Blogs

Crucible Alloys Performance Based on UNS N07718 Principles for High-Temperature Metallurgy
Crucible Alloys Performance Starts Where Other Metals Fail
Crucible alloys performance is rarely discussed—until something melts, cracks, or catastrophically fails.
Inside furnaces operating above 1,200°C, within induction systems holding molten superalloys, and in laboratories replicating aerospace-grade thermal cycles, conventional steels quietly exit the conversation. At those temperatures, strength, stability, and chemical predictability are no longer optional—they are survival traits.
What remains are crucible alloys—materials engineered not merely to withstand extreme heat, but to remain chemically inert, mechanically stable, and dimensionally predictable across repeated thermal cycles.
At DOMADIA™, crucible alloys performance is not treated as a product feature. It is treated as a system-critical requirement for high-temperature metallurgy.
What Are Crucible Alloys? (And Why They Still Matter)
Crucible alloys are specialized high-temperature metallic materials designed for direct and repeated contact with molten metals, aggressive slags, and reactive atmospheres.
Unlike structural alloys that primarily carry load, crucible alloys must excel simultaneously in:
- Thermal shock resistance
- Chemical inertness to molten metals
- Oxidation and carburization resistance
- Microstructural stability at extreme temperatures
Despite advancements in ceramics and composite materials, crucible alloys performance remains irreplaceable in many industrial and research environments where repeatability, purity, and reliability matter more than theoretical temperature limits.
Chemical Composition: Built for Heat, Not Convenience
Crucible alloys are typically based on nickel-, cobalt-, or iron-nickel systems, often aligned with UNS N07718-class metallurgy principles for high-temperature performance.
Typical Alloying Elements & Their Roles
| Element | Function in Crucible Alloys Performance |
| Nickel (Ni) | High-temperature strength and oxidation resistance |
| Chromium (Cr) | Protective oxide layer formation |
| Iron (Fe) | Structural stability and economic balance |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | Enhanced creep resistance |
| Carbon (C) | Grain boundary strength control |
| Silicon (Si) | Improved oxidation resistance |
DOMADIA™ crucible alloys are composition-controlled to minimize contamination of molten metals—an often-overlooked but critical factor in precision metallurgy and alloy development.
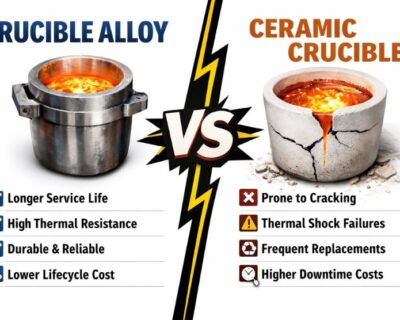
Why Crucible Alloys Performance Beats Alternatives
A common misconception persists: “Ceramics are always better at high temperatures.”
The reality inside industrial furnaces is different.
Ceramics can fracture under thermal shock, shed particles into melts, and fail unpredictably during rapid heating or cooling cycles. Crucible alloys performance offers advantages ceramics simply cannot:
- Ductility under heat
- Repairability and extended service life
- Reduced scrap contamination
- Predictable thermal expansion behavior
This makes crucible alloys indispensable in repeat-cycle industrial operations, where downtime and inconsistency carry real costs.
Key Properties That Define Crucible Alloys Performance
| Property | Industrial Importance |
| Melting Stability | Prevents deformation during long holds |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Survives rapid heating and cooling |
| Oxidation Resistance | Extends service life in air furnaces |
| Chemical Inertness | Protects melt purity |
| Creep Resistance | Maintains geometry over time |
At DOMADIA™, crucible alloys performance is engineered to remain consistent not just at peak temperature, but across thousands of thermal cycles.
Technical Specifications (Indicative Range)
| Parameter | Typical Range |
| Maximum Service Temperature | 1,300–1,400°C |
| Density | 8.1 – 8.5 g/cm³ |
| Thermal Conductivity | Moderate, controlled heat flow |
| Oxidation Resistance | Excellent |
| Operational Lifecycle | Multi-year (application dependent) |
Actual specifications vary based on alloy system, furnace atmosphere, and operating discipline.
Applications Where Crucible Alloys Still Rule
Crucible alloys performance defines success across demanding sectors:

Metallurgical & Research Furnaces
- Alloy development laboratories
- Vacuum melting systems
- Controlled-atmosphere experiments
Induction & Resistance Melting
- Nickel-based superalloys
- Specialty steels
- Copper and copper-based alloys
Industrial Heat Treatment
- Brazing furnaces
- Sintering operations
- Powder metallurgy melting stages
Aerospace & Defense Metallurgy
- Prototype alloy melting
- High-purity experimental heats
Shapes Available from DOMADIA™
DOMADIA™ supplies crucible alloys performance-optimized in:
- Cylindrical crucibles
- Rectangular melting boxes
- Custom-machined crucible liners
- Rings, sleeves, and furnace inserts
- Precision laboratory crucibles
Custom geometries are supported to match unique furnace designs and thermal profiles.
Standards, Validation & Quality Control
While crucible alloys may not always fall under a single commodity standard, DOMADIA™ benchmarks against:
- UNS-aligned chemistry controls (including UNS N07718 principles)
- ASTM high-temperature alloy practices
- Internal metallurgical validation protocols
- Thermal cycling performance qualification
Traceability, repeatability, and consistency are treated as non-negotiable.
Why Crucible Alloys Performance (UNS N07718) Matters Today
Crucible alloys performance aligned with UNS N07718 metallurgy continues to gain relevance as industries push toward higher temperatures, cleaner melts, and longer furnace cycles. As aerospace, energy, and advanced manufacturing demand tighter tolerances and reduced contamination, high-temperature crucible alloys remain essential for process stability and operational efficiency.
Search interest around crucible alloys performance, UNS N07718 high-temperature alloys, and nickel-based crucible materials reflects a growing shift toward lifecycle-driven material selection, not just upfront cost comparison.
Environmental Impact: An Overlooked Advantage
Crucible alloys performance directly supports sustainability:
- Longer lifecycle means fewer replacements
- Reduced scrap and recycling frequency
- Lower contamination-driven re-melting
- Reduced furnace downtime and energy waste
At DOMADIA™, this is not marketing—it is responsible metallurgy in practice.
The Real Cost Equation Engineers Often Miss
Yes, crucible alloys cost more upfront.
But real expenses come from:
- Furnace shutdowns
- Melt contamination
- Frequent crucible replacement
- Scrap losses
Crucible alloys performance minimizes all four—quietly, consistently, and over time.
Crucible Alloys Performance: The Quiet Backbone of High-Temperature Metallurgy
Crucible alloys performance does not trend on social media.
It does not announce itself during procurement meetings.
But when temperatures rise and failure is not an option—it is the only material class still standing.
At DOMADIA™, crucible alloys are engineered not for catalog appeal, but for metallurgical reality.
Upgrade to Crucible Alloys That Perform When It Matters Most
Connect with DOMADIA™ to specify crucible alloys engineered for long life, thermal stability, and real-world metallurgical reliability.
Click Contact Us to speak with DOMADIA™ experts and get crucible alloy solutions engineered for your exact high-temperature application.
Talk to: Er.Pankaj Domadia | Kairav Domadia | Aadil Domadia | Pragati Sanap | Pooja N N
#MuMetalAudioShielding #UNSN14080 #AudioEngineering #EMIShielding #DOMADIA
Directly whatsapp us for an Enquiry: https://wa.link/kairav