Blogs

Where Thermostatic Bimetals Excel: Real-World Applications
Thermostatic bimetals may not be flashy—but they’re fundamental. These smart mechanical components bend with heat, showcasing a diverse range of Thermostatic Bimetals Applications, activating everything from simple appliance switches to mission-critical safety devices—no electronics needed.
In this blog, we’ll explore where thermostatic bimetals truly excel—across industries, use cases, and even in products you use every day. You’ll find a full breakdown of how these tiny metal strips offer self-regulating thermal control in applications that require reliability, simplicity, and performance.
1. Temperature Control and Regulation
Appliances
Bimetallic strips are the heart of many thermostat-driven devices in your home:
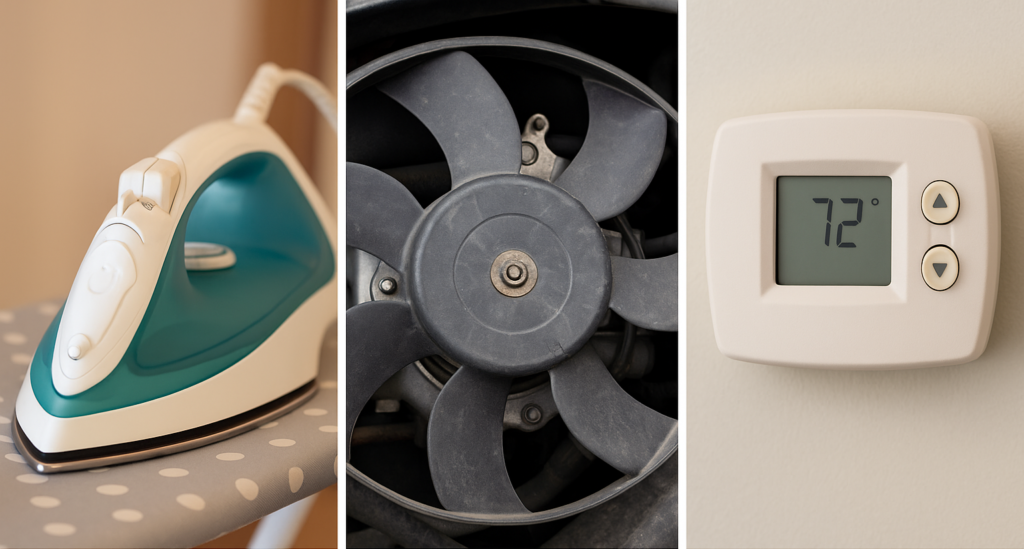

- Electric irons shut off automatically once optimal temperature is reached.
- Toasters use bimetals to trigger the pop-up mechanism after heating.
- Refrigerators & ovens maintain ideal cooling and baking temperatures via bimetal controls.
⚡ No batteries. No sensors. Just heat = motion.
HVAC Systems
In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning:
- Room thermostats use coiled bimetals to expand/contract and open/close electrical contacts.
- Fan limit switches activate fans when internal temperatures exceed safe levels.
- Thermal valves regulate fluid flow passively.
Automotive
In vehicles, thermostatic bimetals ensure thermal stability:
- Engine fans turn on/off based on coolant temperature.
- Thermostats control flow between radiator and engine block.
- Defoggers use thermal triggers for time-delayed operation.
Label: “Temperature Regulation Applications”
2. Temperature Indication
Thermometers
Spiral-shaped bimetallic strips power:
- Dial thermometers in industrial and home settings
- Probe thermometers in kitchen or medical use
- Chart recorders in labs and shipping containers
When the temperature changes, the coil expands or contracts, rotating a needle on the dial.
Temperature Sensors
Bimetals are also found in analog:
- Industrial gauges
- Food safety indicators
- HVAC duct sensors
🧠 A simple, fail-safe way to read temperature—no electronics required.
