Blogs

Understanding Beryllium Copper Health Hazards: An In-Depth Tutorial for Workers
Introduction
In the realm of industrial safety, the handling of beryllium copper presents a dual-edged sword: its remarkable properties as a non-sparking, durable alloy make it invaluable for tools used in hazardous environments, yet its potential health risks cannot be overlooked.
- Chronic beryllium disease (CBD) looms as a significant threat, often developing silently over decades.
- Acute exposure can lead to immediate respiratory distress.
As industries increasingly rely on beryllium copper tools, understanding the associated health risks, implementing stringent safety practices, and adhering to regulatory standards becomes imperative.
This article delves into the essential safety measures, compliance requirements, and health monitoring strategies that procurement managers must prioritize to protect their workforce and ensure operational integrity in environments where exposure to this alloy is a concern.
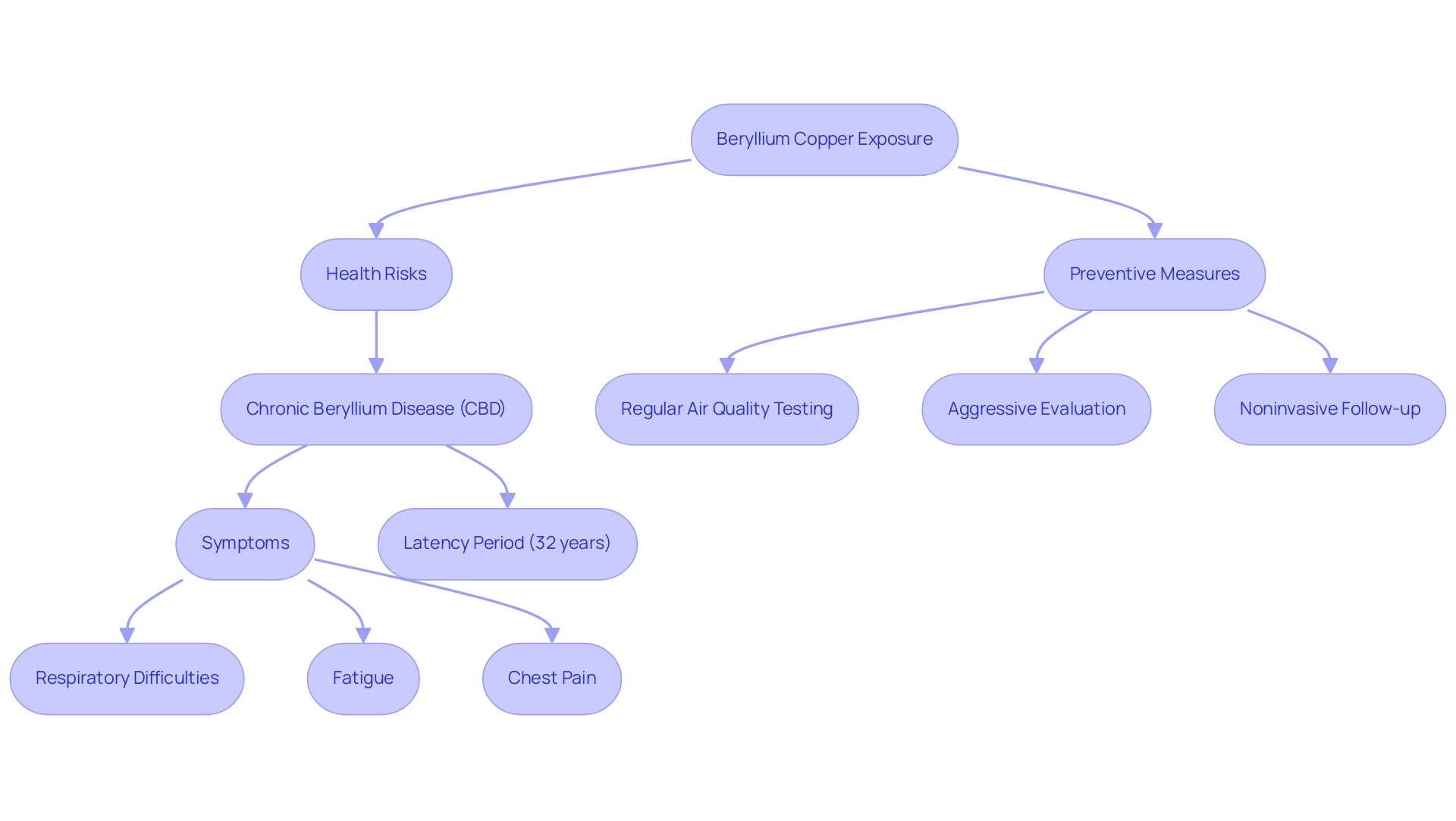
Health Risks of Beryllium Copper Exposure
Beryllium copper, a highly conductive alloy, is widely employed across various sectors, particularly in the production of non-sparking tools such as the Beryllium Copper Non-Sparking Wrench. This wrench is specifically designed to minimize the risk of sparks in hazardous environments, making it an essential tool for industries where flammable materials are present. It features excellent tensile strength and corrosion resistance, ensuring durability and reliability during use.
