Blogs
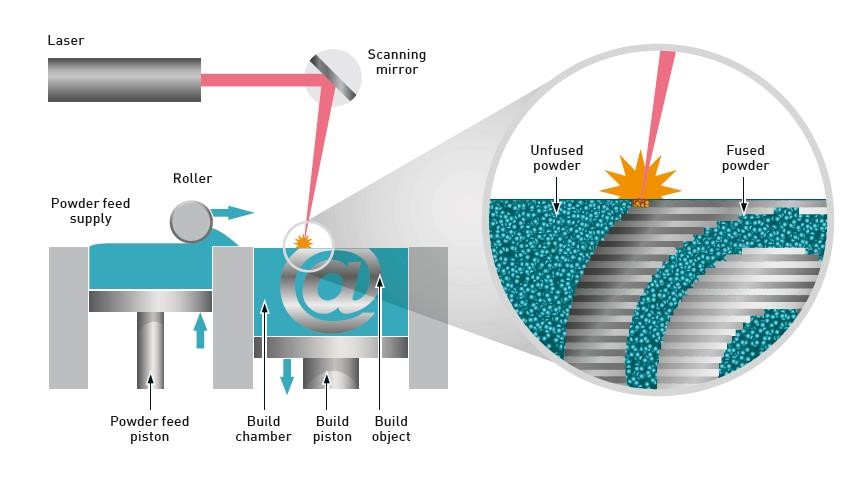
Powder Shape Particle Size in Additive Manufacturing: Why Microstructure Starts Before the Laser Fires
Powder Shape Particle Size Is the First Process Parameter—Not the Last
Powder Shape Particle Size is often treated as a procurement specification.
In reality, Powder Shape Particle Size is the first and most decisive process variable in additive manufacturing.
Before a laser scans.
Before an electron beam melts.
Before a single voxel solidifies.
The Powder Shape Particle Size and its distribution already determine:
• Powder bed density
• Melt pool stability
• Porosity formation
• Microstructural uniformity
• Fatigue life and repeatability
At DOMADIA™, Powder Shape Particle Size engineering is approached as process design, not raw material supply.
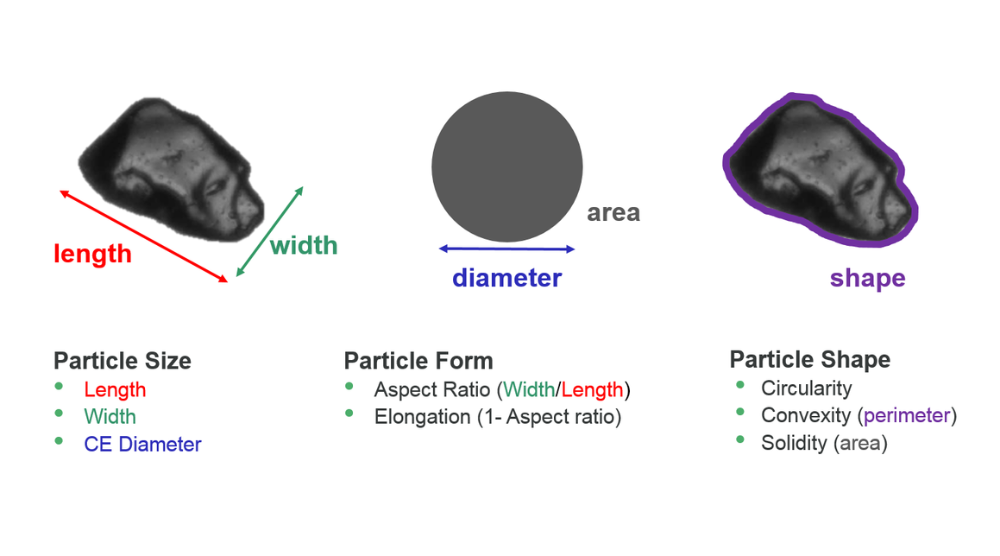
Particle Shape: Why Sphericity Is a Functional Requirement
Spherical Powders Are Not About Appearance
Highly spherical particles—typically produced via gas atomization or plasma spheroidization—are preferred not for aesthetics, but for predictable physics.
Key Technical Impacts of Particle Shape
| Property | Irregular Particles | Spherical Particles |
| Flowability | High inter-particle friction | Low friction, stable flow |
| Packing efficiency | Voids & bridging | Dense, repeatable packing |
| Recoater interaction | Blade drag, streaks | Smooth layer deposition |
| Laser absorptivity | Inconsistent | Uniform energy coupling |
Irregular or satellite-rich powders introduce localized density gradients in the powder bed. These gradients directly translate into:
- Melt pool instability
- Balling defects
- Lack-of-fusion porosity
Once porosity is formed at this stage, no post-processing can fully reverse it.
