Blogs

How to Drill Inconel 625: A Step-by-Step Guide for Precision Machining
Introduction
Inconel 625 stands out as a premier alloy renowned for its exceptional mechanical properties, particularly its remarkable resistance to oxidation and corrosion in high-temperature environments. Comprising nickel, molybdenum, and iron, this versatile material thrives in demanding applications across various industries, including:
- Aerospace
- Chemical processing
- Marine
However, the challenges associated with machining Inconel 625 cannot be overlooked; the alloy’s tendency for work hardening can complicate drilling operations, necessitating a strategic approach to tool selection and machining parameters. This article delves into the essential properties of Inconel 625, the intricacies of effective drilling techniques, the critical role of coolants and lubricants, and advanced strategies for achieving precision. By understanding these facets, procurement managers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and ensure optimal performance in their manufacturing processes.
Understanding Inconel 625: Properties and Applications
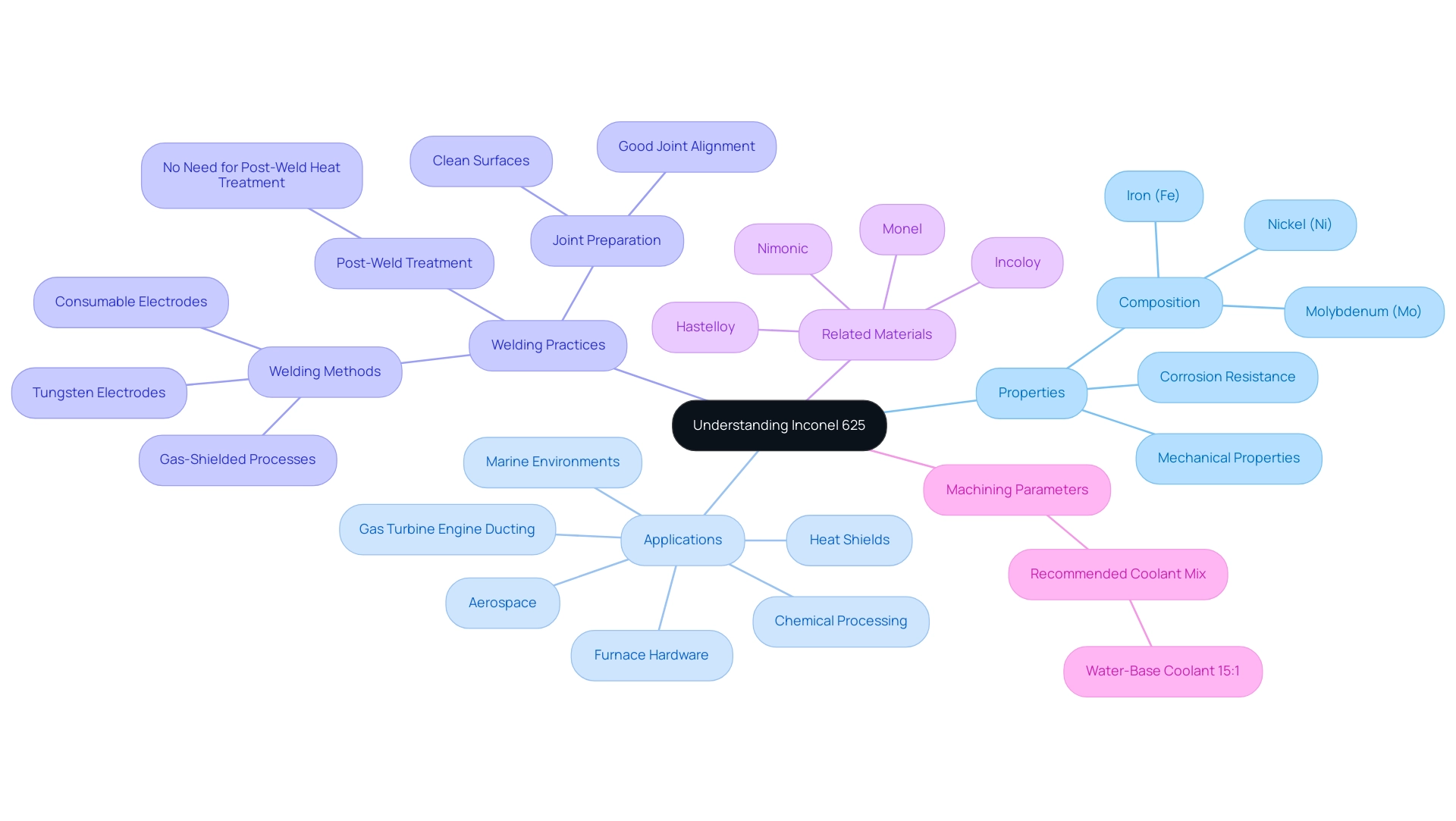
Alloy 625 is celebrated for its superior mechanical properties, specifically its remarkable resistance to oxidation and corrosion, which are critical in high-temperature applications. Composed of Nickel (Ni), Molybdenum (Mo), and Iron (Fe), this alloy retains its strength at temperatures reaching 2000°F (1093°C), positioning it as an essential material for components in the aerospace sector, chemical processing equipment, and marine environments. Its excellent mechanical properties ensure structural integrity and longevity while maintaining performance under extreme conditions.