Nonetheless, utilizing this copper alloy entails significant beryllium copper health hazards, particularly the risk of developing chronic beryllium disease (CBD) from prolonged exposure to its dust or fumes. Symptoms of CBD include respiratory difficulties, fatigue, and chest pain, severely impacting the quality of life for affected individuals. Reports indicate a concerning latency period, with an overall mean of 32 years before symptoms manifest, underscoring the importance of diligent monitoring and assessment.
Statistical significance has been noted with:
– p < 0.0001 for definite/probable CBD versus normal
– p = 0.02 for definite/probable versus normal
This highlights the critical nature of these health risks. Additionally, severe disease may appear after a solitary, high-level contact, leading to intense lung inflammation. Regular air quality testing in environments where copper alloy is processed or utilized is essential in identifying hazardous conditions.
As Dr. Balmes emphasizes, ‘Aggressive evaluation using bronchoscopy may be warranted in certain cases, but noninvasive follow-up is preferable in populations with low CBD rates.’ Following established protocols is crucial to protect workers’ health and avoid contact with beryllium copper health hazards, thereby reducing the associated risks linked to this alloy. Preventive actions and awareness are crucial in safeguarding employees from the potentially harmful impacts of exposure to toxic materials, particularly the beryllium copper health hazards associated with using tools like the Copper Non-Sparking Wrench that are created with protective features to reduce risks in dangerous environments.
Product tags for Beryllium Copper, Kovar, Mu-Metal, and Nickel materials are also relevant for procurement managers seeking safe and effective tools for their operations.
