Blogs

Understanding Inconel 718 P Number: An In-Depth Tutorial for Engineers
Overview:
The article focuses on the significance of the Inconel 718 P number classification, specifically P-4, which is crucial for ensuring proper welding techniques and compliance with safety standards in engineering applications. It supports this by detailing how understanding the P number influences material compatibility, enhances quality assurance in high-stress environments, and is essential for maintaining the structural integrity of components made from this nickel-based superalloy.
Introduction
Inconel 718 stands as a testament to the advancements in material science, particularly in the realm of high-performance alloys. Renowned for its exceptional mechanical properties and remarkable resistance to extreme environmental conditions, this nickel-based superalloy has become a cornerstone in industries such as aerospace, oil and gas, and nuclear engineering. Its ability to maintain strength and toughness under intense stress makes it indispensable for critical applications, from gas turbines to high-temperature components. Coupled with innovative technologies like additive manufacturing, Inconel 718 is evolving to meet the complex demands of modern engineering challenges. This article delves into the properties, applications, and processing techniques of Inconel 718, providing procurement managers with essential insights to make informed decisions in sourcing and utilizing this remarkable material.
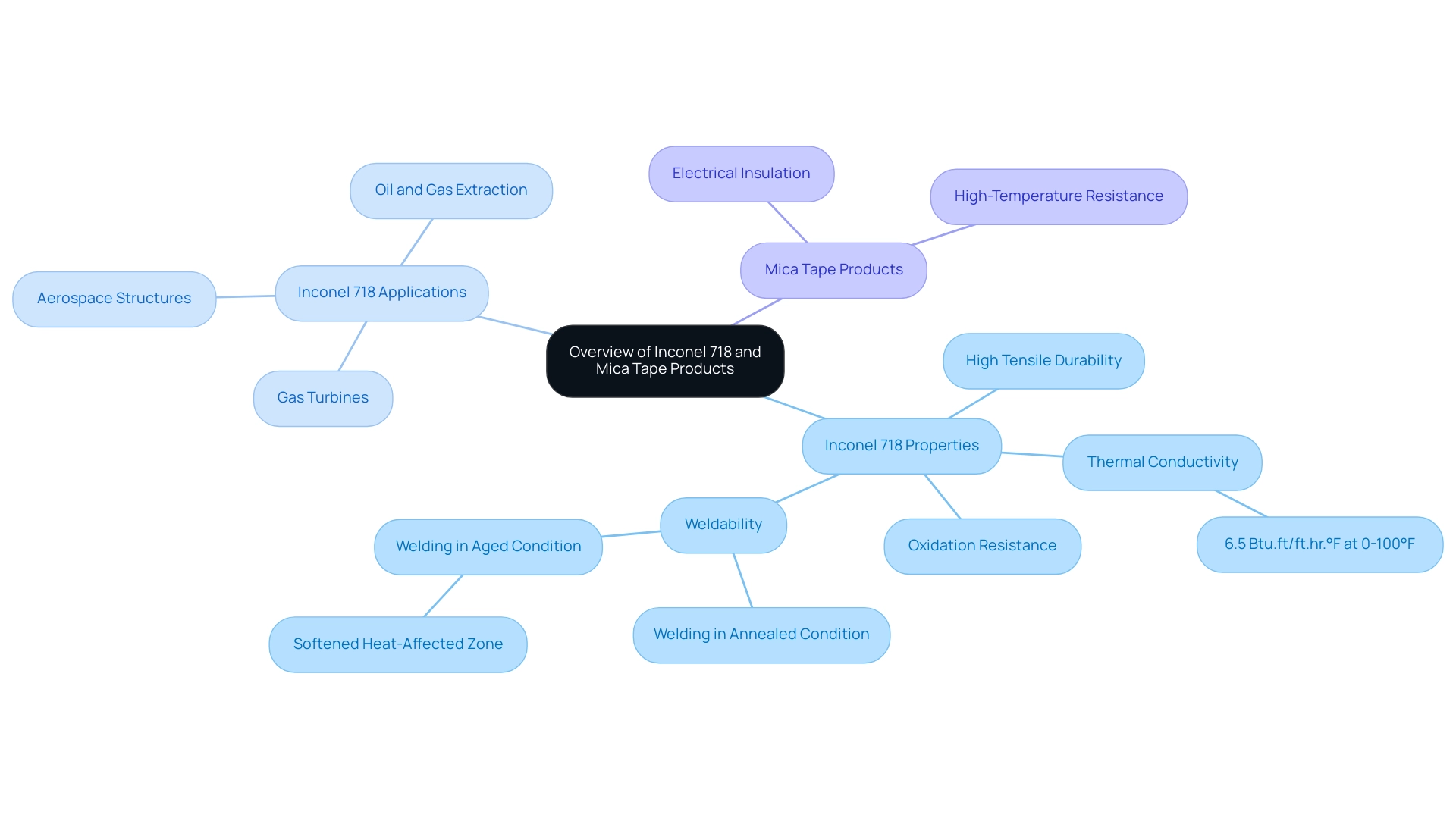
Overview of Inconel 718: Properties and Applications
Inconel 718, a nickel-based superalloy, is renowned for its exceptional mechanical properties and its ability to withstand extreme environmental conditions. This alloy displays high tensile durability and exceptional resistance to oxidation, especially at increased temperatures, rendering it an ideal choice for challenging uses. Its thermal conductivity at temperatures between 0-100°F is measured at 6.5 Btu.ft/ft.hr.°F, which further underscores its utility in thermal management within high-performance components.