Furthermore, the superior corrosion resistance and precision manufacturing of this alloy make it particularly suitable for demanding environments. A recommended coolant mix for water-base coolant is 15:1, which is valuable for selecting appropriate machining parameters. Additionally, related materials such as Incoloy, Monel, Hastelloy, and Nimonic offer alternatives and complementary options for procurement managers.
Understanding these properties is pivotal not only for predicting the material’s behavior during drilling inconel 625 processes but also for ensuring optimal welding practices. For instance, the case study titled ‘Weldability of Alloy 625‘ illustrates that welding can be accomplished using gas-shielded processes with tungsten or consumable electrodes, without the need for post-weld heat treatment. The mechanical properties of the weld follow the same trends as the base metal, emphasizing the importance of clean surfaces and good joint alignment.
As industries increasingly depend on alloy 625, its use in heat shields, furnace hardware, and gas turbine engine ducting further highlights its versatility and performance in challenging conditions. Furthermore, procurement managers should consider Mica Tape products, which are designed for high-temperature resistance and electrical insulation, making them ideal for critical applications in electrical engineering. These tapes ensure reliability in various industries, from aerospace to industrial machinery, and are essential for maintaining safety and performance in electrical insulation systems.
Challenges in Drilling Inconel 625: Tool Wear and Work Hardening
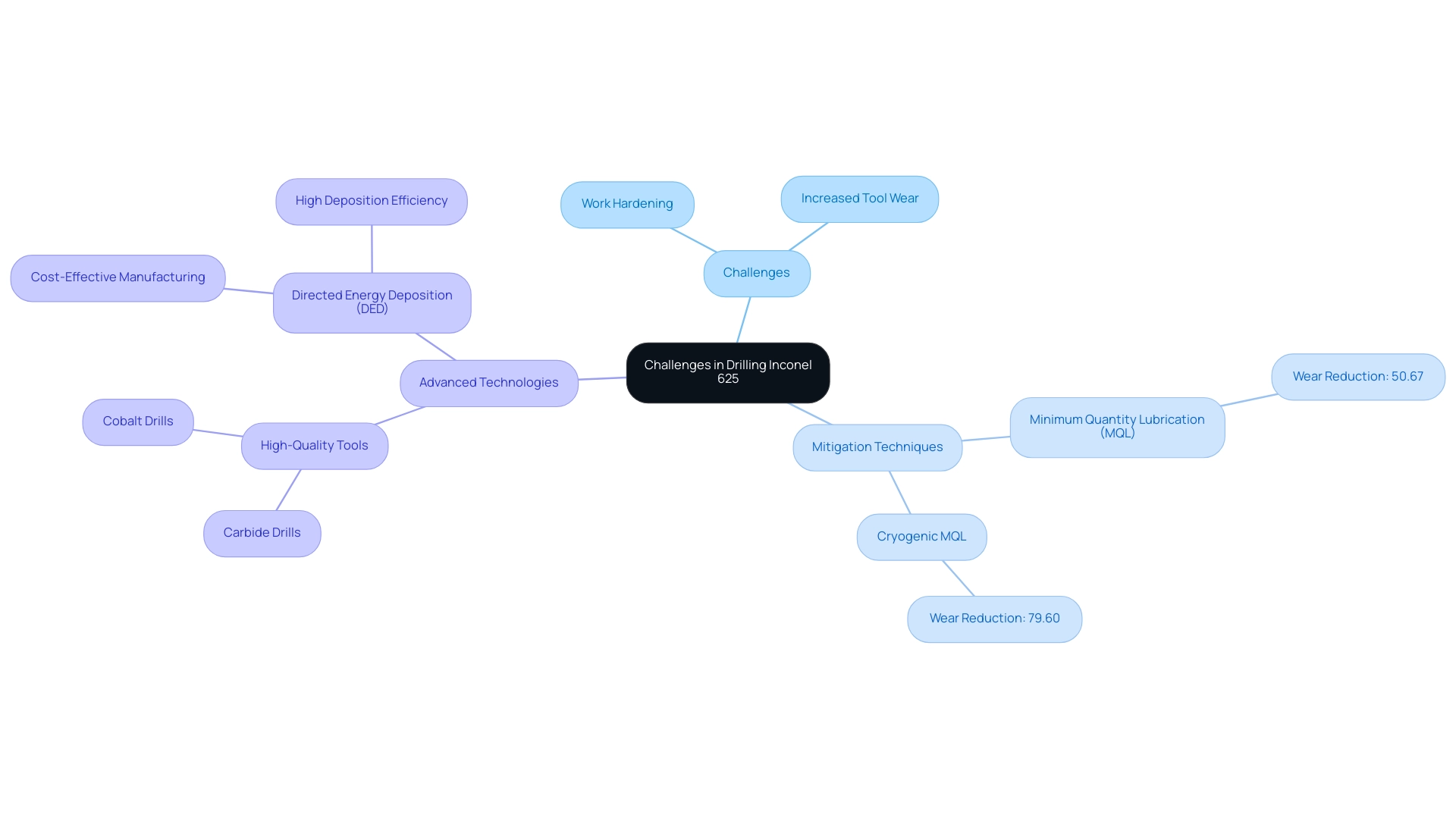