Essential Safety Practices and Protective Equipment for Workers
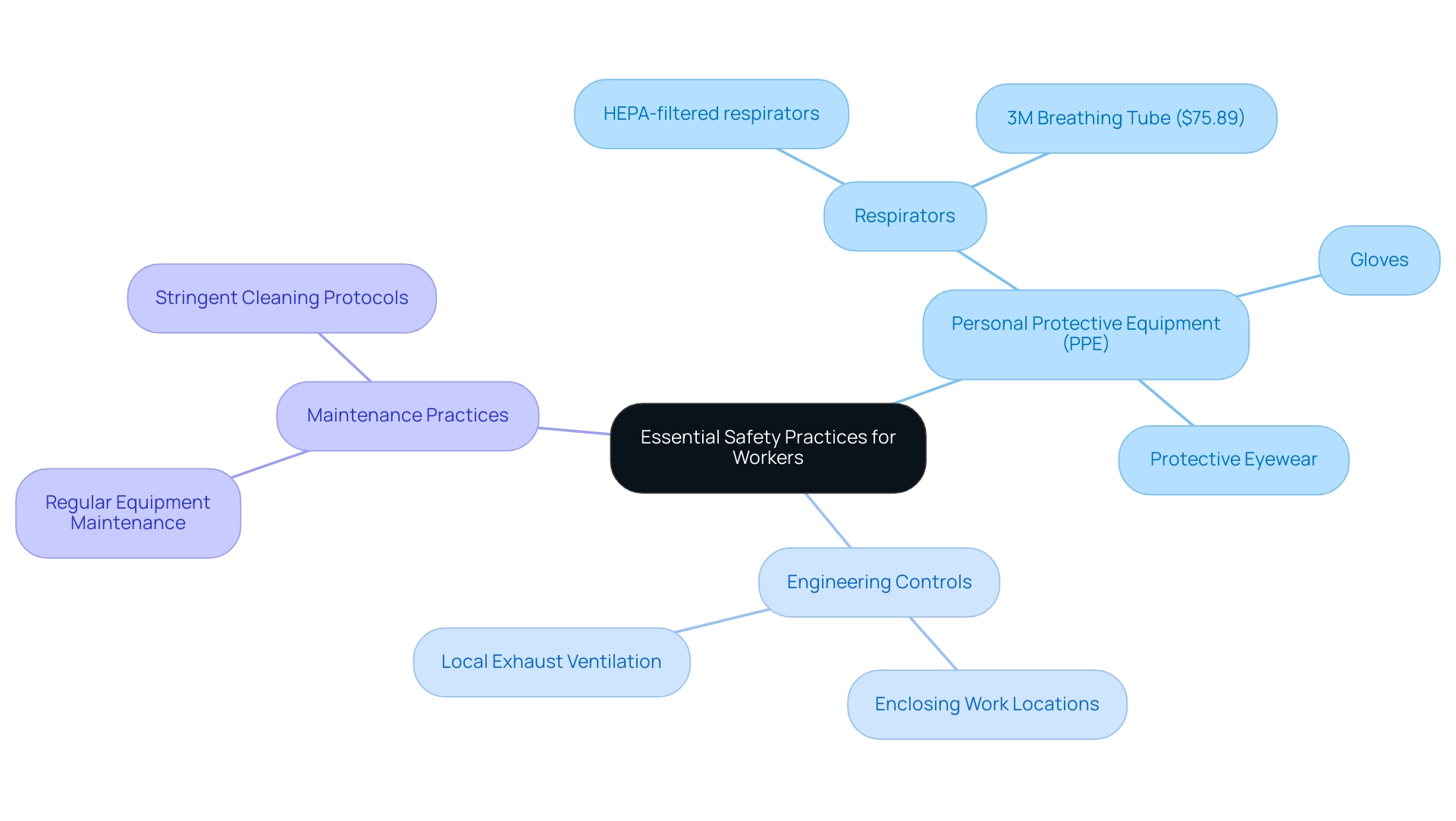
When working with copper alloy, it is essential to follow established protocols to reduce the beryllium copper health hazards and exposure risks. Domadia is committed to equipping procurement managers with high-quality beryllium copper wire, ensuring project success through exceptional customer service. Workers must don appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including:
- Respirators designed for fine particulate filtration
- Gloves
- Protective eyewear
The effectiveness of these protective measures is underscored by the Sampling and Analysis Subcommittee Task Group of the Beryllium Health and Health Committee, which asserts that ‘HEPA-filtered vacuuming is considered to be the most effective method for cleaning surfaces.’ Ongoing training programs centered on secure handling methods are essential, ensuring that employees stay informed about beryllium copper health hazards and the latest protection technologies.
Engineering controls, such as:
- Enclosing work locations
- Utilizing local exhaust ventilation
are critical strategies to mitigate airborne particles of a certain metal, particularly emphasized in case studies of welding operations, which demonstrate the importance of these methods in maintaining safety during primary metal production and alloy fabrication.
