Blogs

Complete Tutorial on Monel Welding: Techniques and Best Practices
Overview
The article provides a comprehensive tutorial on Monel welding, detailing techniques, best practices, challenges, and safety considerations essential for successful welding of this nickel-copper alloy. It emphasizes the importance of selecting appropriate welding methods, such as TIG and MIG, and addresses common issues like hot cracking and porosity, while also highlighting the necessity of safety measures and proper equipment to ensure quality and reliability in welding processes.
Introduction
In the realm of advanced materials, Monel alloys stand out for their remarkable properties and versatility, particularly in challenging environments. Comprised predominantly of nickel and copper, these alloys are engineered to resist corrosion and maintain structural integrity under extreme conditions, making them indispensable in industries such as marine engineering, chemical processing, and aerospace.
For procurement managers, understanding the composition, welding techniques, and unique characteristics of Monel is crucial for making informed decisions that enhance project outcomes.
This article delves into the essential aspects of Monel alloys, from their composition and welding best practices to the challenges faced during fabrication and the safety measures necessary for effective handling.
By exploring these facets, professionals can gain valuable insights that not only streamline procurement processes but also ensure the longevity and reliability of their applications.
Understanding Monel: Composition and Properties
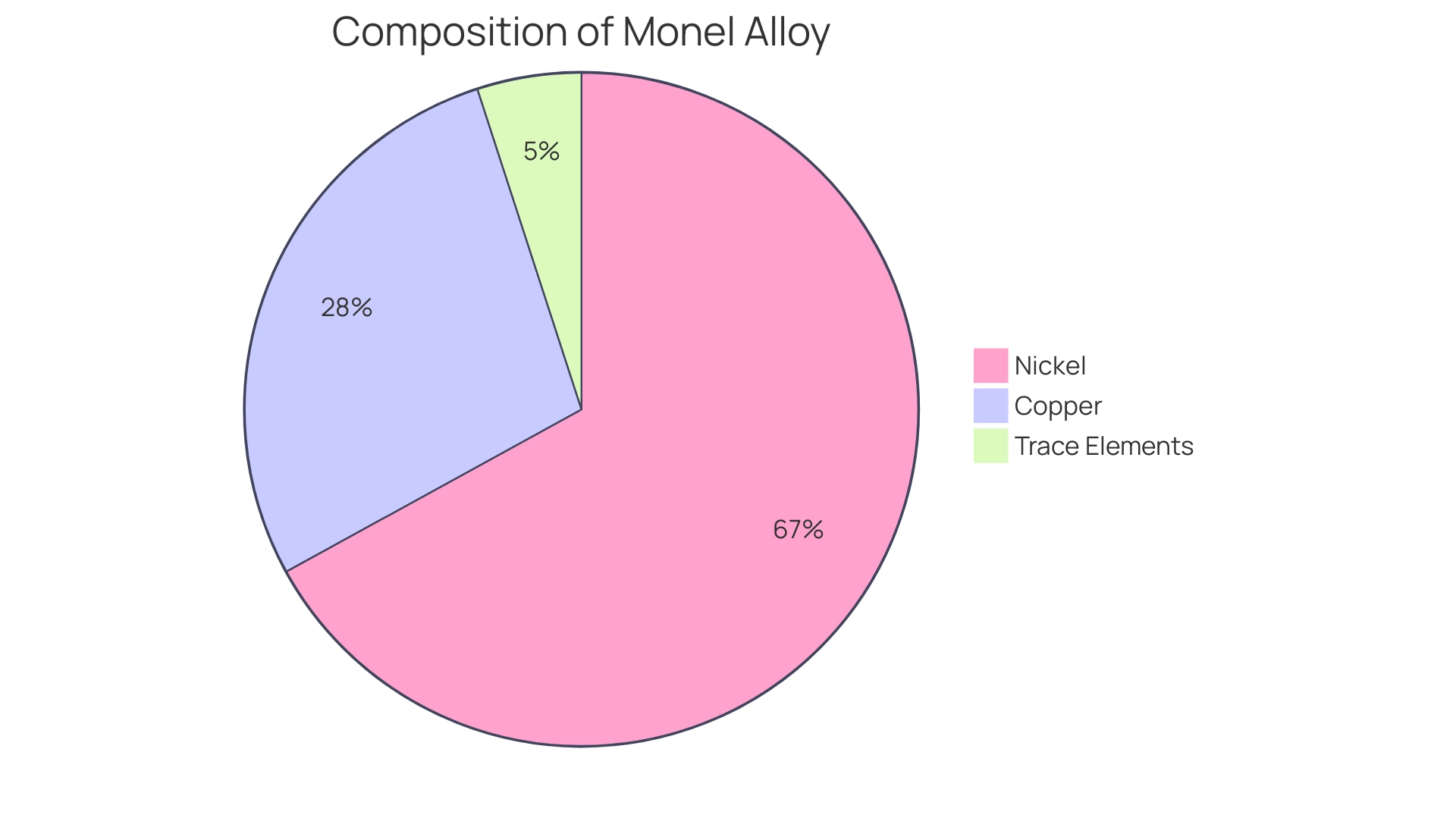
