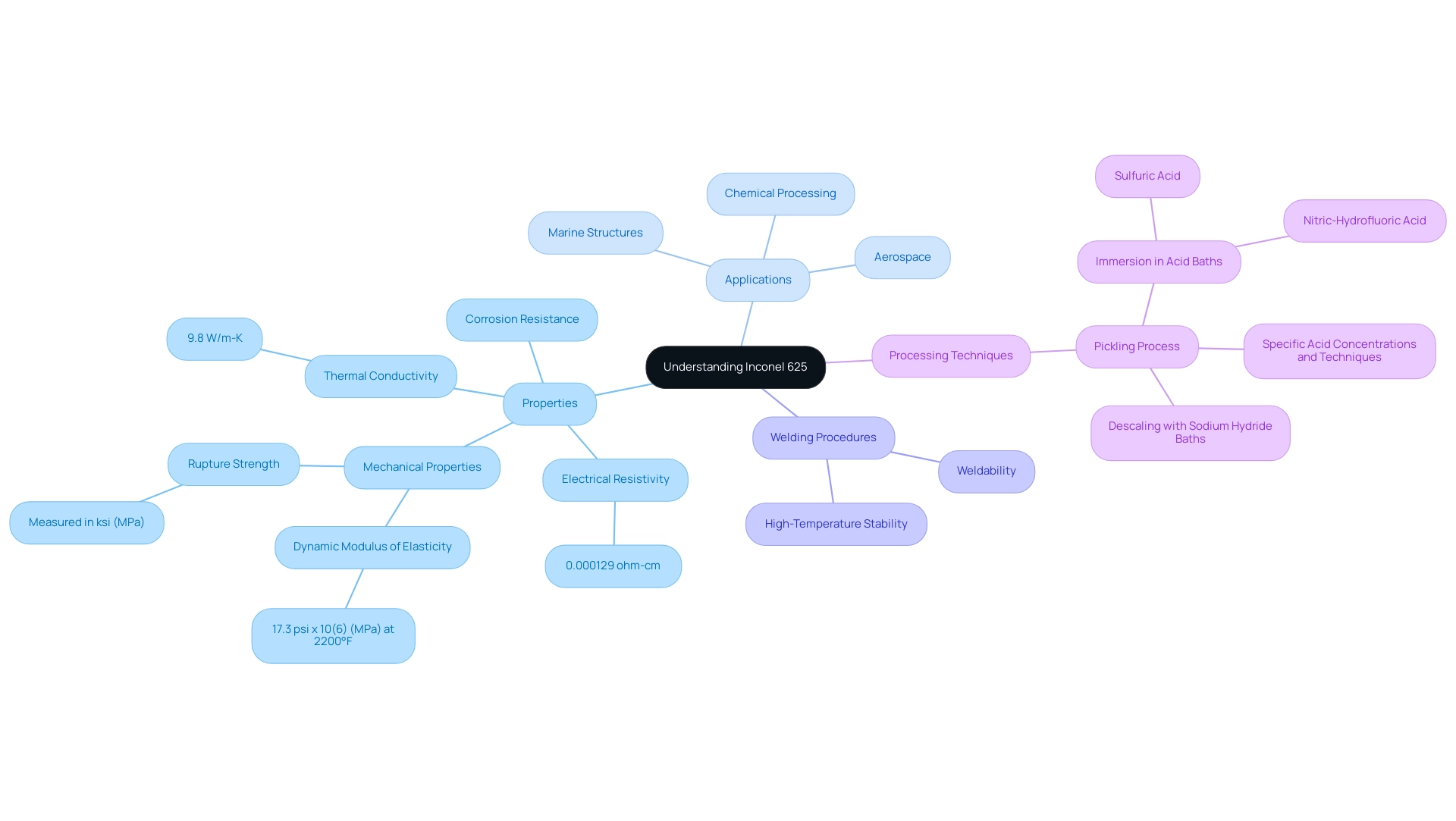
Understanding Inconel 625: Properties and Applications
Alloy 625 is a highly regarded nickel-chromium blend celebrated for its remarkable resistance to oxidation and corrosion, particularly in extreme temperature environments. Composed of Nickel (Ni), Molybdenum (Mo), and Iron (Fe), this alloy exhibits superior corrosion resistance and excellent mechanical properties, making it ideal for critical aerospace components, chemical processing equipment, and marine structures. With an average dynamic modulus of elasticity of 17.3 psi x 10(6) (MPa) at 2200°F, this alloy demonstrates significant mechanical performance under demanding conditions.