Regular maintenance of equipment and stringent cleaning protocols are indispensable for preventing contamination and mitigating beryllium copper health hazards, thereby safeguarding workers’ health. The benefits of copper alloy tools, including their non-sparking, corrosion-resistant, and durable nature, make them essential in industries operating in explosive environments. Non-sparking tools are specifically designed to prevent ignition in hazardous situations, ensuring protection in explosive atmospheres.
Additionally, it’s important to note that the 3M Breathing Tube, a necessary component for specific respirators, costs approximately $75.89, emphasizing the investment required in PPE. By rigorously implementing these safety measures and staying updated with OSHA’s new requirements and definitions regarding exposure assessment, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of hazards related to copper exposure. For further details on our high-quality copper wire and tools, and to discover how we can support you in achieving your project objectives, please reach out to Domadia today.
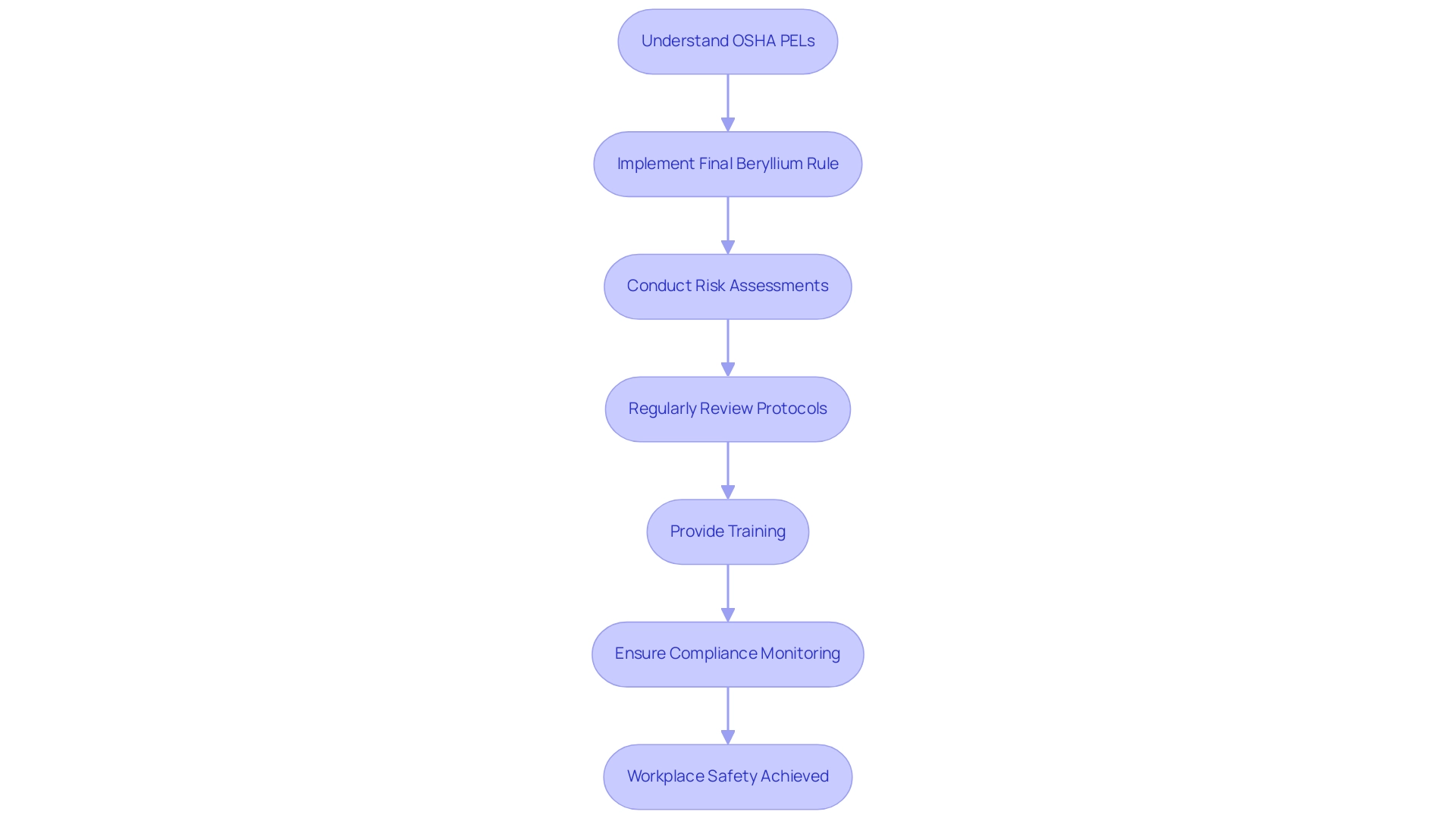
Regulatory Standards and Compliance for Beryllium Copper Handling
Organizations that manage copper alloys, especially through the use of non-sparking wrenches, carry a crucial obligation to adhere to strict regulatory standards to protect worker well-being. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has defined allowable contact limits (PELs) for the element, establishing the threshold at 0.2 micrograms per cubic meter of air over an eight-hour shift, with a short-term contact limit of 2.0 micrograms per cubic meter over a 15-minute duration. This final regulation, implemented in January 2017, safeguards approximately 62,000 workers, including those in construction and shipyards, from the beryllium copper health hazards linked to beryllium contact.
Significantly, the Final Beryllium Rule is anticipated to avert 94 fatalities and 50 severe health issues each year, indicating a major update to outdated safety limits that had been enforced for 67 years, which is crucial for addressing beryllium copper health hazards. Furthermore, the American Conference of Governmental and Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH) provides threshold limit values (TLVs) that serve as additional guidelines for managing exposure levels. Employers must ensure that their non-sparking wrenches, made from beryllium copper, are utilized in compliance with these standards to mitigate beryllium copper health hazards, as they are designed to minimize the risk of sparks in potentially hazardous environments.
It is essential for employers to regularly examine and revise their protocols in accordance with these standards to reduce legal risks and improve workplace security. Non-compliance not only exposes workers to increased health risks from beryllium copper health hazards but may also lead to significant legal repercussions. To ensure ongoing adherence, organizations should implement regular training and awareness programs that keep all team members informed about the latest regulations and their implications for workplace well-being.
As Treena V. Garrett, the Federal Register Liaison Officer at the U.S. Department of Energy, states, compliance is essential for protecting workers and ensuring a safe working environment. Moreover, the released document (2024-05735) highlights the dedication of regulatory agencies to maintain these quality standards, especially regarding the use of copper products such as non-sparking wrenches.