These materials, primarily made up of 67% nickel and 28% copper, along with trace elements of iron, manganese, carbon, and silicon, are renowned for their exceptional corrosion resistance across various environments. At Domadia, we provide a varied selection of copper nickel blends designed for various uses, including marine engineering and electronics. In marine settings, these metal mixtures demonstrate corrosion rates as low as 0.01 mm/year, rendering them highly efficient in preventing damage from seawater exposure.
The material’s high strength and toughness make it especially appropriate for challenging uses, particularly in the marine and chemical processing sectors. With a melting point ranging from 1300°C to 1350°C (2372°F to 2462°F), the thermal properties of this alloy are vital for determining optimal welding parameters and techniques. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for procurement managers aiming to ensure superior quality and performance in monel welding.
Furthermore, case studies on the functionality of these metallic materials demonstrate how their characteristics influence manufacturing processes and product design, ensuring robust solutions that enhance product longevity and contribute significantly to performance efficiency in applications where corrosion resistance is paramount. Explore our extensive product catalog to find the perfect copper nickel mixture solution for your project needs.
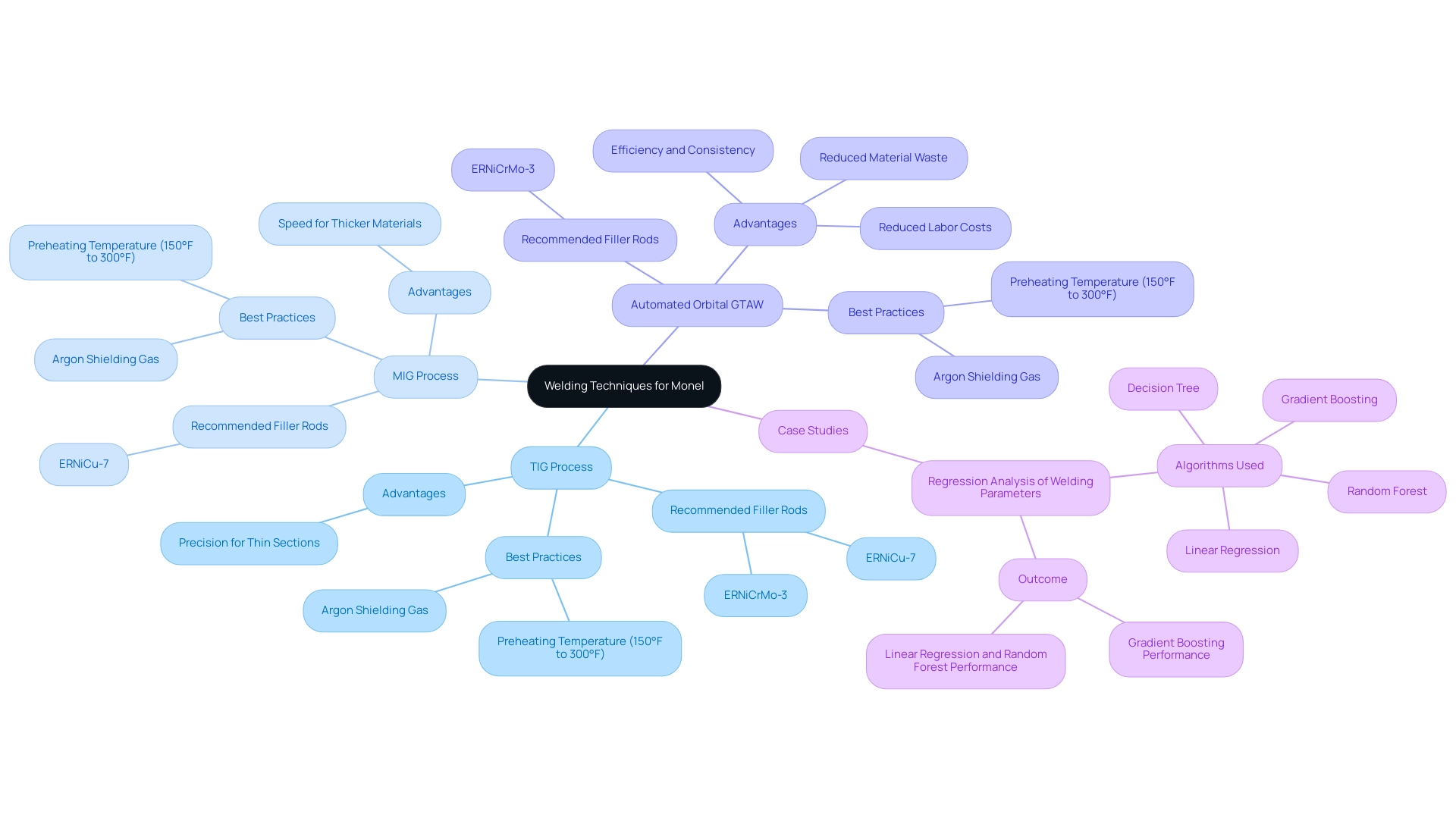
Welding Techniques for Monel: Best Practices and Methods
When evaluating the most efficient joining techniques for specific alloys, Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) processes and Metal Inert Gas (MIG) methods stand out as the top approaches. TIG processes are particularly favored for their precision, making them ideal