Drilling Inconel 625 poses significant challenges, especially because of the alloy’s tendency for work hardening. As the drill bit penetrates this material during the process of drilling Inconel 625, it can undergo rapid hardening, complicating subsequent drilling operations. This phenomenon leads to increased equipment wear, with recent studies indicating that wear can be minimized by implementing techniques such as Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) and Cryogenic MQL, which have demonstrated reductions in wear rates of 50.67% and 79.60%, respectively, compared to traditional cryogenic machining.
To effectively mitigate these work hardening effects, it is crucial for machinists to employ high-quality, wear-resistant cutting implements, such as carbide or cobalt drills. Moreover, careful observation of extraction conditions enables prompt modifications to parameters, enhancing performance and extending equipment lifespan. As noted by industry experts, addressing tool wear not only enhances operational efficiency but also contributes to the overall cost-effectiveness of machining operations.
Integrating approaches from recent case analyses, such as those concentrating on Thermally Assisted Machining (TAM) processes, which explore optimal preheating ranges for specific alloys, can further guide best practices for working with Inconel 625, assisting professionals in managing the intricacies of this challenging material. Furthermore, as Ali Günen notes,
- ‘Directed energy deposition (DED) technology is a cost-effective additive manufacturing method widely used in the production of complex-shaped parts made of various engineering alloys as well as superalloys due to its advantages such as high deposition efficiency, low-cost and flexible production possibilities.’
This emphasizes the potential of alternative manufacturing techniques pertinent to alloy 625.
It is important to note that the opinions and data presented in this guide are solely those of the authors and contributors.