The inconel 625 welding procedure benefits from its high-temperature stability, excellent weldability, and precision manufacturing—crafted to meet the most demanding requirements—further enhancing its application range and establishing it as a preferred material across various industries. Notably, the electrical resistivity of the alloy 625 is measured at 0.000129 ohm-cm, and it boasts a thermal conductivity of 9.8 W/m-K, which are crucial factors in the inconel 625 welding procedure. The rupture strength of alloy 625 is measured in ksi (MPa) for specified aging times at various temperatures, underscoring its mechanical robustness.
Understanding these properties is essential for ensuring successful outcomes in applications that require reliability and performance, particularly in aerospace and marine sectors where the inconel 625 welding procedure is vital, as failure is not an option. Recent developments in 2024 continue to showcase the versatility of alloy 625, reaffirming its status as a vital material in modern industrial applications. Furthermore, the use of mica tape products, known for their high-temperature resistance and superior electrical insulation properties, complements the applications of this nickel-chromium alloy.
These tapes are indispensable in the construction of coils, capacitors, and other components that require high-grade insulation to maintain safety and performance. Mica tape products are also widely utilized in household appliances and industrial machinery, ensuring reliability across various applications. A practical illustration of alloy 625’s processing techniques can be seen in the pickling process, which involves descaling with sodium hydride baths followed by immersion in sulfuric and nitric-hydrofluoric acid baths at specified temperatures and durations.