for thin sections, while MIG techniques prove advantageous for thicker materials due to their faster deposition rates. Additionally, automated orbital GTAW processes are emphasized for their efficiency and consistency in joining materials, reducing labor costs and material waste.
To attain optimal results, it is essential to choose a filler rod that matches the alloy being utilized; for certain uses, ERNiCu-7 is a popular selection, although ERNiCrMo-3 has also been recognized for its effectiveness in dissimilar joints, as emphasized in recent studies. The performance of ERNiCrMo-3 in various applications highlights its significance in the context of nickel-copper alloy joining, contributing to the overall integrity of the welds. Setting the right parameters is essential for preventing defects such as cracking.
A preheating temperature range of 150°F to 300°F is recommended to ensure weld integrity, along with the maintenance of an argon shielding gas environment to mitigate contamination risks. By adhering to these best practices, welders can significantly enhance the integrity and performance of their Monel welding, aligning with industry standards and expectations. Furthermore, a case study titled ‘Regression Analysis of Welding Parameters‘ demonstrates the importance of selecting appropriate algorithms for accurate predictions in fabrication outcomes, offering analytical insights that reinforce the significance of technique and material selection.
As P. Mithilesh aptly states,
This paper investigates the weldability, metallurgical and mechanical properties of the dissimilar joints of Inconel 625 and AISI 304, underscoring the critical nature of selecting appropriate techniques and materials in the joining process.