Essential Tools and Techniques for Drilling Inconel 625
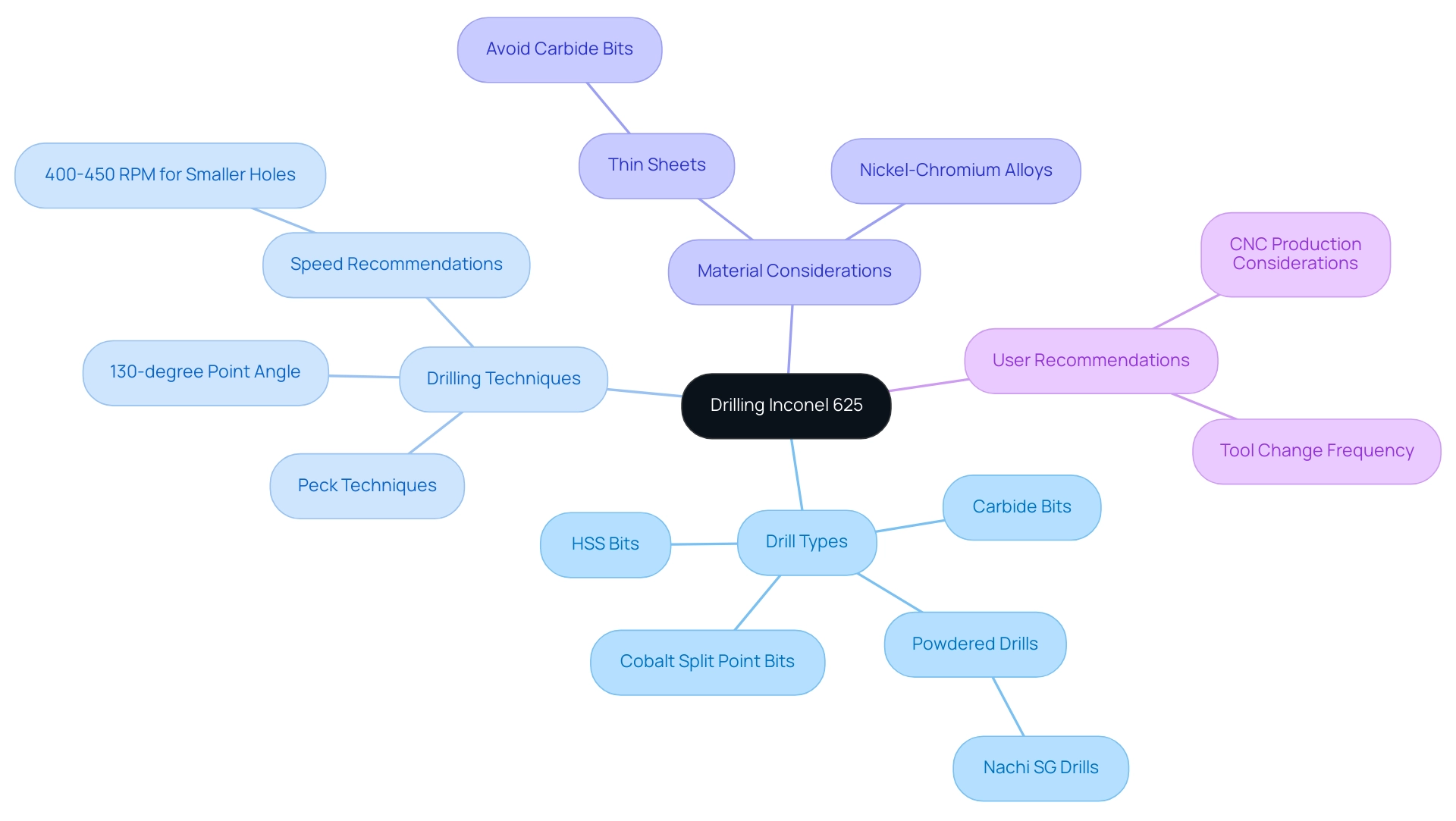
For effective drilling Inconel 625, particularly for holes with a diameter of 3mm, it is advisable to utilize high-speed steel (HSS) or carbide drill bits specifically engineered for drilling Inconel 625 and other hard materials. A twist drill featuring a 130-degree point angle enhances penetration, making it more efficient for this challenging alloy. Utilizing peck techniques, where the bit is advanced in small increments, significantly aids in managing heat generation and mitigates the risk of work hardening, ensuring a smoother process.