This meticulous process ensures effective cleaning and preparation of the alloy for further applications, utilizing specific acid concentrations and electrochemical techniques for macro-inspection.
Choosing the Right Welding Technique: Focus on TIG Welding
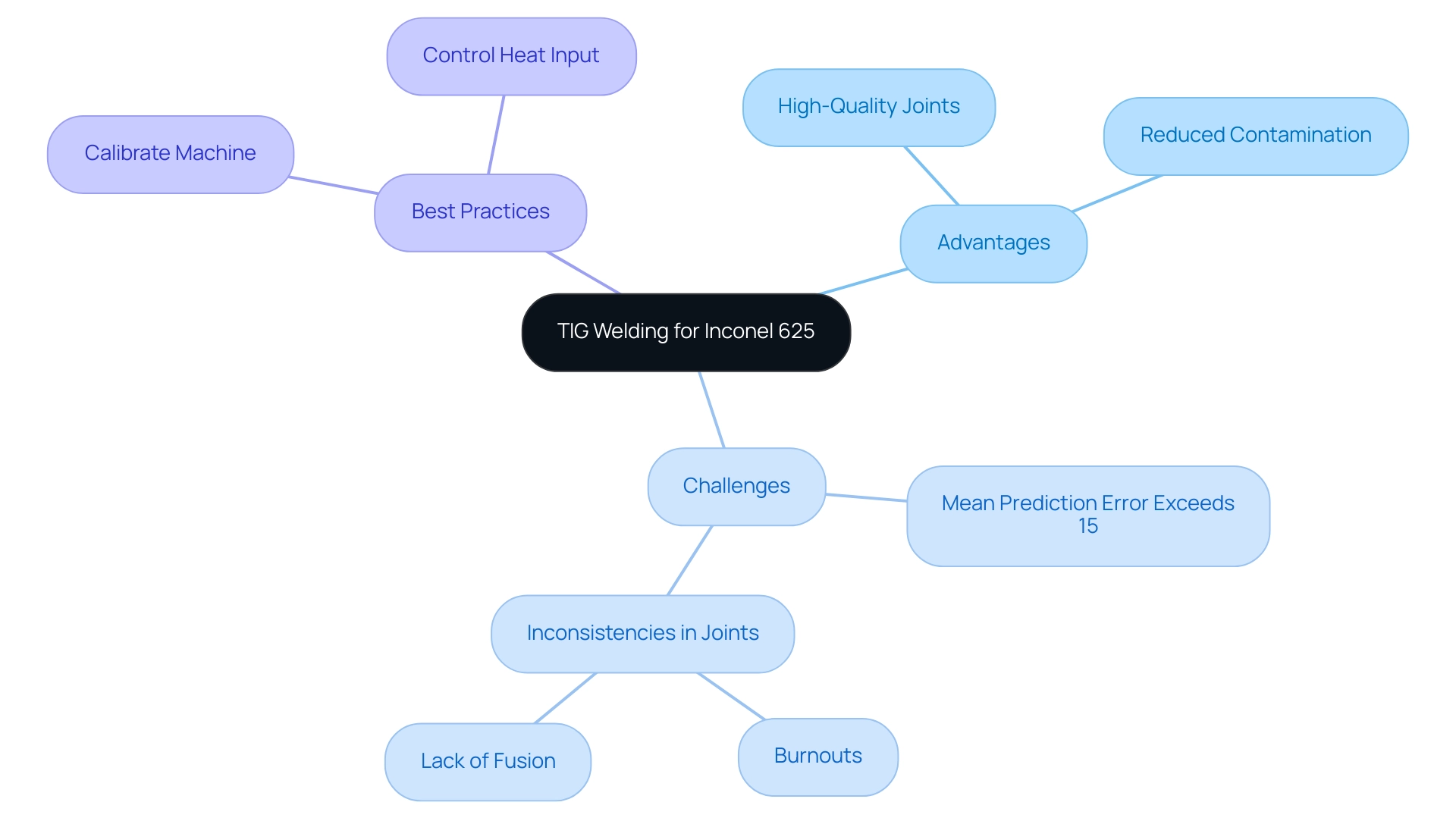
TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding is recognized as the top method for connecting this alloy in the inconel 625 welding procedure due to its ability to produce high-quality, precise joints while reducing contamination risks. This process employs a non-consumable tungsten electrode with an inert gas, usually argon, which effectively protects the joint area from atmospheric impurities. Such a controlled environment is essential for maintaining the integrity of the weld, especially in the inconel 625 welding procedure, considering the unique properties of Inconel 625.
However, it is important to note that the mean prediction error for the linear model in the heat-affected zone (HAZ) area exceeds 15%, indicating precision challenges in the joining process. Furthermore, digital X-ray examination has confirmed inconsistencies in the joints, including burnout and lack of fusion in certain samples, which highlight potential pitfalls in the joining process. Precise control over heat input is critical to prevent overheating and distortion, both of which can compromise the performance of the weld.
As noted by Manjunath BN, a researcher in the field, ‘I have no personal relationships or associations with individuals or organizations that could influence the conduct or interpretation of this research.’ To ensure optimal results in the inconel 625 welding procedure, it is essential that the machine is calibrated with the suitable parameters designed for alloy 625, thus adhering to current best practices in TIG techniques.
