Blogs

Mastering Inconel Isotropic Superfinishing: An In-Depth Tutorial for Engineers
Overview:
The article focuses on the techniques, benefits, and future trends of Inconel isotropic superfinishing, emphasizing its importance for engineers in high-performance applications. It highlights that this advanced finishing process enhances material properties such as fatigue resistance and corrosion resistance, while also promoting economic and environmental sustainability through reduced waste and improved operational efficiencies.
Introduction
The evolution of manufacturing processes is a testament to the relentless pursuit of efficiency and performance, particularly in high-stakes industries such as aerospace and automotive. Among the forefront of these advancements is Inconel isotropic superfinishing, a sophisticated technique that significantly enhances the surface properties of Inconel alloys. This precision finishing method not only reduces surface roughness but also bolsters fatigue and corrosion resistance—critical factors for components operating under extreme conditions.
As engineers delve into the intricacies of this process, understanding its methodologies, benefits, and economic implications becomes essential for optimizing material performance. With recent innovations paving the way for enhanced durability and sustainability, the strategic integration of isotropic superfinishing promises to redefine manufacturing standards and elevate operational efficiencies across various sectors.
Introduction to Inconel Isotropic Superfinishing
Inconel isotropic superfinishing signifies a state-of-the-art technique that significantly enhances the characteristics of Inconel alloys. This technique effectively reduces surface roughness, leading to enhanced fatigue resistance and corrosion resistance, which are crucial for the longevity and reliability of components in demanding environments. For engineers involved in high-performance fields like aerospace and automotive, understanding the complexities of isotropic surface finishing is essential.
By attaining a uniform, mirror-like finish, this method significantly enhances performance in high-stress applications where material integrity is critical. Recent advancements have demonstrated that employing inconel isotropic superfinishing can yield notable performance improvements, positioning Inconel alloys as superior choices for high-performance applications. Notably, studies indicate that at 1400°F for 1000 hours, the Stress for Rupture reaches an impressive 758 ksi, underscoring the material’s durability when processed with advanced finishing techniques.
As highlighted by S.-D.M. and colleagues, the conceptualization and methodology behind these procedures are vital for ensuring optimal results. Furthermore, a case study on the ‘Suitability for High-Performance Materials’ illustrates that unconventional machining processes are particularly effective for Inconel alloys, requiring matching training and expertise to achieve successful implementation.
Techniques and Methodologies in Isotropic Superfinishing
Isotropic superfinishing utilizes various advanced methods, particularly abrasive flow machining (AFM), vibratory finishing, and magnetic abrasive finishing (MAF), each designed to meet specific quality requirements for inconel isotropic superfinishing of Inconel alloys. AFM stands out due to its use of a viscous medium filled with abrasives that adapt to the contours of the workpiece, enabling effective smoothing of imperfections. This method not only improves finish quality but also aids in better observation of microcracks—critical for maintaining structural integrity—by allowing for a resolution better than 0.5 μm.
Alan notes, ‘The highly reflective bright finish is also suitable for a number of decorative applications, particularly where the shape of the item requiring polishing is extremely complex.’ Vibratory finishing, conversely, entails placing Inconel parts within a vibratory bowl alongside abrasive media, creating a gentle yet effective grinding action that can uniformly polish complex geometries through inconel isotropic superfinishing. MAF applies magnetic fields to direct abrasive particles, providing a unique approach for achieving exceptional finishes on intricate shapes.
A case study on the electrolytic in-process dressing (ELID) technique illustrates how specific parameters, such as voltage and coolant flow rate, significantly affect quality, reinforcing the importance of selecting the right technique. When choosing the suitable method, engineers must take into account key factors such as:
- The geometry of the part
- The desired surface finish
- Production volume
Staying updated with the latest developments, such as the recent research highlighting the efficacy of micro texturing drill tools to minimize energy loss during machining operations, further informs the choice of method.
By approaching the selection process strategically, procurement managers can ensure optimal outcomes in the inconel isotropic superfinishing procedures of Inconel materials.
Benefits of Isotropic Superfinishing for Inconel Alloys
Inconel isotropic superfinishing presents significant advantages for Inconel alloys, particularly in enhancing fatigue life, minimizing friction, and boosting corrosion resistance. By attaining an exceptionally smooth finish, the risk of crack initiation is substantially reduced, which is crucial for components operating under high-stress conditions. The impact of this process is underscored by recent studies demonstrating a twofold increase in fatigue life following appropriate treatment, along with the aging treatment increasing the fatigue life of the remelting zone (RZ) by a factor of 2.