Moreover, ensuring the proper clamping of the workpiece is crucial; this stability during the process is essential to achieve precision and consistency. In recent discussions, a user highlighted the advantages of powdered drills like Nachi SG drills for unstable cutting conditions, particularly when working with very thin sheets, suggesting a strategic approach to drill selection based on specific material characteristics and operational requirements. Furthermore, as one user observed, utilizing cobalt split point bits for smaller openings at a speed of 400-450 RPM can be effective, particularly when boring up to 1.75 inches in diameter and 6-8 inches deep in a nickel-chromium alloy.
This understanding, along with the recommendation against carbide bits for extremely thin sheets, offers a strong basis for choosing the most suitable instruments and methods for drilling Inconel 625.
The Importance of Coolants and Lubrication in Inconel Machining
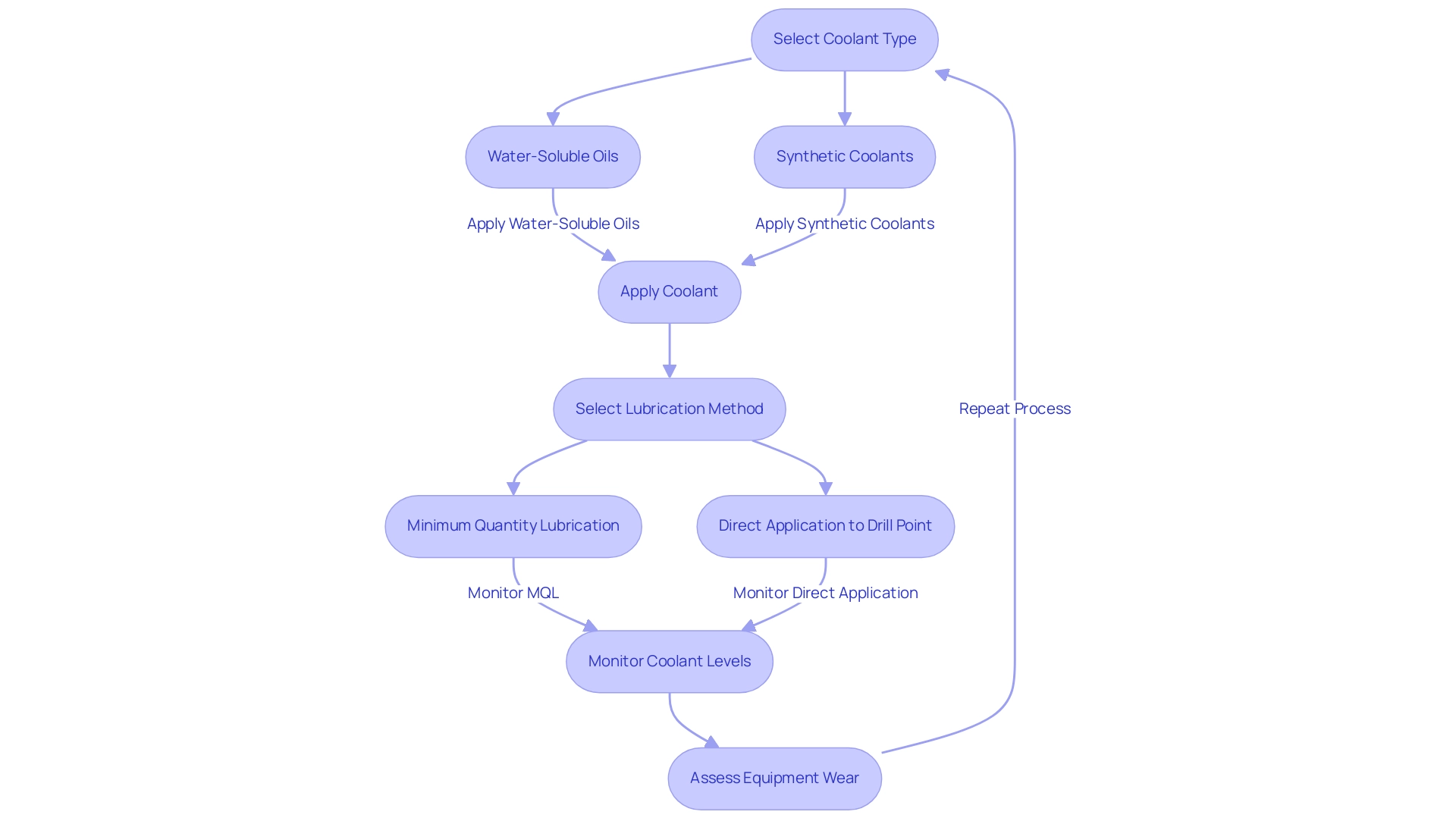
The utilization of suitable coolants is paramount when drilling Inconel 625, with the most effective choices being water-soluble oils and synthetic coolants. These coolants play a vital role in dissipating the heat generated during the drilling Inconel 625 process, which is essential for minimizing equipment wear and preventing work hardening. Research indicates that effective lubrication can reduce equipment wear significantly, enhancing operational efficiency.