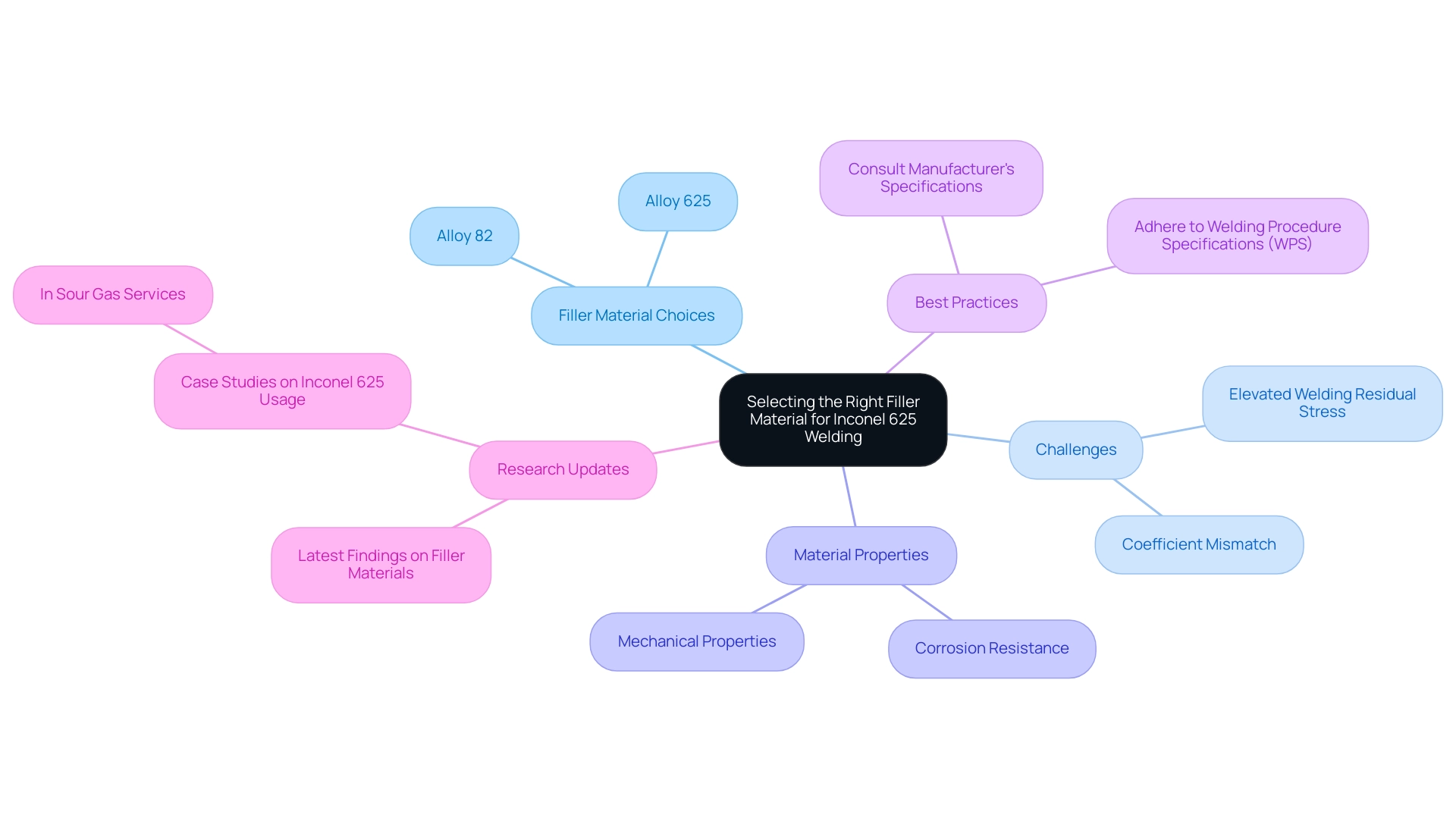
Selecting the Right Filler Material for Inconel 625 Welding
The choice of suitable filler material is crucial in the inconel 625 welding procedure, as it directly affects both compatibility and performance. Elevated welding residual stress is anticipated with alloy 625 during the inconel 625 welding procedure due to the coefficient mismatch between the filler material and the base metal, which can present considerable challenges. Among the most effective choices are alloy 625 and alloy 82, both renowned for their exceptional corrosion resistance and strong mechanical properties.
For example, the use of Inconel 625 in sour gas services is considered to minimize the risk of stress corrosion cracking (SCC) and sulfide stress cracking (SSC). However, while it offers resistance to SCC, it does not reduce the hardness of the carbon steel heat-affected zone (HAZ), and increased residual stress may occur. To ensure optimal results, it is imperative to consult the manufacturer’s specifications and adhere to the inconel 625 welding procedure specifications (WPS).