Particle Size Distribution (PSD): More Than Just Microns
PSD Is a Statistical Control System
Advanced AM systems do not work with a single particle size—they operate within a carefully engineered distribution window.
Typical laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) ranges:
- D10: ~15–20 µm
- D50: ~30–40 µm
- D90: ~45–60 µm
But the shape of the distribution curve matters more than the average.
Narrow PSD: Precision With Risk
Advantages
- Predictable melting behavior
- Consistent energy absorption
- Cleaner microstructure control
Risks
- Poor interstitial filling
- Reduced powder bed density
- Increased sensitivity to recoater defects
Narrow PSD powders demand tight machine calibration and controlled atmospheres.
Wide PSD: Density With Complexity
Advantages
- Finer particles fill voids between coarse particles
- Higher green density
- Improved layer cohesion
Risks
- Fine particles oxidize faster
- Increased spatter generation
- Powder aging and segregation
DOMADIA™ often recommends engineered bimodal PSDs for high-density structural components—when oxidation control is robust.
Powder Flowability: The Hidden Process Bottleneck
Flowability governs:
- Layer thickness uniformity
- Recoater blade stress
- Build interruption frequency
Technically, flowability is influenced by:
- Particle shape factor (aspect ratio)
- Surface roughness
- Van der Waals forces (dominant <20 µm)
- Moisture adsorption
Below ~20 µm, cohesive forces dominate gravity, causing powder clumping—even if particles are spherical.
This is why ultra-fine powders do not automatically improve resolution in AM—they often degrade process stability.
Packing Density → Melt Pool Physics → Microstructure
Powder shape particle size directly defines powder bed thermal conductivity.
- Low packing density → trapped gas → unstable melt pool
- High packing density → predictable thermal gradients
These gradients control:
- Grain morphology (columnar vs equiaxed)
- Solidification rate
- Residual stress accumulation
In fatigue-critical components, even 2–3% variation in local density can reduce fatigue life by 30–40%.
This is why DOMADIA™ treats powder specification as a fatigue-life decision, not a purchasing one.
Defect Formation Mechanisms Linked to Powder Design
Powder-Driven Defects Include
- Lack-of-fusion porosity
- Gas entrapment
- Keyholing instability
- Inconsistent layer bonding
Many of these are misattributed to laser parameters, when the root cause lies in powder morphology inconsistency.
Changing scan speed cannot compensate for:
- Satellite particles
- Broad uncontrolled PSD
- Oxidized fine fractions
Powder Reuse, Aging, and Lifecycle Control
Powder degradation during reuse includes:
- Increase in fine particles (spatter breakup)
- Oxide layer thickening
- Loss of sphericity
This shifts PSD and flow behavior silently over time.
DOMADIA™ supports powder lifecycle management strategies, including:
- Sieving protocols
- Oxygen pickup monitoring
- PSD drift analysis
Long-term AM success depends on powder behavior consistency across builds, not just initial certification.
Why Advanced AM Teams Engineer Powders—They Don’t Just Buy Them
In production AM:
- Powder shape particle size defines yield
- Yield defines cost
- Cost defines scalability
The industry is moving from:
“What alloy are you printing?”
to
“What powder behavior are you controlling?”
DOMADIA™ powders are supplied with process-oriented intent—supporting repeatability, qualification, and fatigue-critical performance.
Final Takeaway: Powder Shape Particle Size Is Structural Design
Powder shape particle size is not a minor variable—it is structural engineering at the microscale.
It governs:
- Flow
- Density
- Thermal behavior
- Defect formation
- Lifecycle reliability
In additive manufacturing, the part’s performance begins before melting starts.
Choose powders engineered for consistency.
Choose distributions designed for process stability.
Choose DOMADIA™—where powder is treated as a performance system, not a commodity.
Stop troubleshooting porosity and flow issues after the build.
Choose DOMADIA™ metal powders engineered for controlled particle size, optimized morphology, and AM-ready consistency. Request specifications today.
Contact us today to get custom sizes and specifications for your project.
Talk to: Er.Pankaj Domadia | Kairav Domadia | Aadil Domadia | Pragati Sanap | Pooja N N
#PowderShapeParticleSize, #AdditiveManufacturing, #MetalPowders, #AMMicrostructure #ParticleSizeDistribution, #LaserPowderBedFusion
Directly whatsapp us for an Enquiry: https://wa.link/kairav