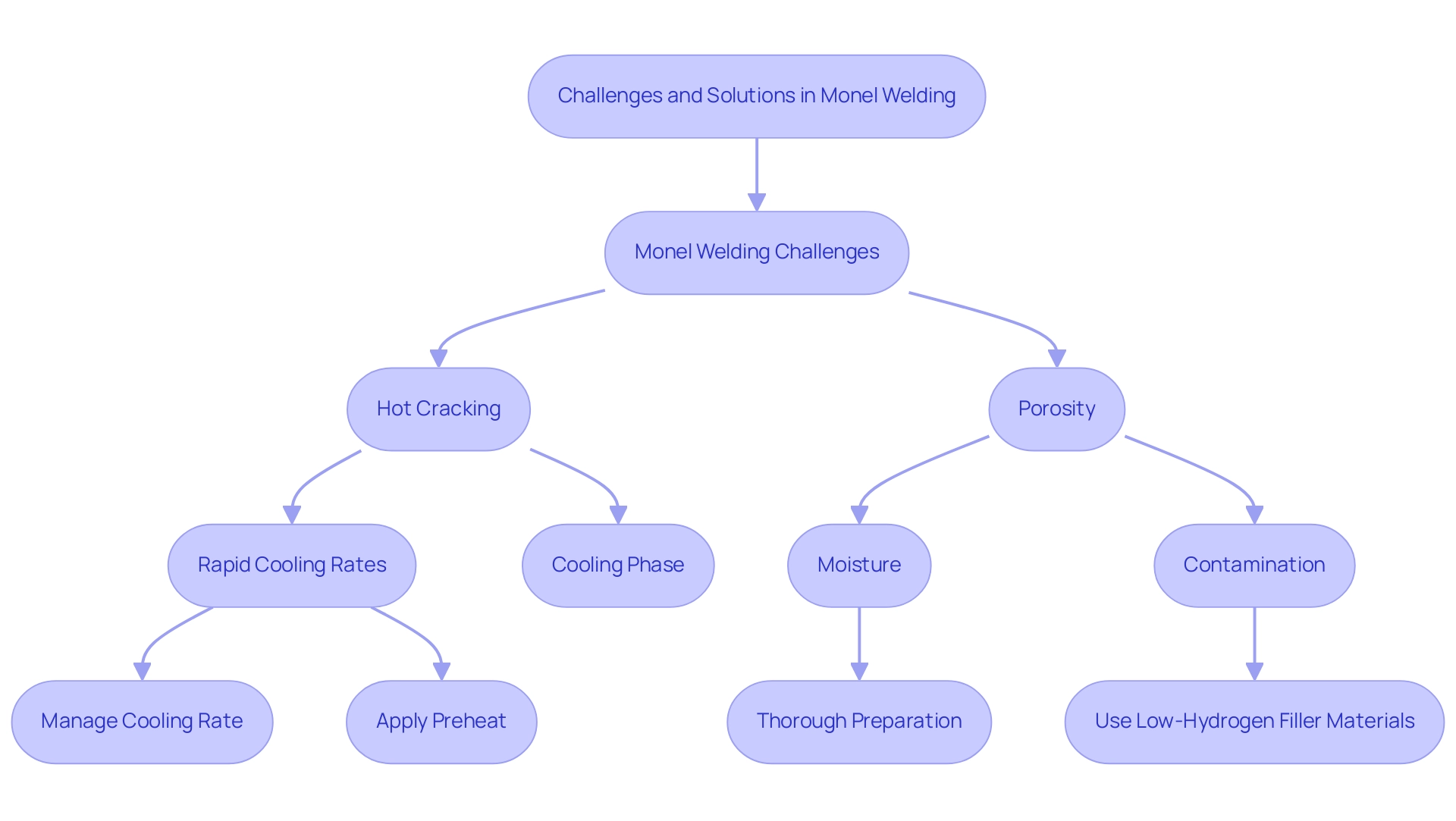
Challenges in Monel Welding: Common Issues and Solutions
Monel welding of this alloy presents several challenges, notably hot cracking and porosity. Hot cracking can occur during the cooling phase, often exacerbated by rapid cooling rates. Schwan and Sher (1969) observed that,
In a gradient field, the pearl chains protrude from the electrode surface,
emphasizing the complexities of joining behavior in variable conditions.
To effectively mitigate hot cracking in monel welding, it is essential to manage the cooling rate carefully and apply an appropriate preheat to the base metal. Additionally, porosity, which can arise from moisture or contamination, necessitates thorough preparation; ensuring that the base metal is clean and free from any contaminants is crucial for successful monel welding. Using low-hydrogen filler materials can further minimize this risk in monel welding.
Implementing a robust inspection process, including thorough visual assessments and non-destructive testing, is vital for early detection and resolution of potential issues. The capacitance per meter of a conductor, roughly 7.6 pF/m, may also contribute to comprehending the behavior of the alloy during the joining process. Furthermore, assessing structure-property relationships through optical microscopy and SEM/EDAX techniques can offer insights into the material’s reaction to joining processes.
