Blogs

How to Choose and Use Inconel 718 Welding Wire: A Comprehensive Guide
Overview:
Choosing and using Inconel 718 welding wire involves understanding its properties, selecting the right wire composition and diameter, and following best welding practices to ensure optimal results. The article highlights the importance of matching the wire’s chemical composition to that of alloy 718, managing heat input during welding, and applying post-welding treatments to enhance mechanical properties, thereby ensuring the integrity and performance of the welded components in demanding applications.
Introduction
Inconel 718 stands as a hallmark of engineering excellence, particularly in sectors where resilience and performance are non-negotiable. This nickel-chromium alloy is celebrated for its outstanding mechanical properties, enabling it to thrive in extreme conditions, from the high-stress environments of aerospace applications to the corrosive challenges faced in the oil and gas industry.
With attributes such as:
- Exceptional strength retention at elevated temperatures
- Remarkable resistance to various forms of corrosion
Inconel 718 is not just a material of choice; it is a strategic asset in the toolkit of procurement managers and engineers alike. As industries increasingly turn to advanced manufacturing techniques and innovative welding practices, understanding the full spectrum of Inconel 718’s properties and applications becomes essential for making informed decisions that drive operational success and enhance product reliability.
Understanding Inconel 718: Properties and Applications
Nickel-chromium alloy 718 is well-known for its outstanding mechanical characteristics and strong performance in harsh conditions. This alloy demonstrates remarkable oxidation and corrosion resistance, making it highly suitable for demanding applications in the aerospace and oil & gas industries. Its primary characteristics include:
- High Strength: This alloy maintains its strength even at elevated temperatures, withstanding conditions up to 1300°F (704°C) without significant degradation.
- Corrosion Resistance: It offers excellent protection against pitting, crevice corrosion, and stress corrosion cracking, ensuring longevity in harsh operational settings.
- Weldability: This material can be joined using various techniques, including the use of inconel 718 welding wire, although it requires careful handling to mitigate the risk of cracking during the joining process.
In practice, this alloy is widely utilized in critical components such as gas turbine parts, heat exchangers, and various high-performance aerospace applications. As mentioned in a review on the mechanical characteristics of a certain alloy produced by various metal additive manufacturing (MAM) processes, understanding these traits is essential for selecting appropriate welding methods and materials, such as inconel 718 welding wire, for your projects. The research emphasizes the significance of process parameter optimization for selective laser melting of In718, highlighting the impacts of subsequent heat treatment on mechanical characteristics (Wang et al.).
This comprehensive understanding not only guides procurement decisions but also enhances the strategic application of alloy 718 in engineering solutions. Recent advancements in nickel-chromium alloys further underscore the importance of this material, positioning it at the forefront of engineering innovation. Additionally, the analysis of thick Co-based coatings on cast iron, as published in Surf. Coat. Technology, supports the discussion on the mechanical properties of alloy 718, particularly in relation to its performance in various manufacturing processes.
Furthermore, the case study titled ‘Review of Mechanical Properties‘ provides an engineering perspective on the mechanical response of AM alloy 718, expanding on previous studies to include a broader range of manufacturing methods.
Welding Techniques for Inconel 718: Best Practices and Challenges
Joining Inconel 718 welding wire requires a strategic approach, with several techniques available, including Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) and Metal Inert Gas (MIG) methods. To enhance your joining process, consider the following best practices:
- Pre-Weld Preparation: Thoroughly clean the surfaces to be joined to remove any contaminants. Utilize appropriate solvents to ensure a pristine surface, as this can significantly impact weld quality.
- Heat Management: Carefully control the heat input during the joining process to mitigate warping and cracking. Preheating the material can effectively alleviate thermal stresses, enhancing the overall weld integrity. Efficient heat treatment methods have demonstrated their ability to alleviate residual stresses, thus improving yield strength and toughness.