This diligence not only enhances the integrity of the weld but also contributes to the overall longevity and reliability of the finished product. As metengr noted, ‘I probably need to initiate a separate post for this, but, I’m wondering if you have looked at the Summer NB Bulletin. I have some q’s pertaining to the article on PV efficiency.’
Staying informed about the latest research related to filler materials will further bolster your project’s success.
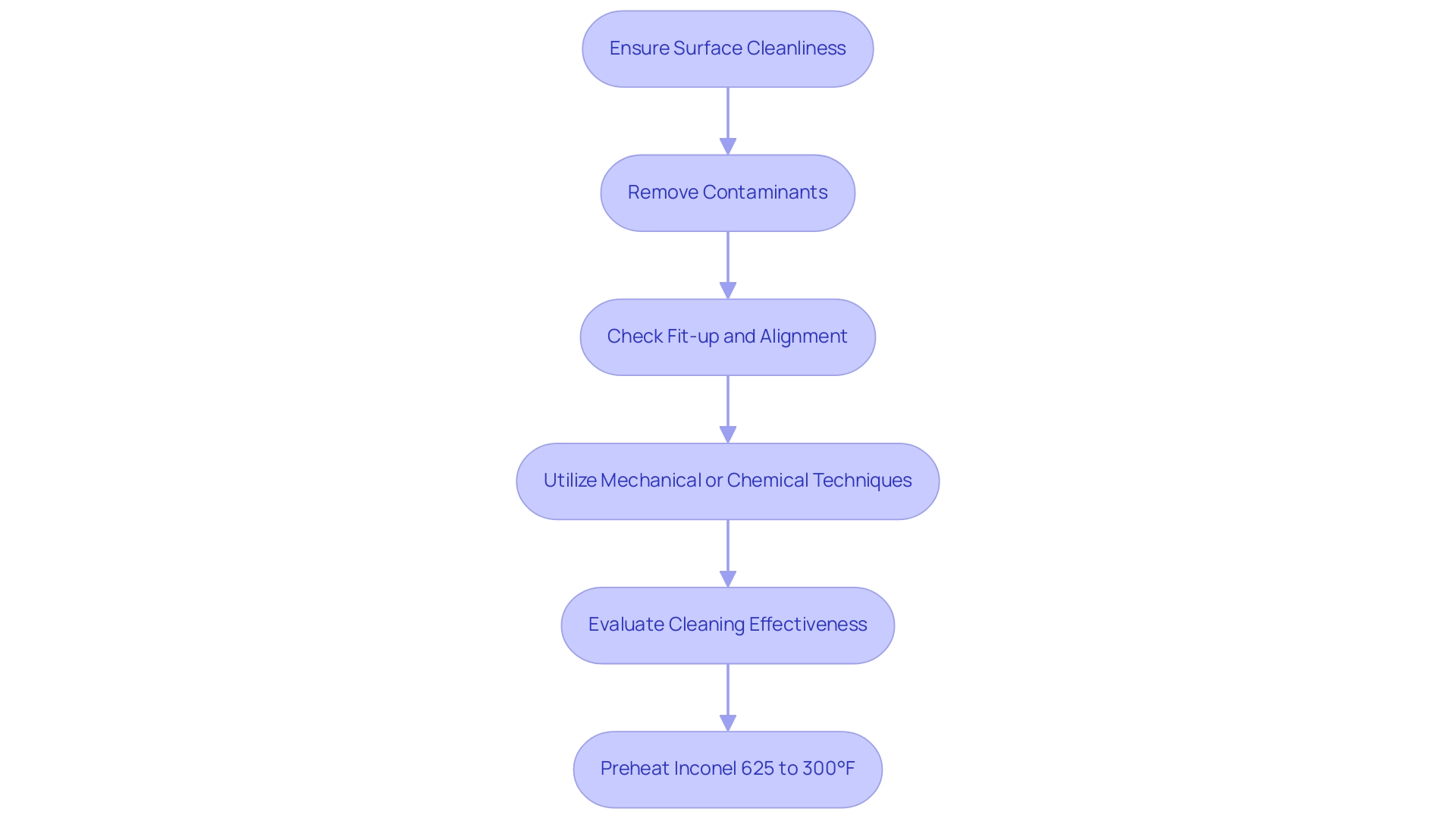
Pre-Welding Preparations: Ensuring Optimal Conditions
Prior to joining Inconel 625, meticulous attention must be given to ensuring that the surfaces are impeccably clean and devoid of contaminants such as oil, grease, and rust. Effective joint preparation is essential, requiring precise fit-up and alignment to eliminate gaps that could lead to defects in the fusion process. Utilizing either mechanical or chemical techniques to remove oxide layers is vital, as these contaminants can significantly undermine the integrity of the joint.
