Blogs

How to Optimize Cutting Speed for Inconel: A Step-by-Step Guide
Overview:
The article focuses on optimizing cutting speed for Inconel by addressing key machining parameters, tool selection, cooling methods, and advanced techniques. It highlights that carefully balancing feed rate, depth of cut, and machining velocity, along with using appropriate cutting tools and effective cooling strategies, can significantly enhance machining efficiency and tool longevity, thereby improving overall production outcomes.
Introduction
Machining Inconel presents a unique set of challenges that require a strategic approach to overcome. Renowned for its exceptional strength and toughness, this alloy can lead to increased tool wear and complicate the quest for optimal surface finishes. As procurement managers seek to implement effective machining solutions, understanding the intricacies of:
- Cutting parameters
- Tool selection
- Cooling methods
becomes paramount. Recent advancements in non-conventional machining processes and innovative techniques offer promising pathways to enhance efficiency and reduce costs. This article delves into the critical aspects of machining Inconel, equipping professionals with the insights needed to navigate its complexities and achieve superior production outcomes.
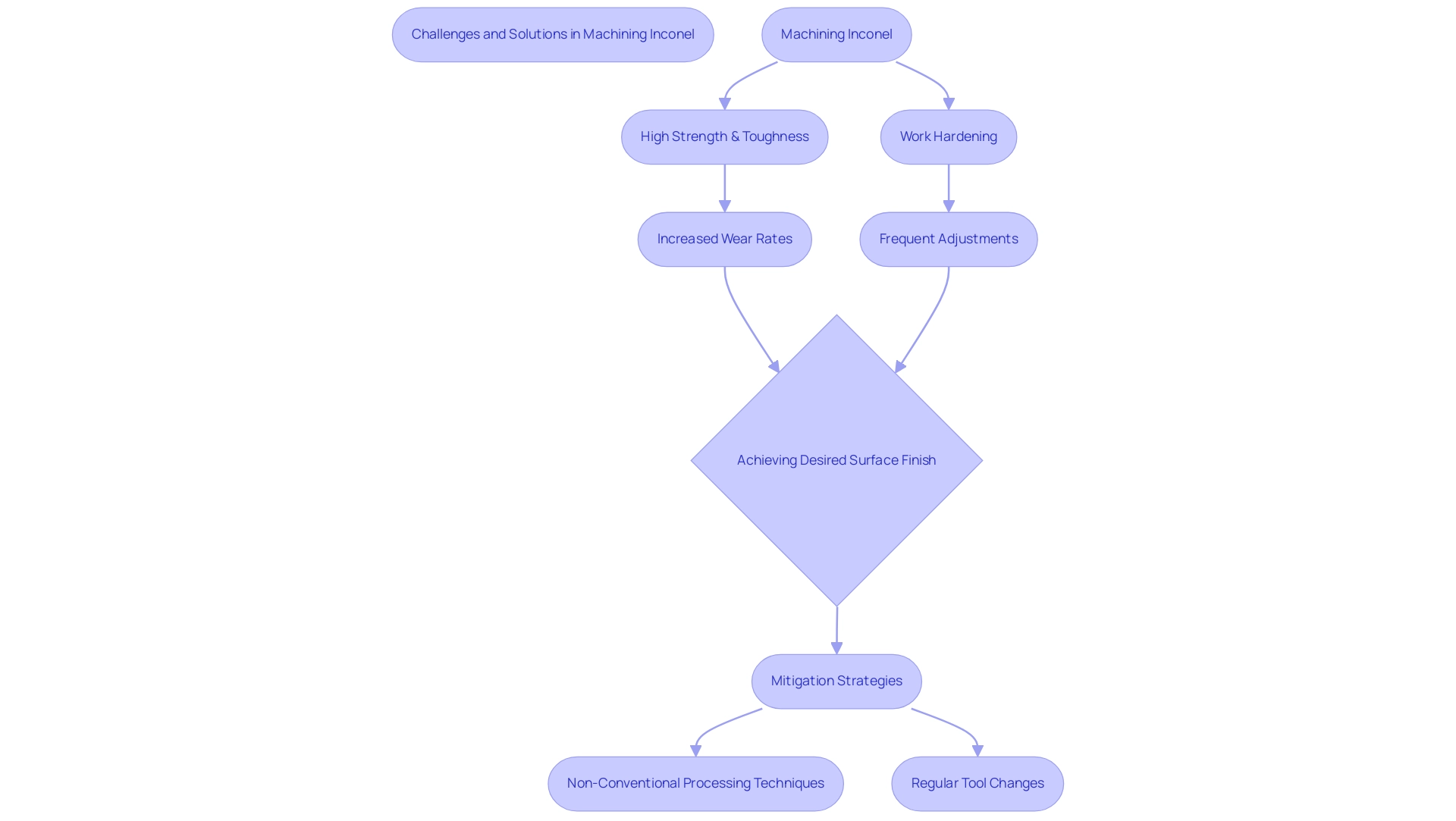
Understanding the Challenges of Machining Inconel
Machining this alloy is inherently challenging due to its exceptional properties, including high strength and toughness, which significantly contribute to increased wear rates of cutting instruments. The total sequential sum of squares for the equipment wear parameter has been quantified at 6765.8, highlighting the severe impact on longevity. Furthermore, Inconel’s tendency to work-harden during processing necessitates frequent adjustments to parameters and regular tool changes, complicating the fabrication process.