For instance, a study on minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) highlighted that hybrid MQL using hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) nanolubricants resulted in maximum lifespan of the cutting instrument and minimized surface roughness at a cutting speed of 40 m/min and a feed rate of 0.1 mm/min. Furthermore, applying lubricant directly to the drill point can mitigate friction and yield a superior surface finish. It is crucial to regularly monitor coolant levels and ensure the lubrication system is functioning optimally, as this maintains ideal conditions for drilling Inconel 625.
As emphasized by industry expert Qin, internal spray cooling can significantly reduce thrust force and enhance equipment longevity, achieving improvements of up to twofold compared to traditional external cooling methods. Applying these practices is crucial for attaining sustainable machining operations, which are progressively significant for the ecological and economic sustainability of manufacturing processes, while ensuring the durability of instruments when drilling Inconel 625 and handling demanding materials.
Advanced Strategies for Precision Drilling of Inconel 625
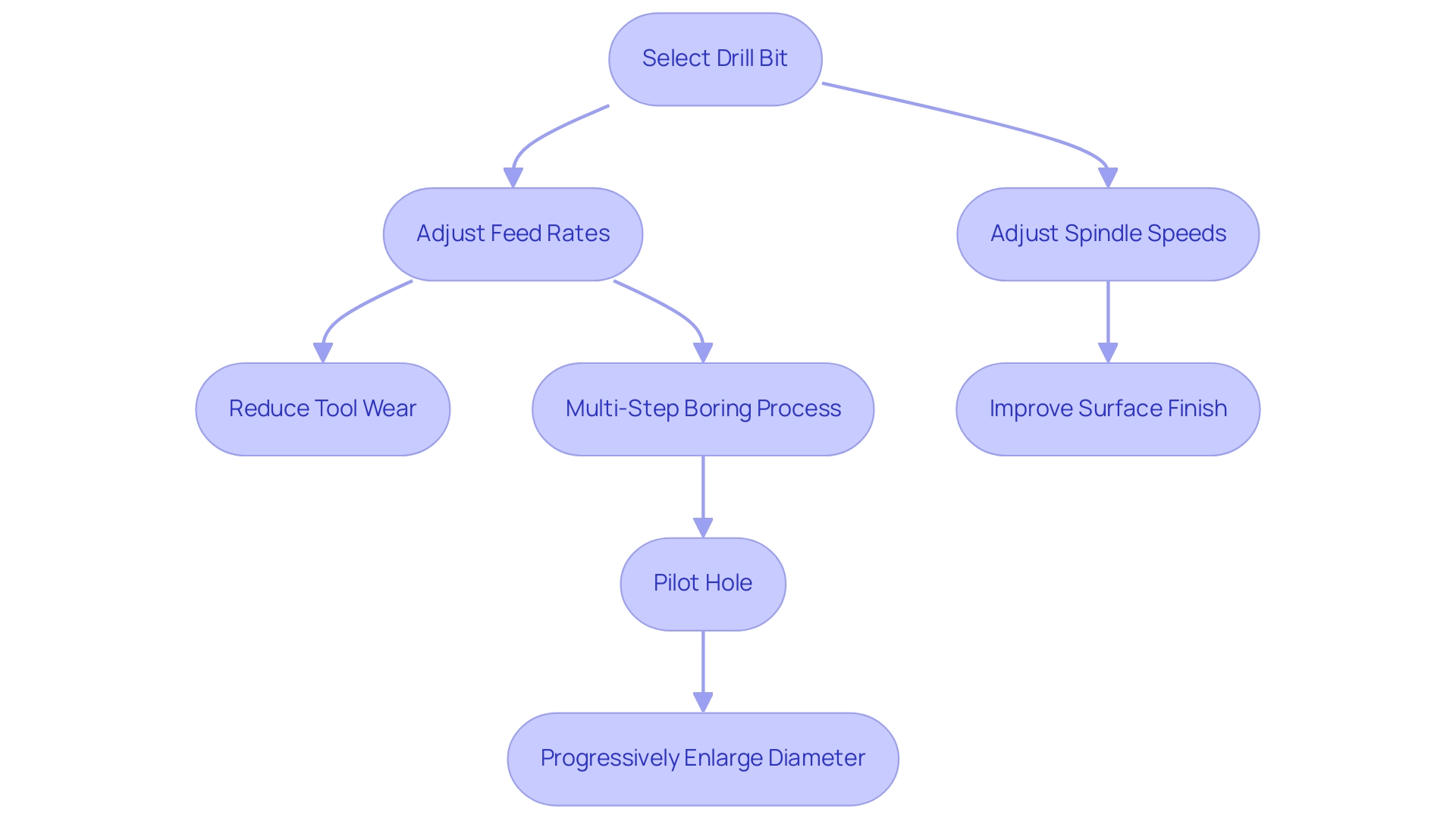
To achieve optimal precision when drilling Inconel 625, it is essential to strategically adjust feed rates and spindle speeds according to the specific drill bit employed. Utilizing slower feed rates can significantly mitigate tool wear, while increasing spindle speeds can enhance the surface finish of the machined part. Notably, higher feeds of up to 100 ipm can be achieved with increased confidence when these parameters are properly managed.
Incorporating a multi-step boring process—initiating with a pilot hole and progressively enlarging the diameter—can further maintain accuracy and minimize stress on the tooling. Regular process monitoring and real-time adjustments based on performance feedback are crucial for achieving superior outcomes, reinforcing the necessity of process control in machining operations. As highlighted by H. Oktem et al. in their research, optimizing cutting conditions is fundamental for enhancing surface quality and operational efficiency (Journal of Materials Processing Technology, vol. 170, p. 11-16).