A study concentrating on the joinability of ductile cast iron, which used a specific alloy for root connections, emphasized the significance of surface preparation in improving fusion results. The findings illustrated that inadequate cleaning can adversely affect the quality of the join, aligning with the observed micro hardness value of 75.3HV, which reflects the material’s ability to withstand stress. Moreover, Manjunath BN, a researcher in the field, emphasizes, ‘I have no personal relationships or associations with individuals or organizations that could influence the conduct or interpretation of this research,’ reinforcing the impartiality of these findings.
Additionally, the Inconel 625 welding procedure advises preheating Inconel 625 to approximately 300°F; this practice not only mitigates the risk of cracking but also enhances overall weld quality. Implementing these preparation steps lays a robust foundation for a successful operation, aligning with the latest best practices in the field.
Post-Welding Procedures: Inspection and Quality Assurance
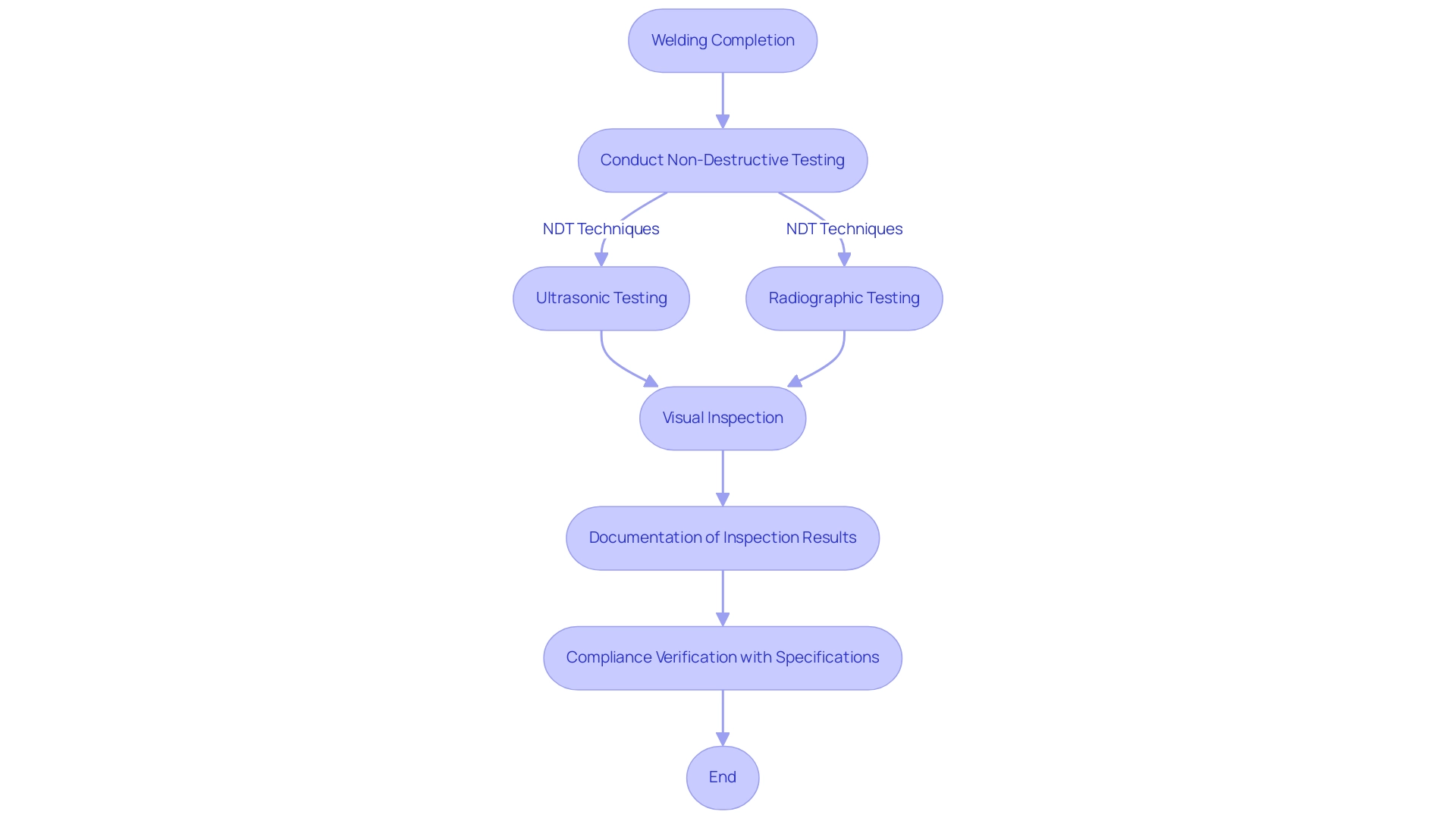
Following the completion of the joining process, a comprehensive inspection of the welded joints is crucial to ensure structural integrity and compliance with industry standards. With more than 30 years of experience in non-destructive testing (NDT), OKOndt GROUP highlights that NDT techniques, especially ultrasonic testing and radiographic testing, are very effective in detecting internal flaws or discontinuities that could undermine the performance of the joints. As Ramakant, a Technical Consultant at Cruxweld, states, “The importance of non-destructive testing cannot be overstated; it is essential for ensuring the reliability of welded components.”
Furthermore, visual inspections must be conducted to detect surface imperfections such as cracks or porosity. It is essential to verify that all welds comply with the specifications detailed in the inconel 625 welding procedure. The documentation of inspection results is not merely a procedural formality; it plays a key role in quality assurance and adherence to regulatory requirements.