As a result, achieving the desired surface finish often becomes a daunting task. Tackling these challenges is vital for optimizing inconel cutting speed and improving overall efficiency. Recent advancements in non-conventional processing techniques, as discussed in the review titled ‘A Review of INCONEL® Alloy’s Non-conventional Processing Techniques,’ reveal promising strategies to mitigate these issues, reduce manufacturing costs, and improve production outcomes.
The validation of confirmatory experiments emphasizes the accuracy of these manufacturing processes and their positive impact on output responses. Companies like 3ERP exemplify effective manufacturing solutions, showcasing a comprehensive range of services and a dedication to quality and efficiency. Comprehending these complexities is crucial for procurement managers aiming to implement effective manufacturing solutions.
Key Machining Parameters for Optimizing Cutting Speed
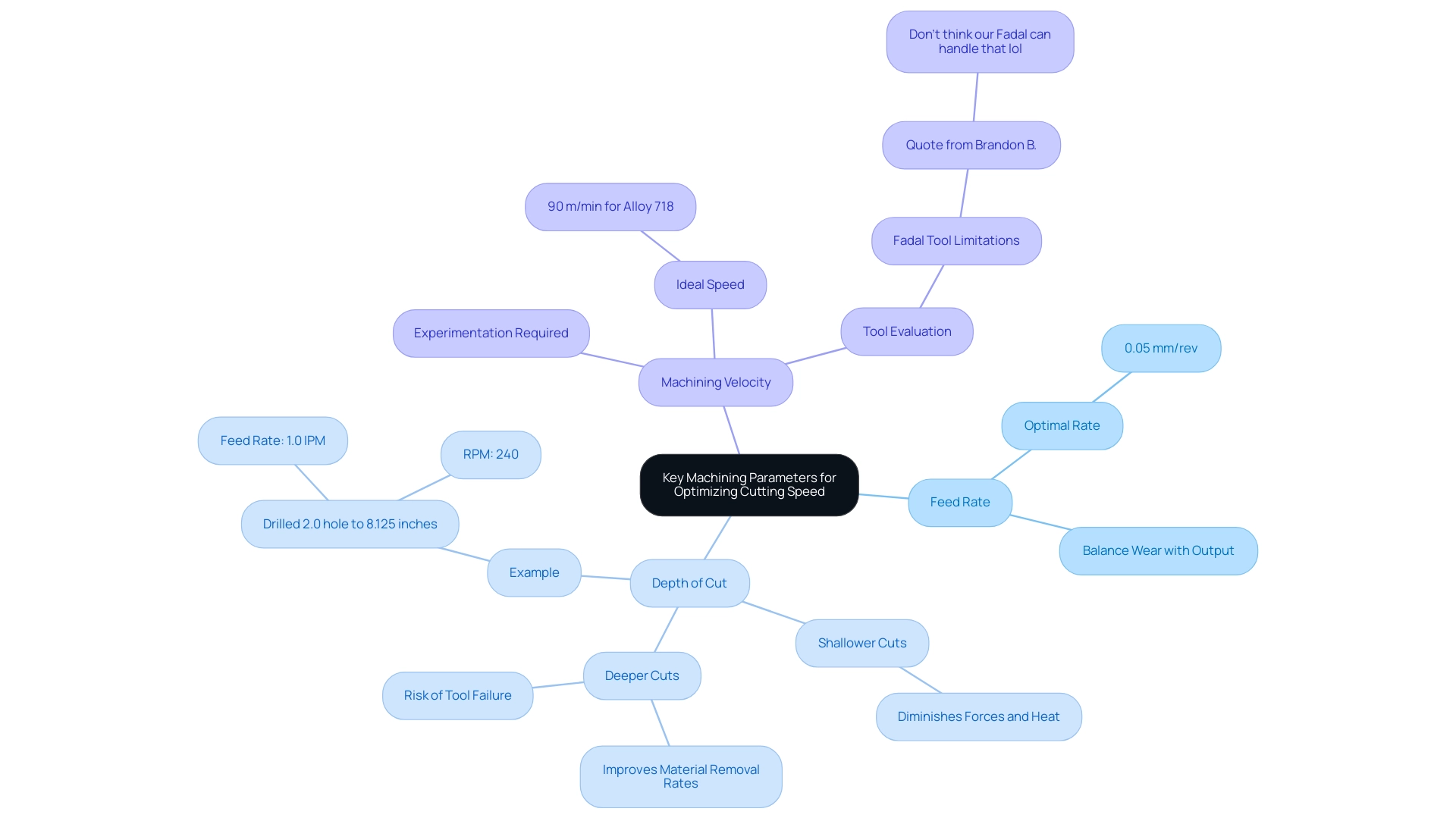
To effectively optimize cutting speed for Inconel alloys, it is crucial to carefully consider several key machining parameters:
Feed Rate: While increasing the feed rate can significantly enhance productivity, it also poses a risk of accelerated equipment wear. A strategic balance must be established to ensure equipment longevity while maximizing output. The latest findings indicate that the inconel cutting speed for machining Inconel 718 is approximately 0.05 mm/rev, which effectively mitigates wear without sacrificing efficiency.
Depth of Cut: Implementing a shallower depth of incision can diminish forces and heat generation, thus extending equipment life. However, deeper cuts can improve material removal rates; they must be managed carefully to avoid tool failure. For instance, a recent model demonstrated that drilling a 2.0 hole to a depth of 8.125 inches with a feed rate of 1.0 IPM at 240 RPM can yield favorable outcomes, aligning well with stress results from advanced simulations.