In parallel, Mica Tape Products offer essential electrical insulation and high-temperature resistance, suitable for critical uses in electrical engineering, including household appliances and industrial machinery. Specifically, Mica Tape’s excellent flame resistance and dielectric capability make it a reliable choice in the manufacture of fire-resistant cables and other critical insulation systems. The applications of inconel 718 p number are extensive and include critical components in gas turbines, aerospace structures, and equipment utilized in oil and gas extraction.
Based on industry input, alloy 718’s ability to retain resilience and toughness under high-stress situations makes it a favored material in sectors that demand reliability and durability. Customer reviews emphasize prompt service, stock availability, and excellent packaging, making both 718 and Mica Tape Products appealing options for procurement managers. According to industry specialists, ‘The inconel 718 p number demonstrates excellent resistance to oxidation and corrosion at temperatures within the alloy’s effective performance range in atmospheres found in jet engines and gas turbine operations.’
This remarkable resistance is supported by case studies such as ‘Resistance to Corrosion and Oxidation of Alloy 718,’ which document its performance in environments typical of jet engines, confirming its suitability for high-temperature applications where failure is not an option, specifically related to inconel 718 p number. Additionally, it is important to note that Alloy 718 can be welded in either the annealed or aged condition; however, welding in the aged condition may result in the formation of a softened heat-affected zone, which is crucial information for procurement managers considering processing techniques. Furthermore, our range of Insulating Mica Tapes is tailored to provide exceptional thermal and electrical insulation properties, making them indispensable in the construction of coils, capacitors, and other components that require high-grade insulation to maintain safety and performance.