Notably, cold working enhances resistance to deformation, leading to greater hardness, which is significant when evaluating the mechanical properties of the alloy in welded applications. These practices not only tackle immediate challenges in monel welding but also improve the overall reliability of the components.
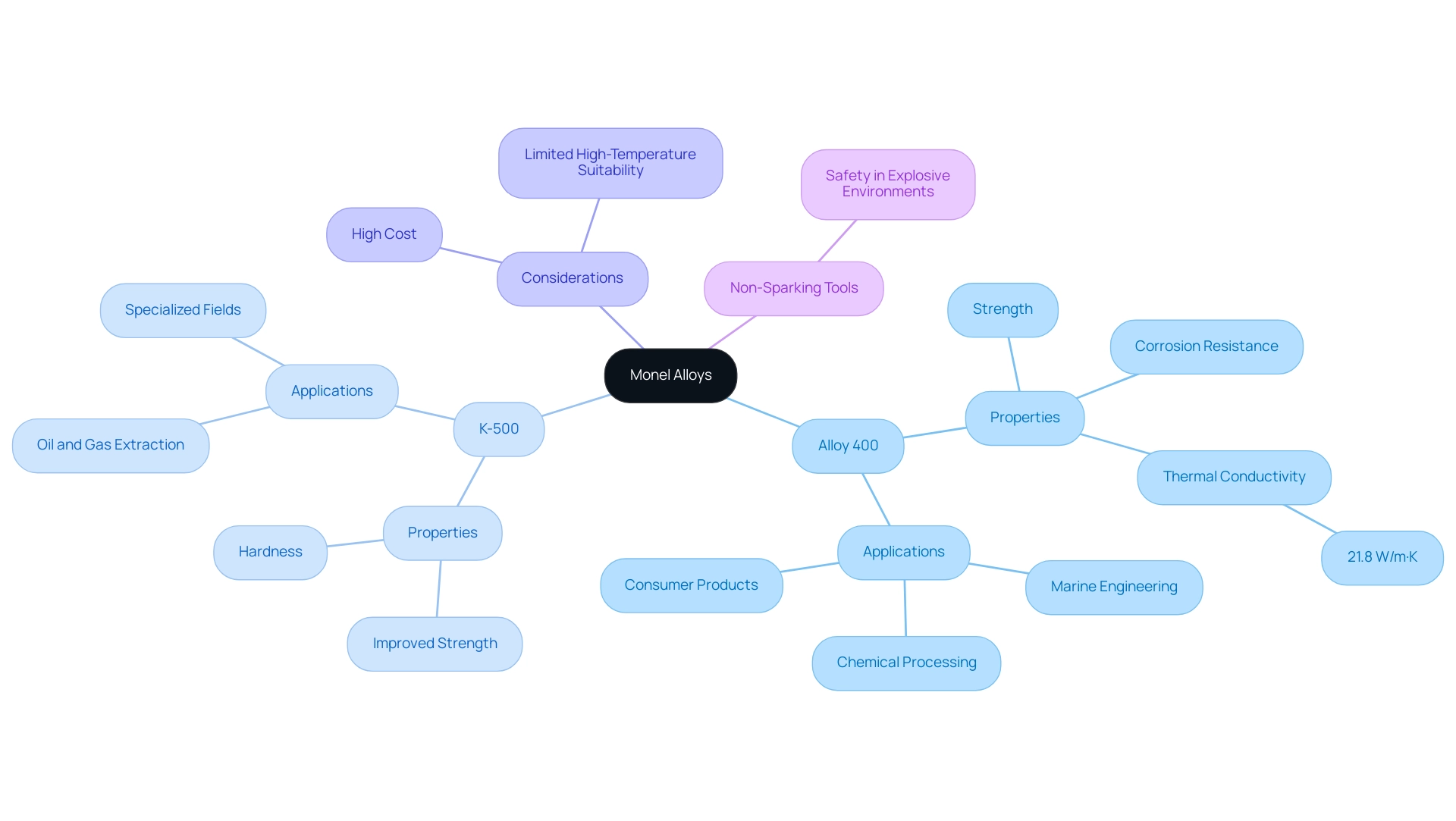
Types of Monel Alloys: Selecting the Right Material for Welding
These metal mixtures include various grades, with grade 400 acknowledged as the most common because of its outstanding resistance to corrosion and elevated strength. This alloy is particularly suitable for uses in marine environments and chemical processing, where durability is paramount. Alloy 400 has a thermal conductivity of 21.8 W/m·K, making it an efficient choice for various applications.