Machining Velocity: The ideal machining velocity for certain alloys varies based on specific alloy grade and tools used. For instance, studies have demonstrated that an inconel cutting speed of 90 m/min is effective for alloy 718. Experimentation and fine-tuning are essential to identify the ideal settings that enhance efficiency without compromising part quality. As mentioned by Brandon B. from EMC Learning Group, “Don’t think our Fadal can handle that lol,” emphasizing the need to carefully evaluate the abilities of manufacturing tools like the Fadal to ensure they meet the requirements of processing nickel-chromium alloys.
Real-world examples support these best practices; a machinist successfully utilized a 5/16″ Hanita Varimill with a TiAIN coating at 1900 RPM and 20 IPM, resulting in a significant cycle time reduction from 13 minutes to just 6 minutes through the strategic use of ceramic inserts. Furthermore, ideal conditions for reducing processing responses during milling of alloy 718 include CO snow, which can further improve performance. This demonstrates the tangible advantages of optimizing inconel cutting speed and feed rates while working with Inconel.
Selecting the Right Cutting Tools for Inconel Machining
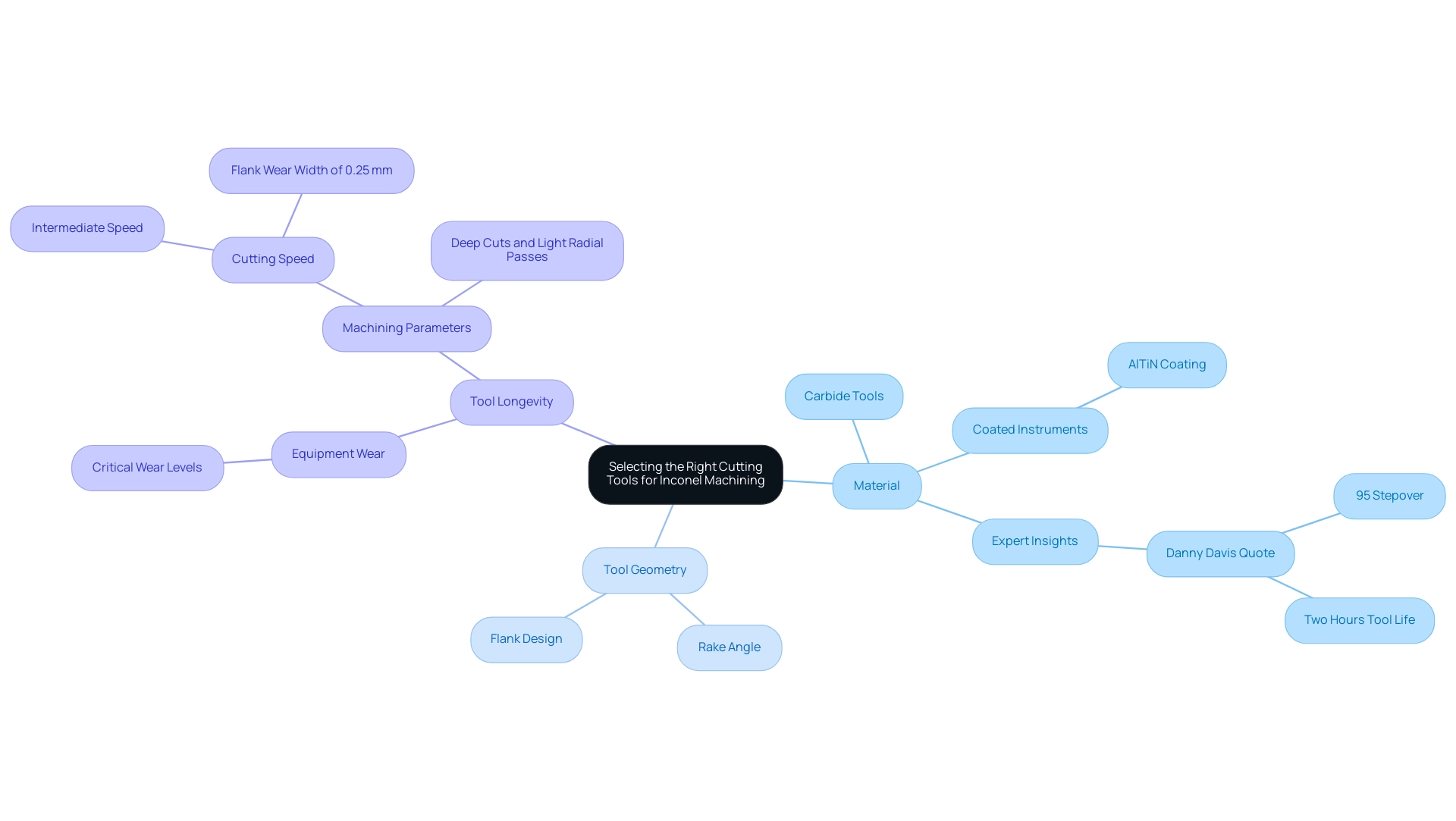
Selecting the right cutting tools for machining Inconel entails careful consideration of several key factors:
Material: Carbide implements are generally preferred for machining Inconel because of their excellent hardness and wear resistance, with HR hardness assessments performed at different temperatures ranging from 300 °C to 700 °C highlighting their performance capabilities. Recent trends indicate