The Mica Sheet Tape provided by Domadia offers a robust solution for insulating large flat surfaces, with high mechanical strength and resistance to high temperatures, making it suitable for challenging environments in the aerospace and automotive industries.
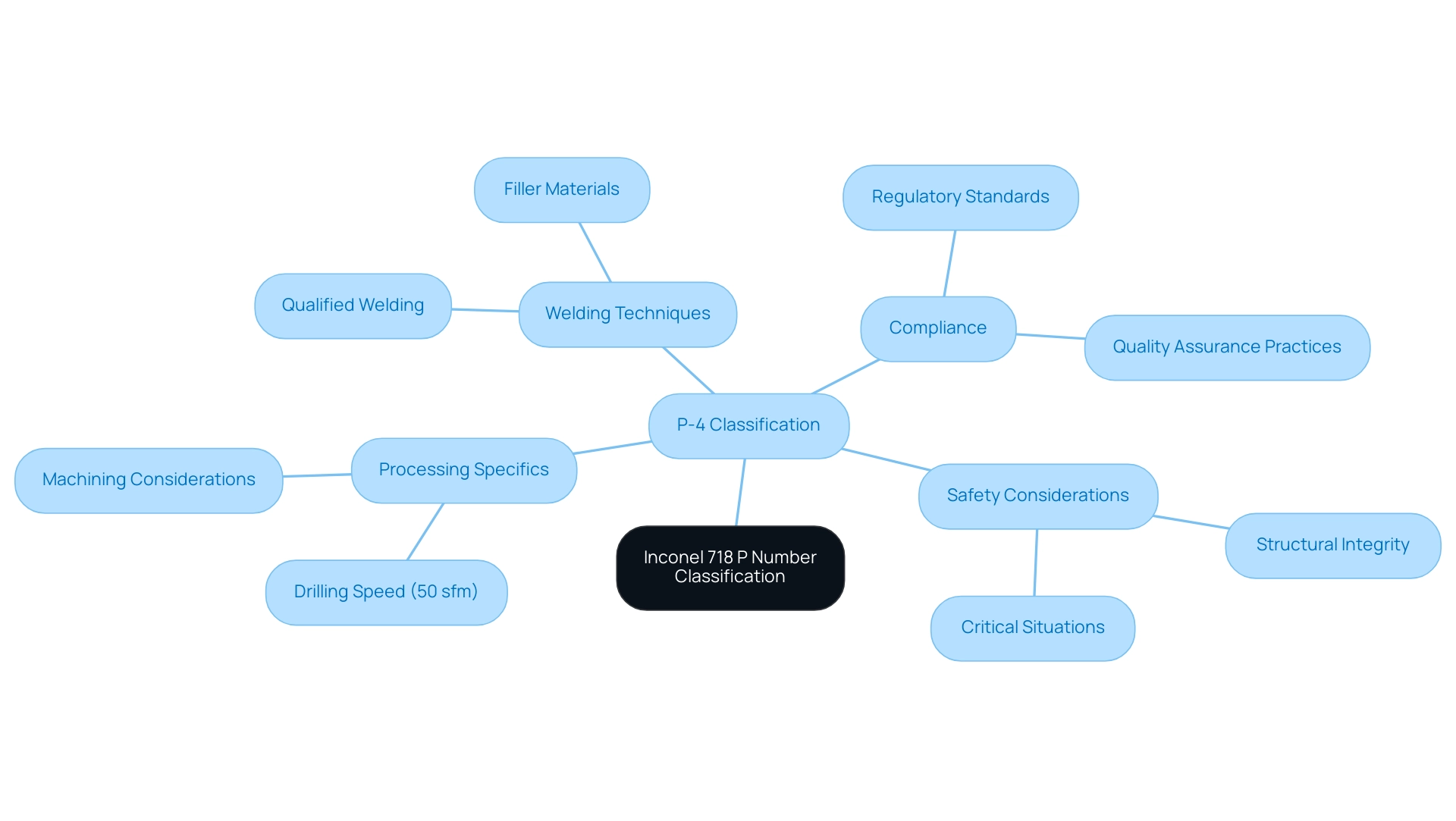
Understanding the P Number Classification for Inconel 718
Alloy 718 is classified under the inconel 718 p number classification of P-4, as specified by the ASME standards. This classification plays a vital role in determining the appropriate filler materials and welding techniques necessary for achieving optimal compatibility and performance. For example, a welder who qualifies on a P1 to the P1 material is also qualified to weld P-1 through P-15F, P-34, and any P-40s, highlighting the importance of understanding P number classifications.
Compliance with these classifications is crucial for engineers responsible for maintaining the structural integrity of parts crafted from inconel 718 p number, especially in critical situations where safety is a major priority. A thorough understanding of P-4 classification not only facilitates compliance with regulatory standards but also enhances quality assurance practices, reinforcing the reliability of welded components in demanding environments. Additionally, the processing of alloy 718 involves specific considerations, such as a drilling speed of 50 sfm, which is crucial for effective machining.
By integrating this knowledge into their processes, procurement managers can ensure that their projects meet the rigorous demands of industry specifications. The alloy 718’s applications in high-performance environments, such as jet engines and nuclear fuel element spacers, further underscore its properties and the necessity of proper welding techniques.