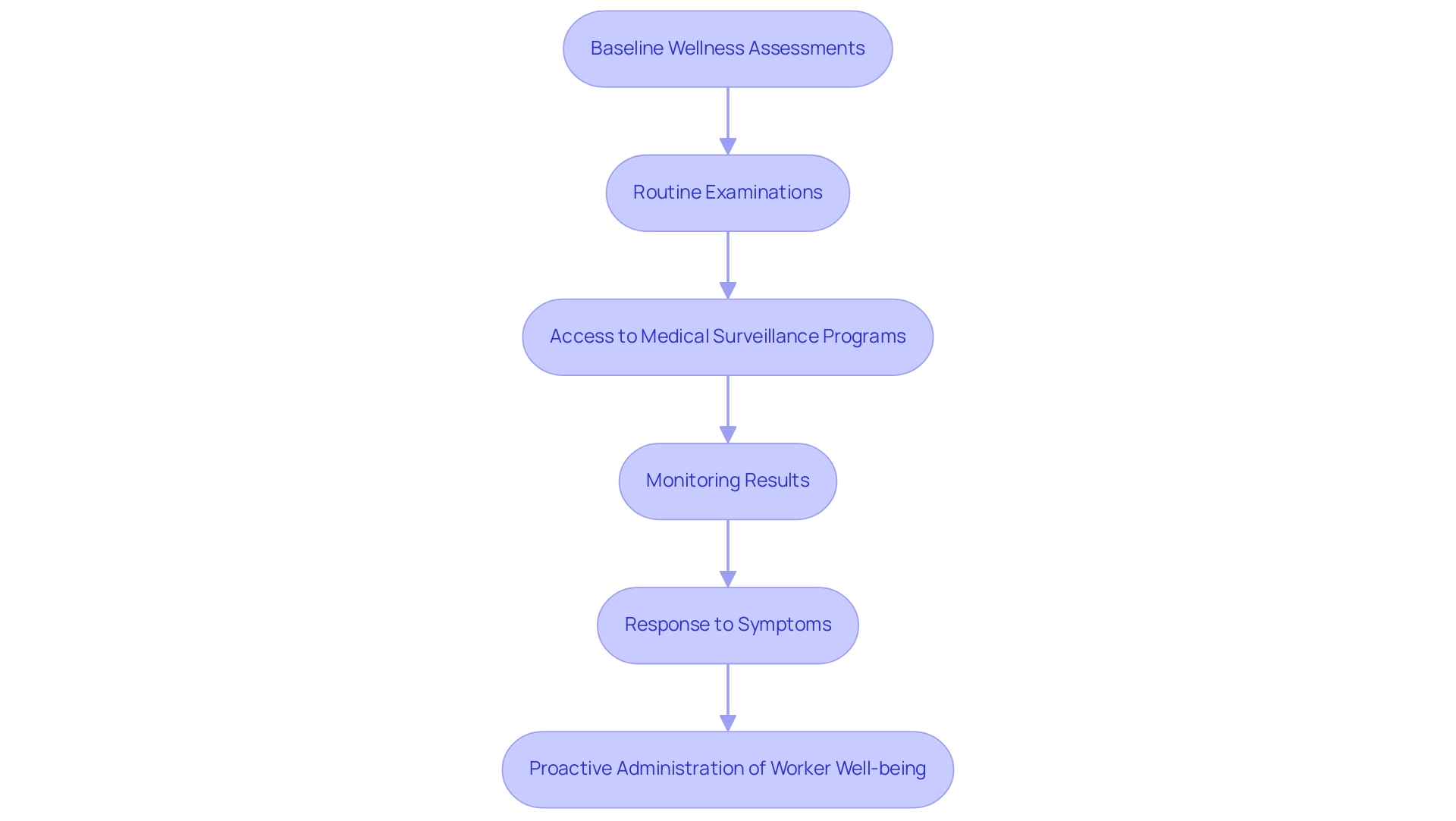
Health Monitoring and Medical Surveillance for Workers
Implementing a comprehensive wellness monitoring program for workers exposed to beryllium copper health hazards is vital to ensuring their safety and well-being, especially when using tools like the Beryllium Copper Non-Sparking Wrench. Such programs should commence with baseline wellness assessments followed by routine examinations aimed at evaluating respiratory function and other pertinent markers. Employers are responsible for providing access to medical surveillance programs that comply with OSHA guidelines, which outline specific protocols necessary for effective monitoring of well-being.
As noted by OSHA, the CBD literature commonly treats individuals as confirmed positive for sensitization through sequentially conducted Belts, underscoring the importance of rigorous monitoring. Monitoring results indicate that only 0.6% of 49,437 individuals exceeded the threshold of 0.2 µg/m, highlighting the importance of proactive measures. Any symptoms reported by workers must be taken seriously, warranting prompt medical evaluations to address potential risks to well-being.