Conversely, K-500 is designed to offer improved strength and hardness, rendering it especially beneficial in specialized fields like oil and gas extraction. Material scientist Shane observes,
These metal mixtures display remarkably low corrosion rates, especially in seawater environments, with rates not surpassing 0.03mm/year.
However, it is important to consider some drawbacks of this material, including its high cost and limited suitability for high-temperature uses.
When choosing a specific metal for monel welding, it is essential to assess particular usage requirements, including exposure to corrosive environments and mechanical stress. For instance, monel welding is extensively applied in marine engineering, aerospace, and chemical processing, as highlighted in the case study titled ‘Real-World Applications of Monel.’ At Domadia, we offer an extensive product catalog featuring a diverse range of copper nickel mixtures, which complements these applications by providing exceptional properties suitable for various industries, including automotive and electrical sectors.
Our copper nickel mixtures are known for their corrosion resistance, high conductivity, and durability, making them ideal for demanding environments. Moreover, for environments with explosive potential, Non-Sparking Tools are essential alternatives, ensuring safety without compromising performance. This strategic approach ensures optimal performance and longevity, allowing procurement managers to make informed decisions tailored to their operational needs.
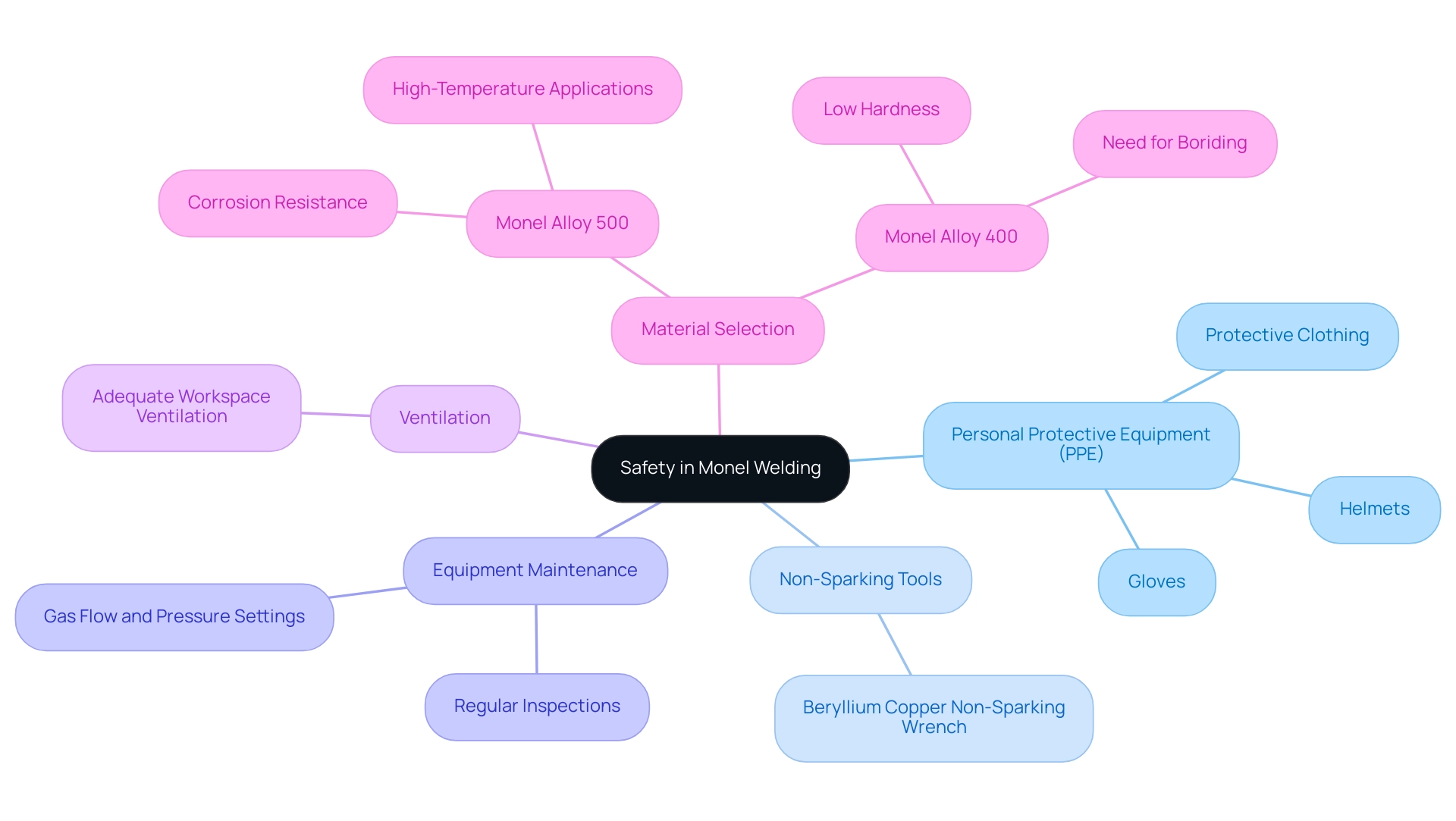
Safety and Equipment Considerations in Monel Welding
Monel welding necessitates a stringent approach to safety, starting with the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). Essential items such as fabrication helmets, gloves, and protective clothing are vital for shielding against sparks and harmful UV radiation. In explosive potential environments, using Non-Sparking Tools, such as the Beryllium Copper Non-Sparking Wrench, is crucial to prevent ignition from tool contact.
The Beryllium Copper Non-Sparking Wrench is designed to withstand high-impact applications while minimizing the risk of sparks, making it an ideal choice for hazardous environments. It is imperative to use well-maintained equipment for joining materials, verifying that gas flow rates and pressures are accurately set to prevent operational hazards. Furthermore, ensuring adequate ventilation in the workspace is critical to mitigate the inhalation of toxic fumes, a concern that should not be overlooked.