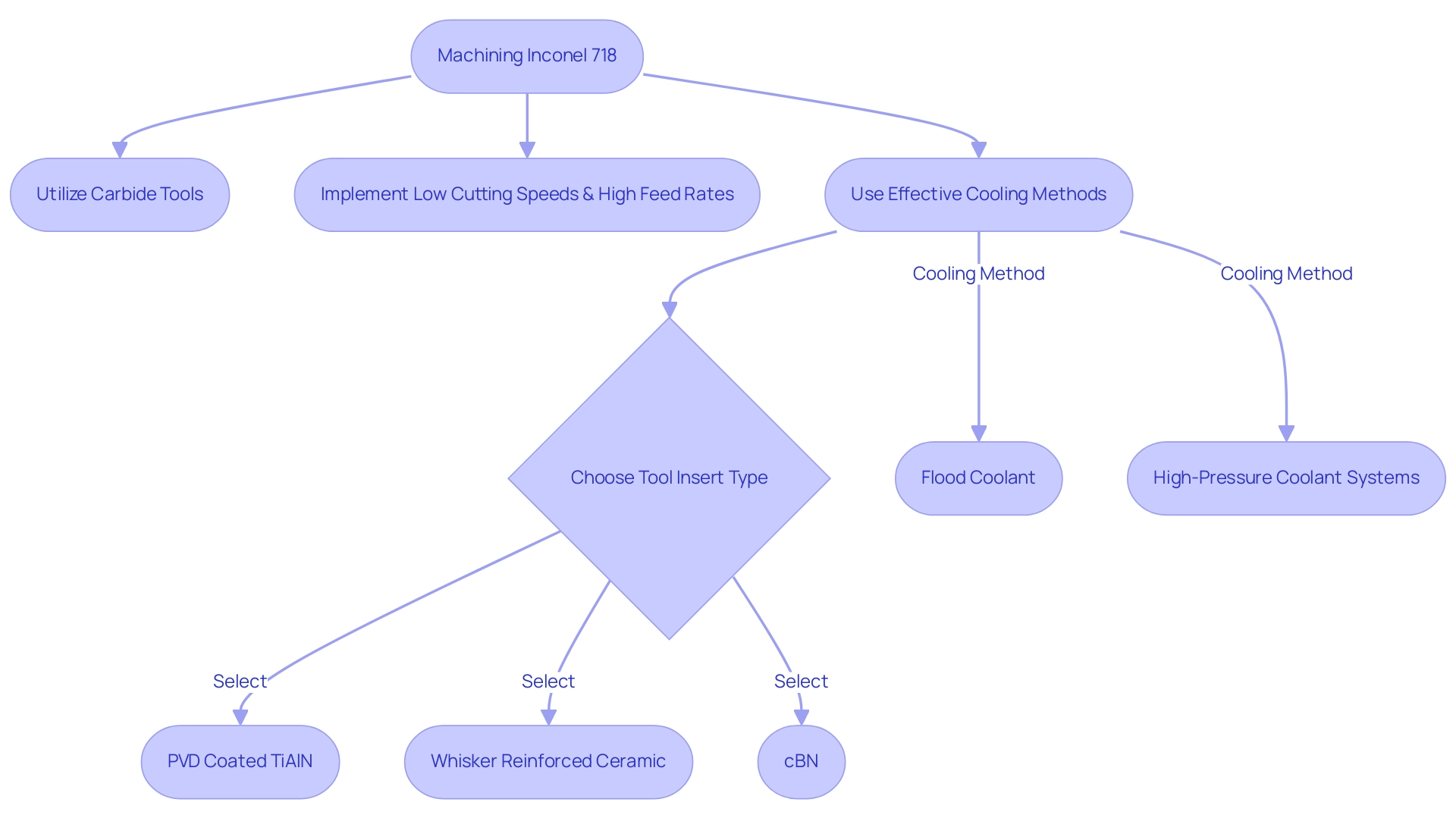
Machining Inconel 718: Techniques and Challenges
Machining this nickel-based alloy presents unique challenges, primarily due to its propensity to work-harden and its inherent toughness. To navigate these difficulties, utilizing carbide tools is highly recommended, particularly when combined with low cutting speeds and high feed rates. This approach helps to minimize heat generation, which is crucial, given the elevated cutting forces associated with machining this nickel alloy.
Effective cooling methods, such as flood coolant or high-pressure coolant systems, significantly enhance tool longevity and improve surface finish, creating a more efficient machining environment. Furthermore, as highlighted by Anthony Xavior, co-author of a recent study,
The objective of this work is to determine the machining capability of three inserts (PVD coated TiAlN carbide, whisker reinforced ceramic, and cBN) in terms of surface roughness, cutting forces, and flank wear.
Engineers should also consider implementing pre-drilled holes for complex geometries to streamline machining time and bolster accuracy.