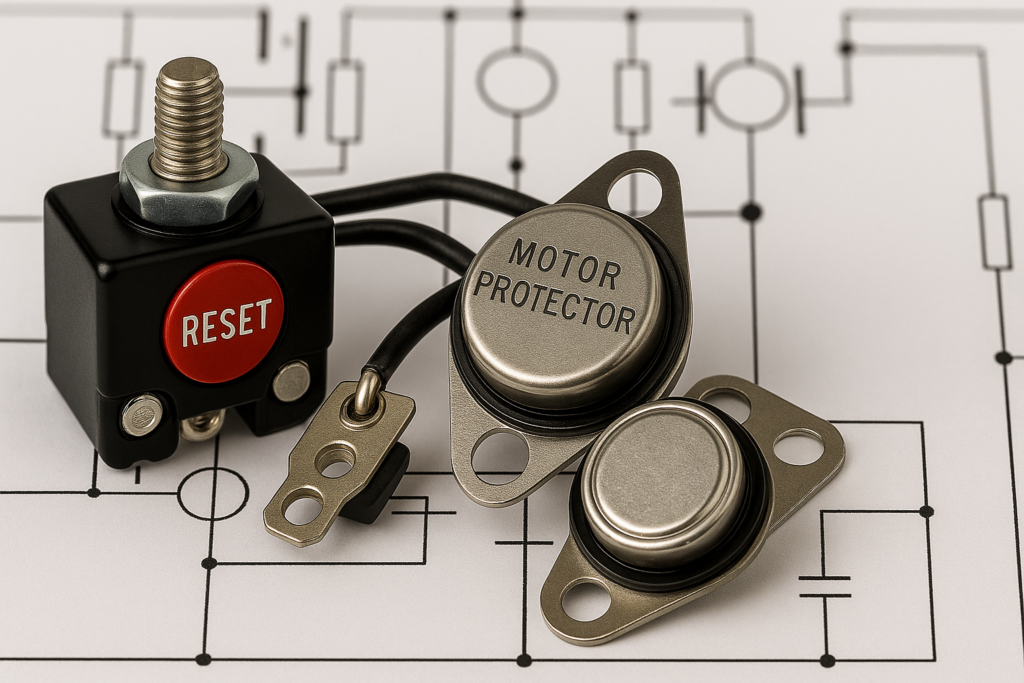
3. Over-Temperature Protection
Thermal Circuit Breakers
When excessive current heats the bimetal strip:
- It bends and disconnects the circuit.
- Once it cools, the circuit resets or stays open (depending on the design).
Used in:
- Electrical panels
- Consumer electronics
- Power supplies
Motor Overheat Protectors
If a motor exceeds safe heat thresholds:
- The bimetal strip bends to cut power.
- This prevents burnout or equipment failure.
Common in:
- Compressors
- Pumps
- Industrial fans
4. Safety Devices
Fire Alarms
A snap-action bimetal is calibrated to trigger at a specific temperature, instantly sounding an alarm.
They’re:
- Self-resetting
- Maintenance-free
- Reliable in power outages
Gas Oven Safety Valves
These use bimetals to detect overheating and shut off the gas if things get too hot, reducing fire or explosion risk.
🔒 A temperature-sensitive safety layer, quietly doing its job.
5. Timing & Mechanical Control
Timers and Relays
Bimetal strips serve as thermal delay devices, bending gradually to control time-based operations:
- Start/stop cycles
- Delayed motor starts
- Relay toggles
Fluorescent Lamp Starters
The strip heats, bends, and closes the starter circuit briefly to ignite the lamp, then cools and opens.
6. Steam Traps and Industrial Efficiency
In steam systems, bimetallic steam traps:
- Remove condensate and air from lines
- Prevent overheating and ensure efficiency
- Self-adjust as temperature rises/falls
Used in:
- Boilers
- Refineries
- HVAC piping networks
Summary of Key Applications
| Category | Applications |
| Temperature Control | Irons, ovens, HVAC fans, car thermostats |
| Temperature Indication | Dial thermometers, chart recorders, sensors |
| Overheat Protection | Circuit breakers, motor protectors |
| Safety Devices | Fire alarms, gas oven valves |
| Timing Devices | Timers, fluorescent lamp starters |
| Industrial Controls | Steam traps, HVAC valves, boiler systems |
Conclusion
As we’ve seen across real-world applications—from appliances and vehicles to industrial systems and safety devices—bimetals offer a rare combination of versatility, simplicity, and autonomy.
Stay tuned for our next blog where we’ll break down the technical and commercial advantages of thermostatic bimetals and how they outperform more complex alternatives in cost, lifecycle, and design flexibility.
Got questions? or got an ideas—we’re always ready to dive deeper!
Contact our experts today!
Talk to: Er.Pankaj Domadia | Kairav Domadia | Aadil Domadia | Pragati Sanap | Pooja N N | Shivani Kanojia
Read our previous blog on https://domadia.net/thermostatic-bimetal/domadia-designing-with-thermostatic-bimetals/