- Filler Material: Choose a suitable filler material like inconel 718 welding wire that corresponds with the characteristics of alloy 718. For TIG joining, inconel 718 welding wire is suggested due to its compatibility and performance.
- Post-Weld Treatment: Apply post-joining heat treatment to alleviate residual stresses, thereby enhancing ductility and overall mechanical characteristics. As noted in a recent review of mechanical properties of AM 718, effective heat treatment processes play a crucial role in enhancing these properties.
While these best practices are essential, challenges such as susceptibility to hot cracking and the necessity for precise heat control must also be acknowledged. Shinozaki et al. highlighted that optimum laser joining conditions without defects were 6 kW with 2.5 m/min and 8 kW with 4.0 m/min for fine-grain sized specimens, providing authoritative support for the techniques discussed. Comprehending these difficulties and utilizing strong joining methods will enable successful results when dealing with alloy 718. Moreover, advancements in digital manufacturing and machine learning are emerging as potential tools to enhance productivity in the machining of this alloy, indicating a promising future for joining technologies in 2024.
Choosing the Right Inconel 718 Welding Wire: Key Considerations
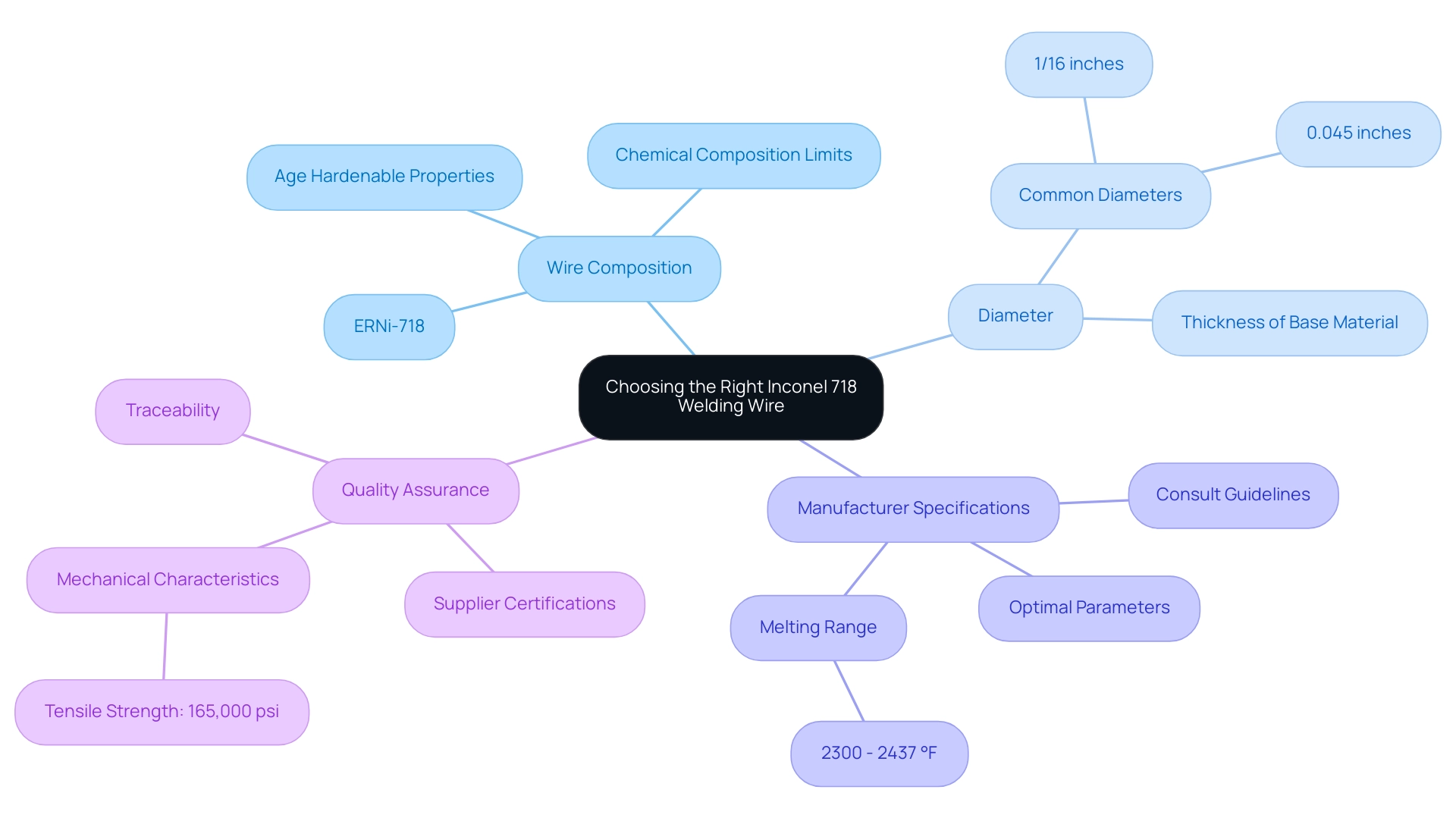
Choosing the suitable inconel 718 welding wire is essential for attaining optimal welding results. Here are key considerations to guide your choice:
