Blogs

What is Heat Treatment of Nickel Alloys? Understanding the Basics
Overview:
The heat treatment of nickel alloys involves a series of controlled processes designed to enhance their mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and overall performance in demanding applications. The article outlines various heat treatment techniques, such as annealing and solution processing, and emphasizes their critical role in optimizing the characteristics of nickel alloys for use in industries like aerospace and automotive, ultimately ensuring improved durability and efficiency.
Introduction
In the realm of advanced materials, nickel alloys stand out for their remarkable performance characteristics, particularly when subjected to precise heat treatment processes. These treatments are not merely procedural steps; they are pivotal in enhancing mechanical properties, improving corrosion resistance, and ensuring the longevity of components used in demanding applications across various industries.
From aerospace to automotive and electronics, the strategic application of heat treatment techniques can significantly influence the efficacy and durability of nickel alloys. As industries increasingly rely on these materials, understanding the nuances of heat treatment becomes essential for optimizing performance and meeting stringent operational requirements.
This article delves into the fundamentals, types, impacts, applications, and innovations in heat treatment technologies for nickel alloys, providing valuable insights for professionals aiming to harness the full potential of these versatile materials.
Fundamentals of Heat Treatment for Nickel Alloys
Heat processing includes a series of carefully regulated procedures aimed at altering the physical and, in certain instances, chemical characteristics of substances, especially copper-based materials recognized for their outstanding performance. The main goals of thermal processing are to enhance mechanical properties, improve corrosion resistance, and alleviate internal stresses inherent within the material. Copper nickel mixtures, recognized for their remarkable strength—typically exhibiting a tensile strength of up to 600 MPa—resistance to corrosion, and high thermal and electrical conductivity, make heat treatment essential for optimizing these attributes in alignment with specific application requirements in demanding environments like marine, automotive, and electrical industries.
The process typically involves:
- Heating the metal to a designated temperature.
- Maintaining that temperature for a predetermined duration.
- Cooling it at a controlled rate.
This systematic approach is crucial, as it guarantees the achievement of desired properties consistently across production batches. For instance, process-control factors in annealing, including the selection of sulfur-free heating materials, precise temperature control, and tailored cooling rates, play a vital role in determining the final properties of the metal.
Notably, each set of in situ measurements took approximately 5 min, highlighting the precision required in these processes. Furthermore, thermodynamic calculations, such as those conducted on AM IN625, have illustrated the significance of understanding elemental segregation, particularly in predicting phase formations like the δ phase. As mentioned by Lass et al., inadequate thermal processing can result in a significant quantity of harmful δ phase precipitates, which can greatly affect the material’s performance and durability.
These progressions in thermal processing methods highlight the increasing focus on precision and control in metallurgical procedures, ensuring that the heat treatment of nickel alloys, especially in the case of copper nickel mixtures, not only satisfies the rigorous criteria of diverse industrial uses but also offers substantial advantages such as enhanced durability and lower maintenance expenses for users.
Types of Heat Treatments for Nickel Alloys
Nickel mixtures undergo several essential processes as part of the heat treatment of nickel alloys, including:
- Annealing
- Solution processing
- Aging
- Hardening
Each process is designed to attain specific material properties.
Annealing is a pivotal process that entails heating the metal to a predetermined temperature and subsequently cooling it slowly, effectively reducing hardness and enhancing ductility. This method is instrumental in improving machinability and relieving internal stresses.
Solution processing aims to dissolve precipitates within the mixture, thereby promoting greater homogeneity and enhancing overall performance.
Aging facilitates the precipitation of strengthening phases, which significantly bolsters the material’s strength and stability under operational conditions.
Hardening techniques, particularly quenching, are employed to augment hardness and strength; however, this can sometimes lead to increased brittleness if not managed properly.
The choice of a suitable thermal process, such as the heat treatment of nickel alloys, is vital, as it directly affects the final characteristics of the nickel blend, requiring a strategic approach based on the intended use.