A notable case study, titled ‘Employing Ceramic Cutting Tools for Continuous Cuts,’ demonstrates how ceramic tools are effective for continuous machining of a specific superalloy, maintaining cut quality over prolonged periods without necessitating frequent tool changes. Notably, brittle damage is the main wear mode for ceramic tools, with SiAlON exhibiting crater-like damage and TiC-whisker-reinforced Si showing whole-layer damage. Understanding these advanced techniques and the associated challenges, such as the high work hardening rate and elevated cutting forces, is essential for ensuring both efficiency and quality throughout the manufacturing process.
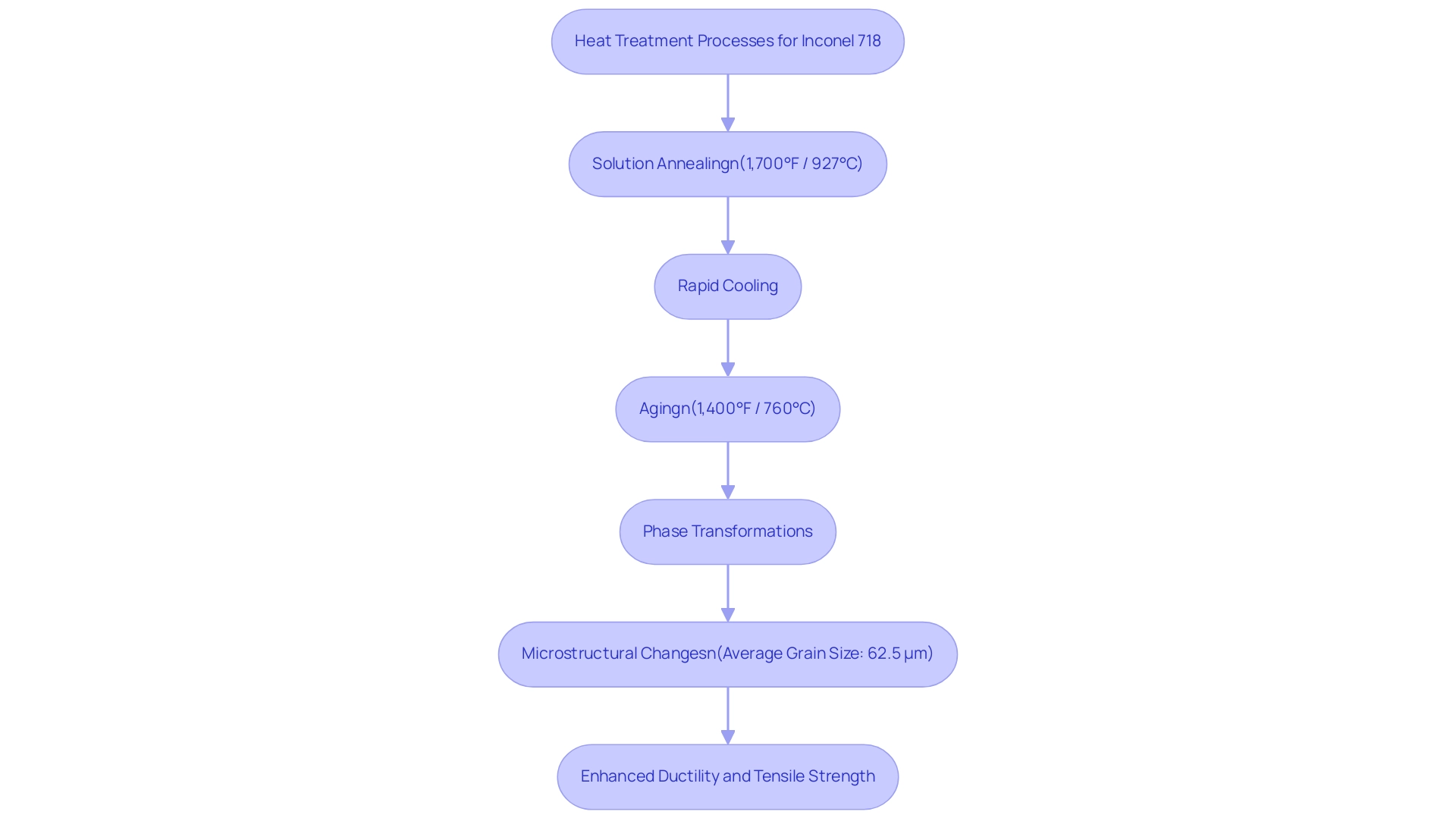
Heat Treatment Processes for Enhancing Inconel 718 Performance
To optimize the performance of Inconel 718, it is essential to understand its inconel 718 p number and apply strategic heat treatment processes such as solution annealing and aging. Solution annealing typically involves heating the alloy to around 1,700°F (927°C), followed by rapid cooling. This process effectively dissolves precipitates, enhancing ductility and preparing the material for subsequent treatments.
