Blogs

Cladding Process: How Are Metals Cladded?
Metal cladding is a critical technique used in numerous industries to enhance strength, resist corrosion, and achieve specific aesthetic or functional properties. But how are metals cladded exactly? The answer lies in the method—and the intended application.
Here’s a closer look at the most common and effective cladding techniques used today.
1. Roll Bonding

What It Is:
Roll bonding is a mechanical method where two or more metals are passed through rollers under high heat and pressure. This process physically fuses the metals, creating a metallurgical bond without melting them.
Best For:
- Large-scale production
- Bimetallic sheets
- Applications requiring consistent surface bonding
Advantages:
- Cost-effective
- Suitable for dissimilar metals
- Strong and uniform bonding
2. Explosive Bonding

What It Is:
In this high-energy technique, a controlled explosion is used to join two metal surfaces. The explosive force propels one metal into another at such a velocity that a solid-state weld is created instantly.
Best For:
- Cladding corrosion-resistant materials
- Bonding thick or complex metals
- Aerospace and marine applications
Advantages:
- No heat-affected zones
- Excellent for dissimilar and tough metals
- High bond strength
3. Laser Cladding
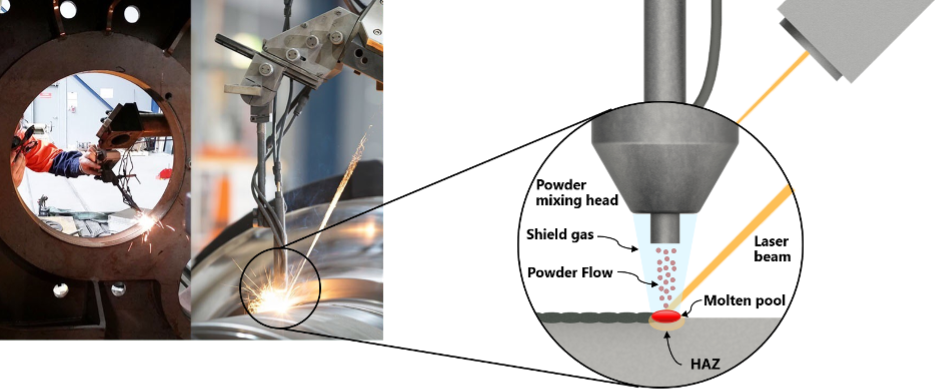
What It Is:
Laser cladding uses a high-powered laser to melt a metal powder or wire onto the surface of another metal, creating a metallurgically bonded layer.
Best For:
- Surface repairs
- Coating high-wear parts
- Medical and aerospace tools
Advantages:
- Precise control
- Minimal heat distortion
- Superior surface properties
4. Diffusion Bonding
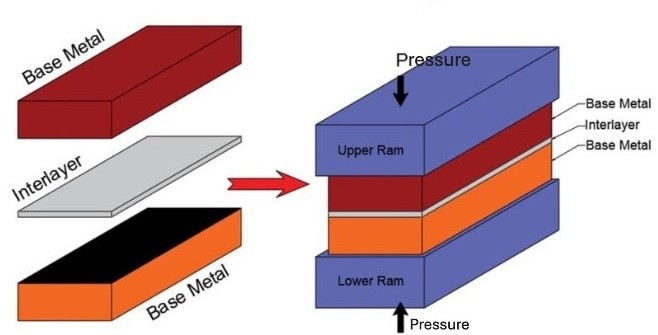
What It Is:
This method involves joining metals through the application of high pressure and temperature over an extended period. Unlike welding, diffusion bonding doesn’t require a filler material.
Best For:
- High-performance alloys
- Aerospace engine components
- Nuclear applications
Advantages:
- Strong atomic-level bonding
- Suitable for complex geometries
- No melting involved
5. Hot Pressure Cladding
What It Is:
Hot pressure cladding bonds metals using a combination of heat and compressive force—usually in a furnace or a hydraulic press.
Best For:
- Producing composite metal panels
- Thermal and wear resistance needs
Advantages:
- Homogeneous and continuous bonding
- Economical for bulk manufacturing
Conclusion
Whether it’s creating durable alloys for the aerospace industry or building corrosion-resistant components for marine use, how metals are cladded directly affects the quality and performance of the end product. Each cladding method—roll bonding, explosive bonding, laser cladding, diffusion bonding, or hot pressure cladding—offers unique advantages based on application needs, cost, and material compatibility.
By understanding these techniques, manufacturers can choose the most efficient and effective process to meet their production goals.
Want to explore the right cladding technique for your application?
📩 Contact our team or explore our material engineering solutions today!
Contact our experts today!
Talk to: Er.Pankaj Domadia | Kairav Domadia | Aadil Domadia | Pragati Sanap | Pooja N N | Shivani Kanojia