Recent research, including the studies of Mahadevan S et al., has explored the evolution of δ phase microstructure in material 718, highlighting that the swift incubation period for the formation of δ-phase particles—under five minutes—can greatly influence the efficacy of thermal processes. This discovery indicates that the prompt application of heat treatment of nickel alloys is crucial for enhancing the characteristics of alloy 718.
Moreover, metallurgist Danieli Aparecida Pereira Reis emphasizes the significance of comprehending the effects of temperature modification, particularly in the heat treatment of nickel alloys such as Inconel 713C.
His insights are backed by various figures and tables that illustrate thermal processing curves and chemical analysis results, offering a visual depiction of how these processes change material properties. The detailed ‘Age-Hardening Practices Summary‘ outlines standardized protocols for achieving desired hardness levels in metal mixtures, ensuring consistency and reliability in manufacturing processes. These insights emphasize the necessity for procurement managers to be well-versed in the nuances of heat processes to optimize material performance and application.
Impact of Heat Treatment on Nickel Alloy Properties
The heat treatment of nickel alloys plays a crucial role in establishing the mechanical characteristics of nickel mixtures, affecting aspects such as tensile strength, yield strength, and ductility. For instance, the heat treatment of nickel alloys during solution processing is well-documented to significantly enhance the tensile strength of nickel-based superalloys, making them particularly advantageous for high-performance applications in demanding environments. Recent studies emphasize the connection between the heat treatment of nickel alloys and corrosion resistance, as this thermal processing can alter the alloy’s microstructure, which is crucial for sectors such as aerospace and marine.
Engineers frequently state that the heat treatment of nickel alloys through customized thermal processes results in significant enhancements in tensile strength; one specialist remarked, ‘The influence of thermal processing and building direction on tensile characteristics and fracture mechanism of Inconel 718 produced by SLM method is profound’ (Ilguk Jo, Metals). Furthermore, it is crucial to take into account the layer thickness in the SLM process, which is 35 μm, as it can affect the efficiency of thermal processing on mechanical properties. Furthermore, case studies examining high-temperature rupture properties demonstrate that at conditions of 900 °C and 275 MPa, higher solution temperatures can initially enhance elongation and reduction in area, although these properties may decline at elevated temperatures.
This emphasizes the essential significance of choosing the appropriate thermal processing parameters, particularly the heat treatment of nickel alloys, to guarantee optimal performance and durability of components in various applications, affirming the strategic role of procurement managers in material selection. Along with heat treatment considerations, copper-based materials stand out for their exceptional corrosion resistance in marine environments, superior thermal and electrical conductivity, ductility, and ease of fabrication. When contrasted with stainless steel, copper-based materials provide significant benefits, especially in situations where resistance to corrosion is essential, like in marine environments, and where electrical conductivity is vital, such as in electrical uses.
These materials also have antimicrobial characteristics, making them a preferred choice for applications where hygiene is a priority, especially in comparison to stainless steel.
Applications of Heat-Treated Nickel Alloys
The exceptional properties of nickel mixtures are pivotal across multiple industries due to the heat treatment of nickel alloys. In the aerospace sector, the heat treatment of nickel alloys is essential for their integral role in turbine engines and structural components, where high strength and resistance to extreme temperatures are required. Recent advancements in the heat treatment of nickel alloys, such as the INCONEL grade 617, exemplify this trend with its remarkable high-temperature strength coupled with oxidation and carburization resistance, making it ideal for challenging aerospace applications.
Significantly, recent advancements in the heat treatment of nickel alloys for aerospace engineering encompass:
- Disc composites
- Low expansion superalloys
- Inconel 718SPF
- Nilo low expansion substances
These highlight their strategic significance in the sector.
The Multi-focus Water-Jet Guided Laser technology has also improved processing capabilities for nickel-based materials, showcasing enhanced cutting performance on Inconel 718 under different laser power conditions. This innovation reflects the ongoing advancements in the processing of these critical substances. In the automotive sector, the heat treatment of nickel alloys is employed in engine components and exhaust systems, capitalizing on their durability and corrosion resistance to enhance performance and longevity.