Aging is then conducted at approximately 1,400°F (760°C) to induce precipitation hardening, which is critical for developing the desired mechanical properties. Recent investigations by Huang et al. emphasize that the dissolution of the brittle δ phase during aging, along with improved precipitation of strengthening phases, is crucial for enhancing tensile performance.
Their findings indicate that higher aging temperatures lead to significant improvements in tensile durability due to effective phase transformations. Notably, the Vickers hardness loading time was measured at 15 s, underscoring the alloy’s performance characteristics post-treatment. Additionally, after undergoing a 4-hour heat treatment followed by a 1-hour solution, distinct microstructural changes were observed, characterized by dominant equiaxed grains and interior annealing twins, suggesting a near-completion of the recrystallization process with an average grain size of 62.5 μm.
It is vital for engineers to carefully choose heat treatment cycles customized to specific requirements, as these processes profoundly impact the inconel 718 p number, along with the alloy’s strength, fatigue resistance, and overall performance. As highlighted by Mamoun Medraj, the enhancement of post-process heat treatment is essential to realizing the complete capabilities of inconel 718 p number in challenging applications.
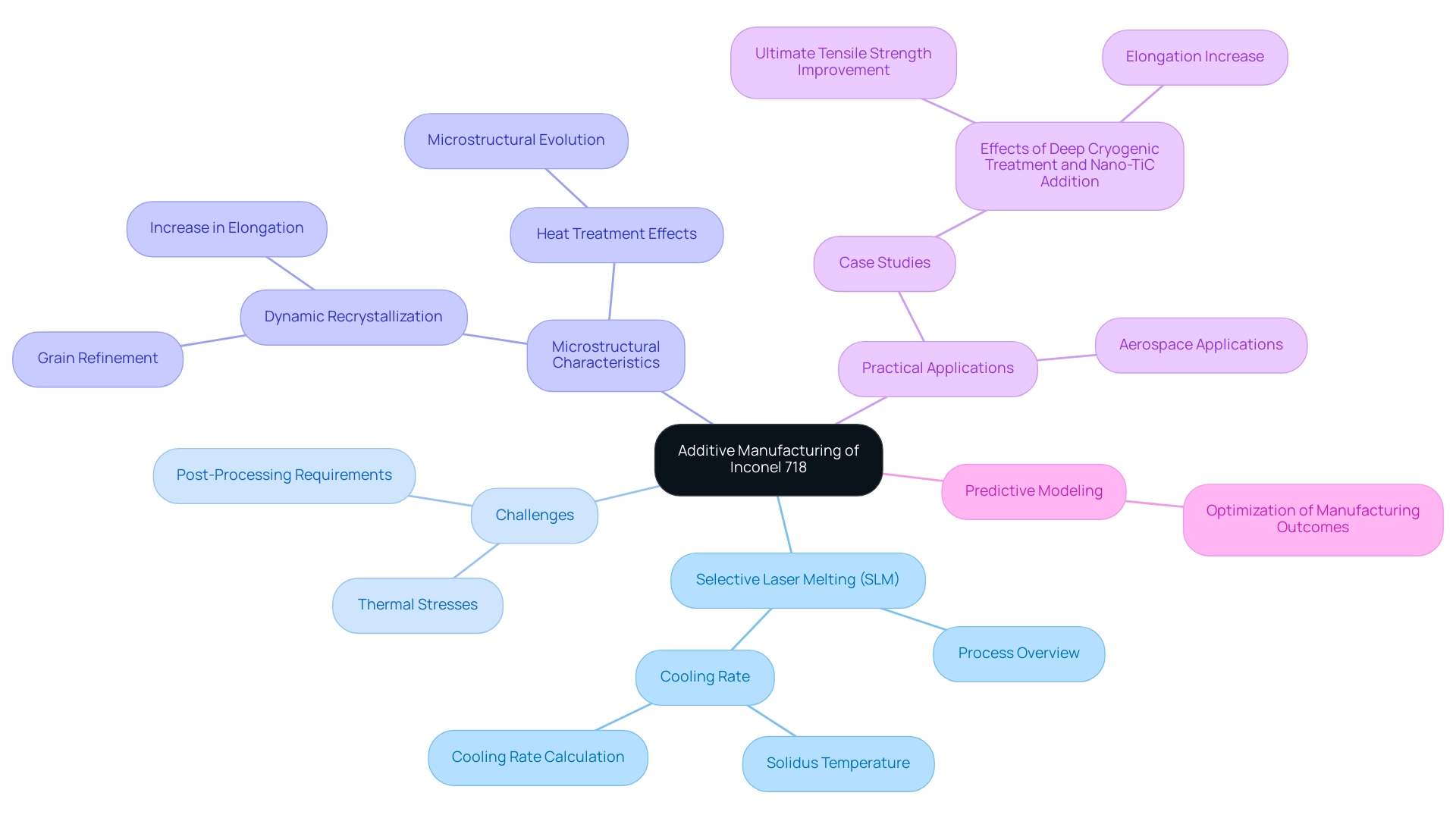
Additive Manufacturing of Inconel 718: Innovations and Implications
Additive manufacturing, especially via selective laser melting (SLM), has fundamentally changed the production landscape for components, specifically those related to inconel 718 p number. This advanced process enables the fabrication of highly complex geometries that traditional manufacturing methods cannot achieve. The cooling rate, calculated between the last crossing of the solidus temperature (1533 K) and 1450 K, plays a crucial role in determining the microstructural characteristics of the final product.
The ability to produce parts that are both lightweight and robust results in significant material savings and enhanced design optimization. However, engineers must navigate certain challenges inherent to SLM, including:
- Managing thermal stresses
- Adhering to post-processing requirements to maintain the integrity and performance of the final product
Recent findings highlight that dynamic recrystallization during deep cryogenic treatment can lead to grain refinement, increasing elongation by approximately 24.8% without compromising strength.