Additionally, insights from the case study titled ‘Modified GMAW Processes: Control of Heat Input’ illustrate advancements in the inconel 625 welding procedure that enhance the weldability of materials like Inconel 625, further supporting the need for rigorous post-welding inspection practices. By implementing these practices, organizations can significantly enhance the reliability and performance of welded components, thereby mitigating the risk of defects that could lead to costly failures in the field.
Conclusion
Inconel 625 emerges as a vital ally in industries requiring materials that can withstand extreme conditions. Its exceptional resistance to oxidation and corrosion, combined with outstanding mechanical properties, positions it as the go-to choice for critical applications in aerospace, chemical processing, and marine environments. The alloy’s unique composition not only ensures high-temperature stability but also facilitates precision manufacturing, making it a reliable option for engineers and procurement managers alike.
The insights into welding techniques, particularly the emphasis on TIG welding, highlight the importance of maintaining a controlled environment to preserve the integrity of the weld. Recognizing the challenges associated with filler material selection and pre-welding preparations is essential for achieving optimal results. Moreover, adherence to rigorous post-welding inspection procedures is paramount to ensure the structural integrity and reliability of components made from Inconel 625.
As industries continue to evolve and demand advanced materials, understanding the properties, application techniques, and quality assurance processes associated with Inconel 625 will empower professionals to make informed decisions. This knowledge not only enhances operational efficiency but also ensures that the components built from this remarkable alloy meet the highest standards of performance and reliability, ultimately safeguarding critical operations across various sectors.