Furthermore, the reduction in surface roughness directly correlates with lower friction coefficients, optimizing performance in dynamic applications. Engineers can anticipate that investing in advanced finishing not only reduces the chances of part failure but also leads to lower maintenance expenses, thus making it a strategic decision in material optimization. As noted by researcher Z.Z., ‘the implications of these enhancements, including inconel isotropic superfinishing, extend to improved operational efficiencies and extended service life for Inconel materials across various industries.’
Additionally, a case study titled ‘Impact of Heat Treatment on Inconel 718 Alloys‘ highlights how heat treatment can significantly affect fatigue strength, further reinforcing the benefits of inconel isotropic superfinishing.
Economic and Environmental Considerations in Superfinishing
In the field of manufacturing, inconel isotropic superfinishing represents a pivotal advancement, yielding not only enhanced performance but also notable economic advantages. By significantly reducing material waste during the finishing process, manufacturers can lower production costs, thereby improving the overall profitability of operations. Furthermore, the enhanced durability of completed items leads to a reduced frequency of replacements and repairs, which can be a significant cost-saving strategy.
The environmental implications are equally compelling; the shift towards more efficient superfinishing techniques substantially reduces the ecological footprint of manufacturing, supporting global sustainability initiatives. As Mike Klein states,
Texture roughness is a component of texture and plays an important role in determining how an object will interact with its environment.
This emphasizes the significance of quality of the exterior not only for performance but also for sustainability.
Engineers and procurement managers should therefore assess both the immediate and long-term economic advantages, along with the environmental effects, when incorporating advanced finishing techniques into their manufacturing workflows. The successful case study of inconel isotropic superfinishing applied to Ti-6Al-4V components produced by electron beam melting (EBM) illustrates a significant decrease in surface roughness to about 4 µm as a direct result of the ISF method, while maintaining the original geometry. This demonstrates the transformative potential of these methods in attaining both economic efficiency and environmental responsibility.
Moreover, the application of centrifugal ISO-finishing technology across various industries, including medical, aerospace, automotive, and jewelry, further emphasizes the broader implications of finishing processes in enhancing quality and sustainability in manufacturing.
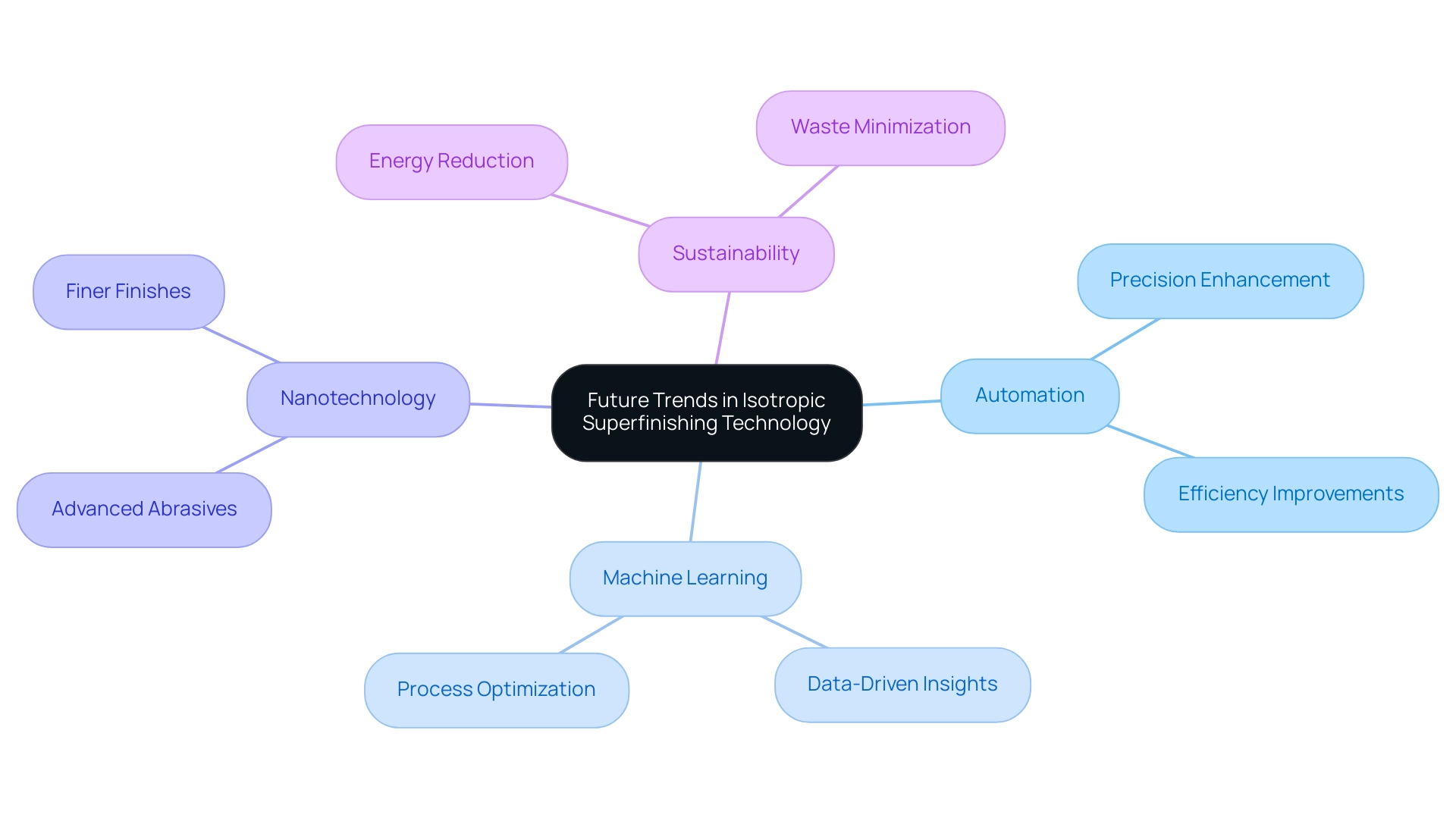
Future Trends in Isotropic Superfinishing Technology
The landscape of isotropic surface finishing technology, particularly with the adoption of inconel isotropic superfinishing, is evolving rapidly, as the integration of automation and machine learning emerges as key trends that significantly enhance both precision and efficiency. These advancements allow for more consistent finishes and reduced variability in production, which is crucial for maintaining quality standards. Moreover, the impact of nanotechnology on advanced abrasives cannot be overlooked; new formulations are being developed that enable even finer finishes, particularly benefiting inconel isotropic superfinishing and driving improvements in product performance.