that utilizing coated instruments, such as those with aluminum titanium nitride (AlTiN), significantly enhances performance by minimizing friction and heat generation during the machining process. Expert insights suggest that employing these coatings can extend equipment life substantially, with Danny Davis, Senior Staff Engineer at Kennametal, noting that during a recent customer visit, experts machined pockets using a 95 percent stepover and achieved up to two hours of equipment life.
Tool Geometry: The shape of the tool—encompassing rake angle and flank design—plays a crucial role in enhancing manufacturing efficiency. Properly designed implements can reduce cutting forces while enhancing chip removal, ultimately leading to better surface finishes and longevity. Comprehending the influence of these geometrical factors is vital in attaining effective production outcomes.
Tool Longevity: Ongoing observation of equipment wear is essential for preserving processing efficiency. Tools should be replaced or re-sharpened prior to reaching critical wear levels to prevent adverse effects on performance. A case study titled ‘Impact of Tool Speed on Tool Wear’ examined the effects of varying tool speeds on the wear rates of Bidemics inserts while machining Ti6Al4V titanium alloy. It was discovered that an intermediate machining speed reduces wear on implements, attaining the finest surface quality at a flank wear width of 0.25 mm, emphasizing the importance of choosing suitable machining parameters. Additionally, general advice recommends using AlTiN coated carbide for cutting Inconel, emphasizing the importance of maintaining an optimal inconel cutting speed with deep cuts and light radial passes for the best results. This demonstrates the significance of strategic resource management in the manufacturing process.