By prioritizing wellness monitoring, organizations not only fulfill regulatory requirements but also mitigate beryllium copper health hazards, fostering a safer work environment and ultimately decreasing the chances of chronic disease (CBD) and sensitivity problems. The Beryllium Copper Non-Sparking Wrench is designed specifically for environments where flammable gases or vapors are present, as it minimizes the risk of sparks that could ignite these materials. The proactive administration of worker well-being can significantly reduce risks, particularly in sectors where contact is common, such as at primary locations like Y-12 and Hanford, where many instances of sensitization have been connected to specific job functions, including crafts and line operator roles.
Additionally, data from a case study at SNL shows an upper confidence limit for F at 44.4, with a percentage exceeding 0.2 µg/m at 23.7, further illustrating the critical need for effective health monitoring programs.
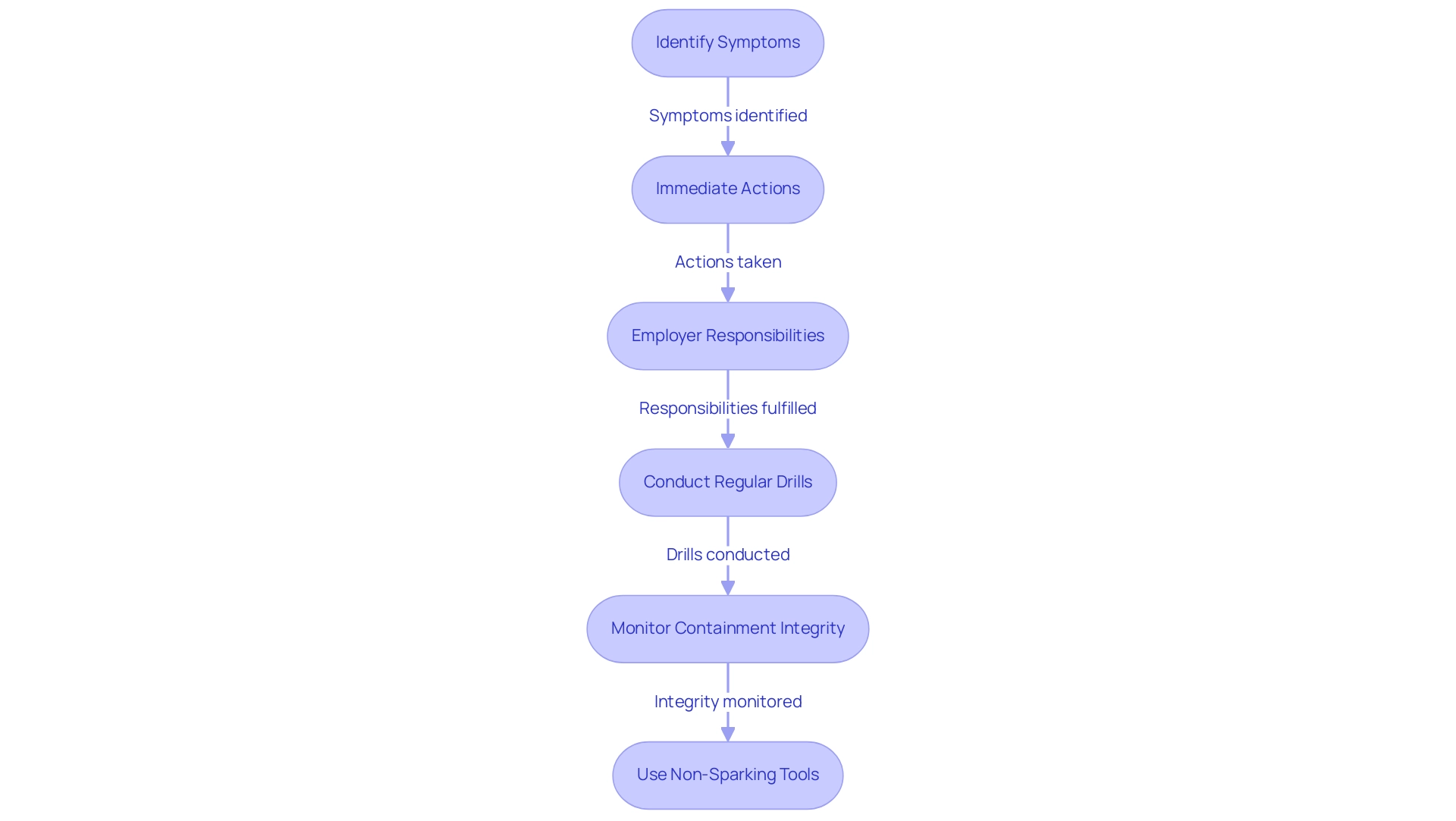
Emergency Response Procedures for Beryllium Copper Incidents
Creating a strong emergency response strategy is crucial for effectively managing situations involving beryllium copper health hazards. Workers must be trained to identify symptoms of contact, which can include respiratory issues and skin irritation, and to take immediate actions, such as relocating to an area with fresh air and seeking medical attention. Employers are responsible for ensuring that first aid kits are readily accessible and that personnel are proficient in their use, particularly in addressing any beryllium copper health hazards.
Regular drills are essential; they not only prepare employees for potential emergencies but also strengthen a culture of protection in the workplace. OSHA emphasizes the significance of training workers, stating that the beryllium copper health hazards include considerable risks of developing sensitization and chronic disease related to exposure, even at levels below the permissible exposure limit (PEL), which is set at 0.2 µg/m (8 h TWA) according to the 10 CFR 850 Rule. Utilizing non-sparking tools, particularly those crafted from copper alloy, is essential in these explosive settings because of their non-sparking, corrosion-resistant, and durable characteristics, ensuring protection and compliance.