Statistics indicate that the use of the heat treatment of nickel alloys in metal mixtures for automotive components is significant, highlighting their role in various engine parts and their strategic importance in automotive manufacturing.
Moreover, the electronics sector benefits from these materials as they are utilized in connectors and circuit boards, where reliability and performance are essential. The versatility of heat treatment of nickel alloys not only underscores their significance in contemporary manufacturing and technology but also highlights the innovative solutions they offer across various applications. As Dynamic Metals UK aptly puts it,
It’s not the sky anymore; it is just the beginning!
This sentiment reflects the ongoing development and broadening uses of nickel-based materials, particularly in high-stakes sectors such as aerospace and automotive, where the heat treatment of nickel alloys plays a crucial role. Additionally, Paulo’s Nadcap approval and advanced aerospace thermal processing capabilities further enhance the credibility of these materials in aerospace applications.
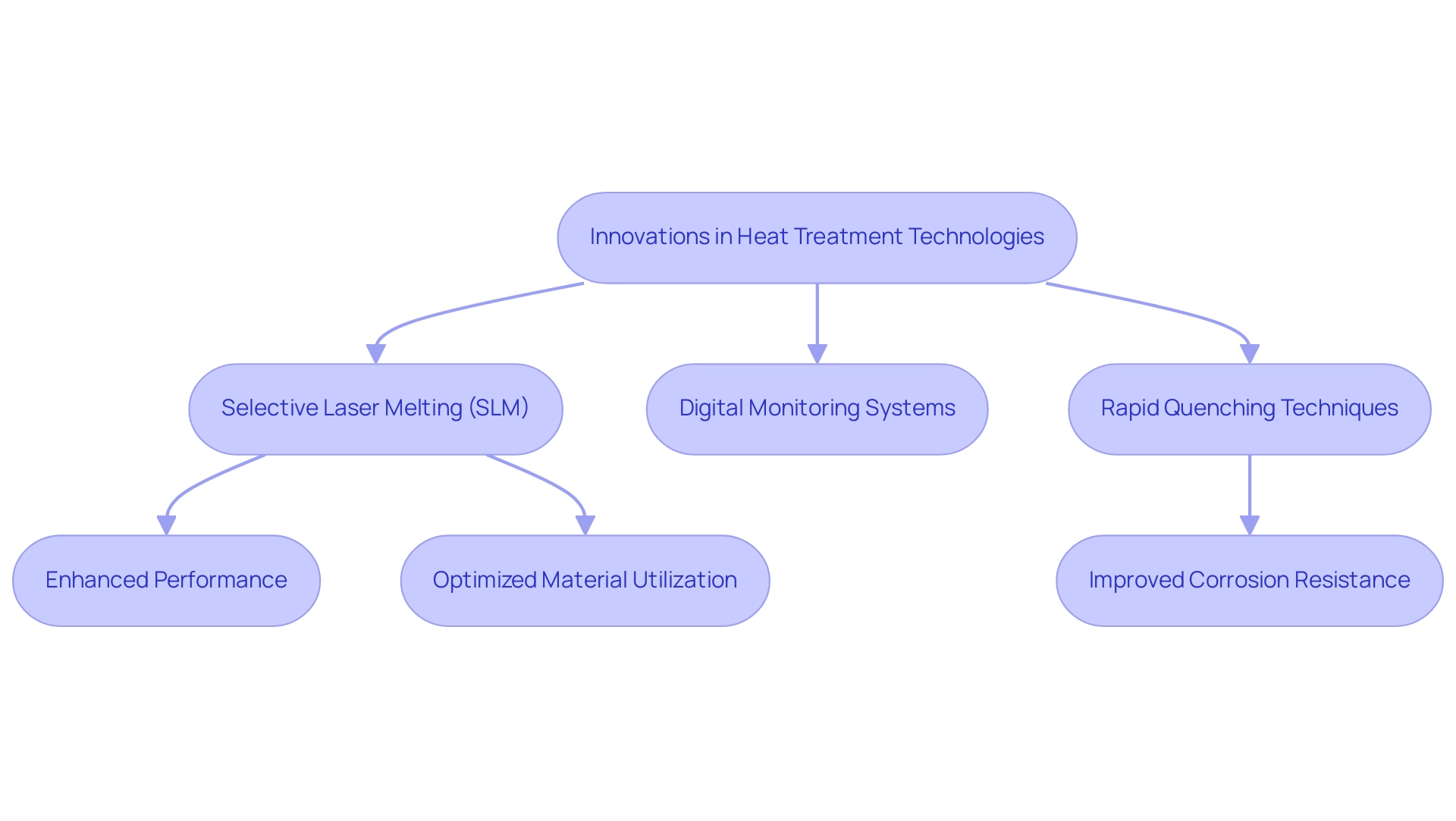
Innovations in Heat Treatment Technologies for Nickel Alloys
Recent advancements in the heat treatment of nickel alloys are transforming the landscape of material production. Innovations such as selective laser melting (SLM) enable the creation of complex geometries with tailored properties, allowing for enhanced performance in demanding applications. This technique not only facilitates the design of intricate components but also optimizes material utilization.
Moreover, the incorporation of digital monitoring systems during the heat treatment of nickel alloys ensures that optimal conditions are consistently upheld throughout the process. These systems specifically tackle the challenge presented by the local makeup of as-built IN625, which may not consistently meet specifications, often requiring the heat treatment of nickel alloys to attain desired performance levels.
The influence of these innovations goes beyond material characteristics; they also play a crucial role in enhancing operational efficiencies. For example, recent studies suggest that the activation energy for the growth of δ-phase precipitates in AM IN625 is (131.04 ± 0.69) kJ/mol, highlighting the complexities involved in achieving optimal material characteristics. As Zachary Cordero, the Boeing Career Development Professor in Aeronautics and Astronautics at MIT, observes,
This could from a baseline perspective lead to lower carbon dioxide emissions, just through improved efficiency of these devices.