- Wire Composition: It is essential to select a wire with a chemical composition that closely resembles alloy 718 to preserve the integrity of the weld. Recommended options include ERNi-718 and inconel 718 welding wire, which are designed to work harmoniously with the base material. The specific chemical composition limits are crucial, as highlighted in the case study on Alloy 718, where the weld metal of Alloy 718 is age hardenable and exhibits mechanical properties comparable to those of the base metals.
- Diameter: The wire diameter should be chosen based on the thickness of the base material and the particular joining process employed. Common diameters usually span from 0.045 inches to 1/16 inches, ensuring the right balance between penetration and bead profile.
- Manufacturer Specifications: Always consult manufacturer guidelines to ensure compatibility with specific applications and determine the optimal parameters. This adherence not only enhances the quality of the weld but also aligns with industry standards. Remember, the melting range of alloy 718 is between 2300 – 2437 °F, which is critical in selecting the appropriate wire for high-temperature applications.
- Quality Assurance: Opt for suppliers that offer certifications and traceability for their products, as this guarantees compliance with industry requirements and meets the necessary standards for high-stakes applications. The basic mechanical characteristics of alloy 718 include a tensile strength of 165,000 psi, emphasizing the importance of selecting the right inconel 718 welding wire for challenging applications.
By carefully evaluating these elements, procurement managers can assuredly choose the correct welding wire, greatly impacting the success of their welding processes.
Applications of Inconel 718: Industries and Use Cases
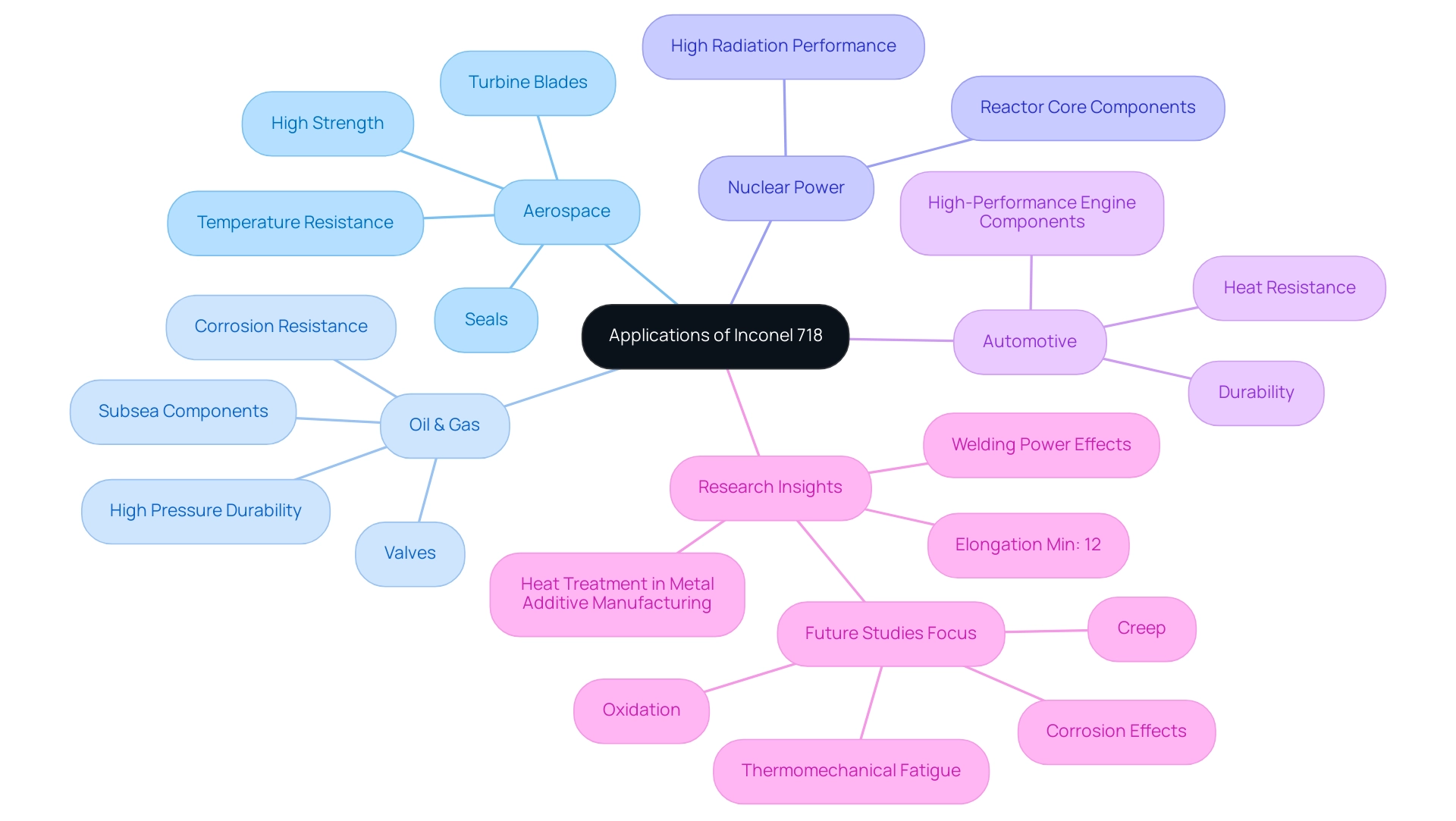
Alloy 718 is acknowledged for its remarkable characteristics, establishing it as a preferred material in various sectors. Key applications include:
Aerospace: In this sector, this alloy is integral for manufacturing components like turbine blades and seals, which necessitate high strength and resistance to extreme temperatures. Its ability to retain structural integrity under high-stress conditions is critical for aerospace applications, where performance and safety are paramount. Notably, the elongation minimum for solution treated plus precipitation heat treated alloy 718 is 12%, underscoring its mechanical reliability in demanding applications.
Oil & Gas: The material is vital for subsea components and valves, which must endure corrosive environments and high pressures. As noted by materials expert Majid Laleh, the alloy 718’s resilience in harsh operational settings positions it as a strategic choice for the oil and gas industry, enhancing the longevity and reliability of equipment.
Nuclear Power: The alloy 718’s robust performance in high-radiation environments makes it suitable for critical components in reactor cores, where performance under extreme conditions is mandatory.
Automotive: The automotive industry leverages the alloy 718 for high-performance engine components, benefiting from its durability and heat resistance, which are essential for modern vehicles.