Domadia’s non-sparking tools are created to meet the highest security standards, providing peace of mind for industries operating in high-risk areas. Additionally, it is imperative to monitor containment integrity and effectively manage the beryllium copper health hazards associated with contamination. Recent updates indicate that employers have the flexibility to choose between disposable and reusable personal protective equipment (PPE) based on hazard assessments, ensuring a customized approach to protection.
A case study on respiratory protection outlines that the total annualized cost for a full-face powered air-purifying respirator is approximately $1460.01 per employee, covering equipment, training, fit testing, and cleaning. This investment in training and equipment, along with the use of high-quality non-sparking tools, is vital for ensuring employee safety and compliance with regulations.
Conclusion
The importance of safeguarding workers in environments where beryllium copper is utilized cannot be overstated. This article has outlined the multifaceted health risks associated with exposure to this alloy, underscoring the potential for chronic beryllium disease and the immediate dangers posed by acute exposure. As industries increasingly integrate beryllium copper tools into their operations, a proactive approach to health monitoring and safety practices becomes essential.
Implementing rigorous safety protocols, including:
- The use of personal protective equipment
- Engineering controls
is critical in minimizing exposure risks. Regular training and compliance with established regulatory standards are not just best practices; they are necessary steps to protect the workforce and maintain operational integrity. The significant updates to permissible exposure limits set by OSHA highlight the ongoing commitment to worker safety and the need for organizations to adapt to these evolving standards.
Moreover, the establishment of comprehensive health monitoring programs and emergency response procedures plays a pivotal role in ensuring the well-being of employees. By fostering a culture of safety and vigilance, organizations can effectively mitigate the risks associated with beryllium copper exposure.
In conclusion, the stakes are high when it comes to handling beryllium copper. By prioritizing safety practices, adhering to compliance requirements, and investing in health monitoring, procurement managers can safeguard their workforce against the potential hazards of this valuable yet dangerous alloy. A commitment to these measures not only enhances worker safety but also fortifies the overall integrity and resilience of operations in high-risk environments.