Moreover, the analysis by Zhang et al. highlights the influence of heat treatment on the microstructural development of nickel-based superalloys, which is essential for engineers dealing with 718. Practical uses of SLM in aerospace illustrate the increasing trend towards employing the inconel 718 p number alloy in high-performance settings, emphasizing the significance of strategic knowledge in this developing area.
For instance, the case study titled ‘Effects of Deep Cryogenic Treatment and Nano-TiC Addition on a Nickel-Based Alloy’ reveals how the addition of 1.5 wt% nano-TiC enhances ultimate tensile strength by approximately 46.81 MPa and increases elongation by about 32.7%, showcasing practical applications of SLM in improving material properties. As stated by Mehrshad Mehrpouya, ‘A Prediction Model for Additive Manufacturing of Inconel 718 Superalloy’ illustrates the critical role of predictive modeling in optimizing manufacturing outcomes for the inconel 718 p number.
Conclusion
Inconel 718 stands out as a premier nickel-based superalloy, celebrated for its exceptional mechanical properties and resistance to extreme environments. The alloy’s high tensile strength and oxidation resistance make it a vital choice for demanding applications across industries such as aerospace, oil and gas, and nuclear engineering. Its adaptability is further enhanced by advanced processing techniques, including additive manufacturing, which allow for the creation of intricate geometries that traditional methods cannot achieve. Understanding the unique properties and applications of Inconel 718 is essential for procurement managers aiming to source reliable materials for high-stakes projects.
The significance of proper processing and treatment cannot be overstated. Techniques like solution annealing and aging are crucial for optimizing the alloy’s performance, enhancing its strength, fatigue resistance, and overall durability. Additionally, recognizing the P number classification for welding and the challenges associated with machining Inconel 718 helps ensure structural integrity and compliance with industry standards. By integrating this knowledge, procurement managers can make informed decisions that align with the rigorous demands of their respective industries.
Ultimately, Inconel 718 is not just a material; it is a strategic asset that can significantly impact project outcomes. As industries continue to evolve and face new challenges, the role of innovative materials like Inconel 718 will become increasingly vital. Embracing these advancements not only enhances operational efficiency but also reinforces a commitment to quality and reliability in critical applications. The insights shared in this article serve as a foundational resource for procurement managers seeking to leverage the full potential of Inconel 718 in their operations.