These applications illustrate the versatility and reliability of the alloy 718, reinforcing its status as a preferred selection for engineers and manufacturers operating in demanding sectors. Furthermore, recent research examining the influence of welding power on the microstructural characteristics and nanoindentation creep behavior of alloy 718 further emphasizes its performance under different conditions. The growing market demand for this alloy, especially in aerospace and oil & gas, is clear as industries keep investigating its potential in recent applications, including those in metal additive manufacturing where effective heat treatment can enhance mechanical characteristics, as demonstrated in the case study on heat treatment for metal additive manufacturing.
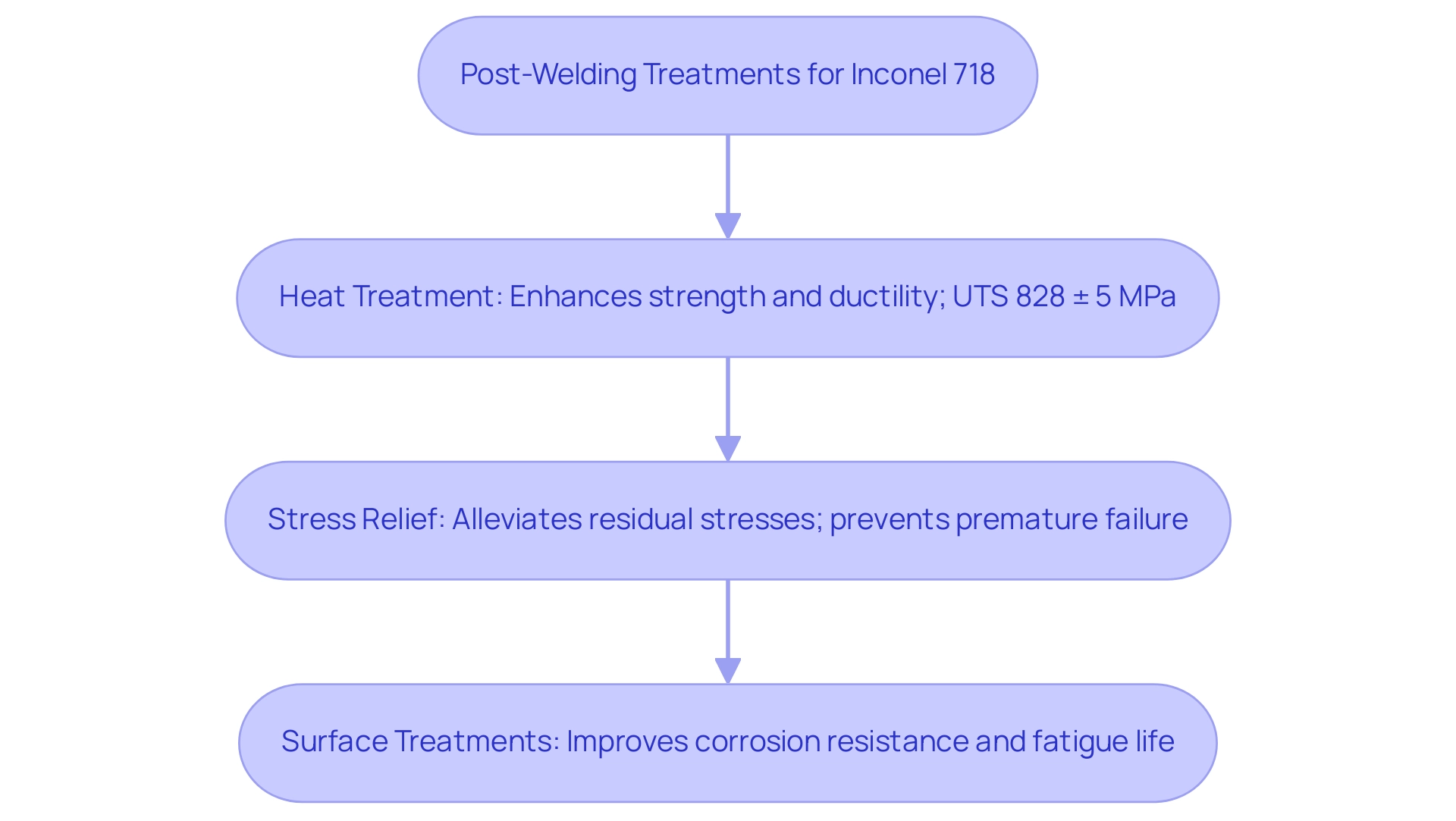
Post-Welding Treatments for Inconel 718: Enhancing Performance
Post-welding treatments for alloy 718 are critical for optimizing performance and durability in demanding applications. The following processes should be prioritized:
- Heat Treatment: A solution heat treatment followed by aging is essential for enhancing strength and ductility. This involves heating the component to approximately 1900°F (1038°C) and then rapidly cooling it.