This perspective is particularly relevant as industries increasingly seek to enhance energy efficiency while reducing environmental impact. The future applications of the heat treatment of nickel alloys could lead to the production of industrial-grade turbine blades with complex shapes and patterns, further enhancing energy efficiency and contributing to reduced carbon dioxide emissions. Moreover, case studies such as the application of rapid quenching techniques on Inconel 625 demonstrate tangible benefits, including a 32% improvement in corrosion resistance and a significant reduction in passivation current density. As the field of nickel alloys continues to evolve, procurement professionals must remain informed about these developments to leverage the latest materials and processes effectively.
Conclusion
The exploration of heat treatment processes for nickel alloys reveals their critical role in enhancing material performance across various demanding industries. From the fundamentals of meticulously controlled heat treatments to the specific techniques employed—such as:
- Annealing
- Solution treatment
- Aging
- Hardening
Each process is tailored to optimize properties like strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. Understanding these processes is essential for professionals aiming to achieve the highest standards in material performance.
The impact of heat treatment on the mechanical properties of nickel alloys cannot be overstated. It directly influences tensile strength, yield strength, and ductility, making these alloys particularly advantageous in high-performance applications, especially in aerospace and automotive sectors. Recent innovations in heat treatment technologies, including selective laser melting and digital monitoring systems, further enhance the capabilities of nickel alloys, allowing for more precise control and improved operational efficiencies.
As industries increasingly adopt nickel alloys, the strategic application of heat treatment techniques becomes paramount. The advancements in this field not only promise enhanced material characteristics but also contribute to sustainability goals through improved energy efficiency and reduced environmental impact. For procurement managers, staying abreast of these developments is crucial in making informed decisions that leverage the full potential of nickel alloys in their respective applications. The future of material science is bright, driven by the continuous evolution of heat treatment technologies that unlock new possibilities for innovation and performance.