By concentrating on these aspects—tool material, geometry, and life—procurement managers can make informed choices that optimize operations and enhance overall productivity.
The Importance of Cooling Methods in Inconel Machining
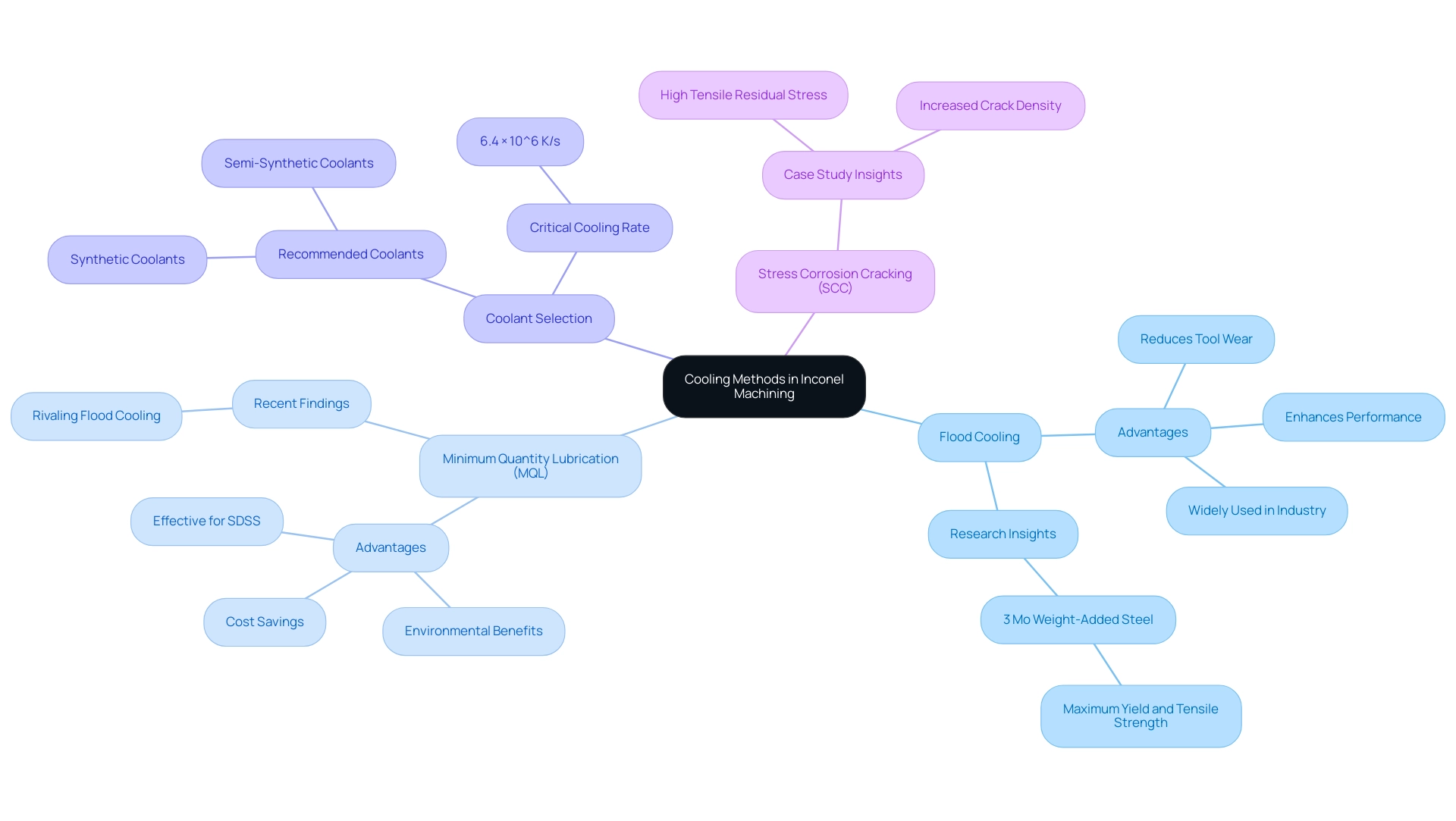
Efficient cooling techniques are crucial for processing Inconel, as they directly impact the inconel cutting speed, making it vital to control the heat produced during the operation for both equipment durability and operational effectiveness. Consider the following strategies:
Flood Cooling: This traditional approach employs a continuous stream of coolant to both dissipate heat and lubricate the cutting area, significantly reducing tool wear and enhancing performance. The advantages of flood cooling are highlighted by its extensive use in industry, where it has demonstrated effectiveness in various processing scenarios. Notably, research indicates that 3% Mo weight-added steel exhibits maximum yield and tensile strength when subjected to optimal cooling conditions, emphasizing the importance of effective cooling methods.
Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL): This innovative method utilizes a minimal volume of lubricant, strategically applied to reduce friction and heat while still providing adequate cooling. MQL is recognized not only for its environmental advantages but also for its potential cost savings. Recent studies indicate that MQL can be especially effective in processing super duplex stainless steels (SDSS), enhancing component service life under recommended conditions. Furthermore, recent findings suggest that MQL offers advantages that could rival traditional flood cooling, supporting its growing adoption in the industry.
Coolant Selection: Choosing the right coolant is paramount for maintaining the best inconel cutting speed in high-performance processing of Inconel. Synthetic or semi-synthetic coolants are often recommended due to their superior cooling and lubrication properties, which are crucial when working with these high-strength materials. As noted in Physical Review Research, “This allows us to directly measure the critical cooling rate of water, which we determine to be 6.4 × 10^6 K/s,” further highlighting the need for effective cooling strategies.
Additionally, a case study on stress corrosion cracking (SCC) behavior revealed that high tensile residual stress on machined surfaces correlates with increased crack density in chloride environments, underscoring the practical implications of cooling methods on manufacturing practices and reinforcing the need for improved techniques.
By implementing effective cooling strategies, manufacturers can significantly enhance production efficiency and prolong tool life, aligning with best practices in the field.
Advanced Techniques for Efficient Inconel Machining
To further enhance the efficiency of machining Inconel, consider implementing the following advanced techniques:
High-Speed Processing (HSP): This method significantly enhances the slicing speed, optimizing processing time and potentially resulting in considerable productivity improvements. Optimal conditions for machining Inconel 718 suggest an inconel cutting speed of 90 m/min with a feed rate of 0.05 mm/rev, particularly when using CO snow for cooling. A case study on high-speed processing demonstrated that participants successfully operated at 4584 RPM and 41.25 IN with a Kennametal face mill, achieving good cutter life and minimal heat generation.
Adaptive Machining: Implement software solutions that dynamically adjust processing parameters based on real-time instrument performance and operational conditions. This adaptive approach not only optimizes machining speeds but also enhances overall efficiency, ensuring that the machining process adapts to varying conditions.
Tool Path Optimization: Leverage advanced Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software to create optimized tool paths. This minimizes cutting time and improves surface finish, effectively reducing cycle times and enhancing productivity.
Sustainability Assessment Models: The ongoing development of sustainability assessment models in manufacturing environments focuses on the impact of production practices on surface integrity and productivity. This shift towards sustainability is becoming increasingly important in contemporary manufacturing practices.
By adopting these advanced techniques, professionals can significantly enhance their Inconel processing methods, which will improve the inconel cutting speed, resulting in better quality and cost-effectiveness. Moreover, with 3erp offering delivery in as little as 5 days, procurement managers can ensure timely access to necessary materials, which is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency. As noted by Mrs. Bhagyashree Chalke from TIFR, “sincere thanks are also extended for assistance in scanning electron microscopy of machined samples,” highlighting the importance of collaborative efforts in advancing machining technologies.
Conclusion
Machining Inconel requires a strategic and informed approach to navigate the inherent challenges presented by this high-performance alloy. Key factors such as cutting parameters, tool selection, and cooling methods play a significant role in optimizing machining efficiency and ensuring tool longevity. By carefully balancing feed rates, depth of cut, and cutting speeds, procurement managers can achieve a fine-tuned process that enhances productivity while minimizing wear on tools.
The choice of cutting tools is equally critical. Utilizing high-quality materials, such as carbide with appropriate coatings, can dramatically improve tool life and performance. Understanding tool geometry and continuously monitoring tool wear further contribute to achieving the desired surface finish and operational efficiency.
Effective cooling methods cannot be overlooked, as they are essential for managing the heat generated during machining. Techniques like flood cooling and Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) not only enhance tool performance but also offer environmental and cost benefits.
Finally, embracing advanced machining techniques such as high-speed machining and adaptive machining can lead to significant productivity gains. By integrating these innovations and maintaining a focus on sustainability, procurement managers can ensure their operations are not only efficient but also competitive in the marketplace. The journey of mastering Inconel machining is complex, yet with the right strategies and tools, it can lead to superior production outcomes and drive long-term success.