The use of advanced drilling strategies in drilling Inconel 625 ensures that parameters are not only aligned with the material’s unique properties but also that they adapt to evolving machining conditions.
Furthermore, a case study on the application of ceramic inserts for turning Inconel illustrates the practical benefits of advanced tooling, showcasing a remarkable improvement in cycle times and affirming that selecting appropriate tooling can lead to heightened machining efficiency, especially in challenging materials.
Conclusion
Inconel 625 is a premium alloy celebrated for its outstanding mechanical properties and exceptional resistance to oxidation, making it essential in aerospace, chemical processing, and marine applications. However, machining this alloy presents challenges, primarily due to work hardening and tool wear.
To effectively drill Inconel 625, it is crucial to use high-quality cutting tools, such as carbide or cobalt drills. Implementing techniques like Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) can significantly reduce tool wear and enhance machining efficiency. Employing specific drilling methods, including:
- Peck drilling
- Precise adjustments of feed rates
- Spindle speeds
is vital for achieving the desired precision and surface finish.
Furthermore, the importance of coolants and lubrication cannot be overlooked, as they are key to dissipating heat and minimizing friction during machining. Regular monitoring of these systems is necessary to maintain tool performance and longevity when working with this challenging material.
In summary, understanding Inconel 625’s properties and adopting effective machining strategies are crucial for maximizing its potential in demanding applications. By selecting the right tools and techniques, manufacturers can enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure reliability, ultimately gaining a competitive edge in the marketplace.