As highlighted in recent studies, this process can lead to yield strengths of around 730 ± 2 MPa and ultimate tensile strengths (UTS) of 828 ± 5 MPa, demonstrating its effectiveness in improving mechanical properties. Santos, F. emphasizes the significance of these processes in his work on weldability assessment, noting that specific thermal histories can significantly impact the mechanical performance of a certain alloy 718.
Stress Relief: To alleviate residual stresses that may arise during the welding process, implementing stress relief procedures is advisable. This typically involves heating the welded component to around 1300°F (704°C) and maintaining that temperature for a specified duration. Such measures are crucial for preventing premature failure in service.
Surface Treatments: Enhancing the component’s corrosion resistance and fatigue life can be achieved through surface treatments like shot peening or specialized coatings. These methods not only protect the material but also improve overall performance longevity.
Furthermore, recent news indicates that weld hardness slightly decreases with increasing joint gap, suggesting that optimizing joint design can enhance the effectiveness of post-welding treatments. Additionally, advancements in brazing technology for plate-fin heat exchangers, as discussed in a recent case study, demonstrate how innovative heat treatment processes can improve the strength and ductility of joints, thereby promoting the long-life operation of components used in solid oxide fuel cells. By adhering to these post-welding treatments, you can ensure that components joined with inconel 718 welding wire meet the rigorous demands of their applications, thus enhancing reliability and operational efficiency. Continuing advancements in heat treatment technologies for nickel alloys further reinforce the importance of these processes, as they contribute to improved microstructural uniformity and performance characteristics.
Conclusion
Inconel 718 emerges as a cornerstone in the engineering landscape, known for its impressive mechanical properties and versatility in extreme environments. This nickel-chromium alloy excels in high-stress applications, particularly within the aerospace and oil and gas sectors, where its strength retention at elevated temperatures and exceptional corrosion resistance are invaluable. The alloy’s robustness is further enhanced by strategic welding practices, which, when combined with appropriate post-welding treatments, ensure optimal performance and longevity.
As industries evolve, understanding the nuances of Inconel 718—from its welding techniques to the selection of compatible filler materials—becomes essential for procurement managers and engineers. By prioritizing best practices in welding and carefully considering wire composition and diameter, organizations can significantly influence the success of their projects. The insights gleaned from recent studies and advancements in manufacturing methods underscore the importance of a strategic approach in utilizing Inconel 718, reinforcing its status as a preferred material in demanding applications.
In conclusion, Inconel 718 is not merely a material but a strategic asset that embodies reliability and performance. Its applications across diverse industries, coupled with ongoing innovations in welding and manufacturing, highlight its critical role in driving operational success. By leveraging the full spectrum of its properties and adhering to best practices, organizations can enhance product reliability and meet the rigorous demands of their respective sectors. The future of engineering solutions is bright with Inconel 718 at the forefront, poised to tackle the challenges of tomorrow’s high-performance applications.