Regular inspections and servicing of joining equipment contribute significantly to optimal performance and safety during operations. As noted by Rohit Kumar,
The microstructure and macrostructure changes alongside the lingering worry of the welded materials exceptionally influence the quality and dependability of the welded joint.
This highlights the necessity of high safety standards, which ultimately enhance both personal safety and the quality of outputs.
Furthermore, overlooking the use of Non-Sparking Tools can result in serious accidents, including explosions, highlighting their essential role in welding practices. The metal 500 maintains outstanding corrosion resistance even after 6 days of immersion in saturated hydrogen sulfide solutions, making it a dependable option for high-precision devices and cryogenic uses, as shown in case studies. In contrast, Monel alloy 400’s low hardness renders it inappropriate for wear uses without additional treatments like boriding, emphasizing the importance of careful material selection in Monel welding procurement.
The integration of Non-Sparking Tools further reinforces the commitment to safety in these critical applications.
Conclusion
Monel alloys are vital in industries requiring superior corrosion resistance and structural integrity, especially in marine engineering and chemical processing. With a primary composition of nickel and copper, grades like Monel 400 and Monel K-500 provide the durability necessary for various applications. A solid understanding of these materials enables procurement managers to make informed decisions that enhance both performance and longevity.
Effective welding techniques, such as TIG and MIG, are essential for ensuring strong welds in Monel alloys. Recognizing challenges like hot cracking and porosity, and employing appropriate mitigation strategies, is crucial for maintaining industry standards during the welding process.
Safety considerations are also paramount when working with Monel alloys. Utilizing personal protective equipment and Non-Sparking Tools is essential to prevent accidents in potentially hazardous environments. Additionally, regular maintenance of welding equipment and ensuring adequate ventilation contribute to safe operational practices.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of Monel alloys, effective welding techniques, and stringent safety measures empower procurement managers to make strategic decisions. This approach not only streamlines procurement processes but also enhances the reliability and performance of projects in demanding environments, underscoring the significance of Monel alloys in advanced material applications.