This shift is supported by an increasing focus on sustainability within the industry; innovations aimed at reducing energy usage and waste during inconel isotropic superfinishing are becoming essential. For instance, recent evaluations of the economic impact of manufacturing chains have underscored the advantages of adopting advanced methodologies, such as inconel isotropic superfinishing, which reduces heat generation and eliminates metallic debris in lubricants. As William P. Nebiolo, a Sales Engineer, states,
‘The presence of asperities results in reduced contact efficiency, friction caused by peak-to-peak contact, increased contact stress in the peak-to-peak contact areas, heat generation due to friction, loss of energy horsepower transfer through these inefficiencies, shortened component life due to contact fatigue wear and pitting, and metal debris in the lube system.’
Therefore, engineers and procurement managers alike should remain vigilant about these trends, ensuring that they incorporate the latest technologies and methodologies to maintain a competitive edge in their respective fields. Understanding these dynamics will be crucial as industries navigate the complexities of modern manufacturing. Additionally, the comparison of energy consumption between hybrid deposition & micro-rolling and conventional approaches highlights the potential for significant sustainability improvements, further reinforcing the need for these advanced processes.
Conclusion
The advancements in Inconel isotropic superfinishing represent a significant leap in manufacturing processes, particularly for industries that demand the highest levels of performance and reliability. By effectively reducing surface roughness and enhancing fatigue and corrosion resistance, this technique not only extends the lifespan of components but also optimizes their operational efficiency. Understanding the various methodologies, such as abrasive flow machining and magnetic abrasive finishing, highlights the importance of selecting the right approach based on specific application requirements.
The economic and environmental benefits of isotropic superfinishing cannot be overstated. With reduced material waste and lower maintenance costs, manufacturers can achieve greater profitability while also contributing to sustainability initiatives. The case studies presented illustrate the transformative potential of these processes across diverse industries, reinforcing the strategic value of investing in advanced finishing techniques.
As the landscape of manufacturing continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest trends in automation, nanotechnology, and sustainable practices will be crucial. By embracing these innovations, procurement managers and engineers can ensure that their organizations remain competitive and capable of meeting the challenges of modern manufacturing. The integration of isotropic superfinishing into production workflows is not merely a technical enhancement; it is a strategic imperative that promises to redefine industry standards and elevate material performance across the board.




